While vital signs are normally measurable markers of a person's physiological health (such as heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and body temperature), recognising early skin cancer symptoms requires monitoring changes in the skin. Skin cancer is a form of cancer that originates in the skin cells and is frequently induced by sun or tanning bed exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. In this blog, we will look at some of the most common signs and symptoms of skin cancer, specifically melanoma, the most severe type of skin cancer.
Key Symptoms and Warning Signs of Skin Cancer
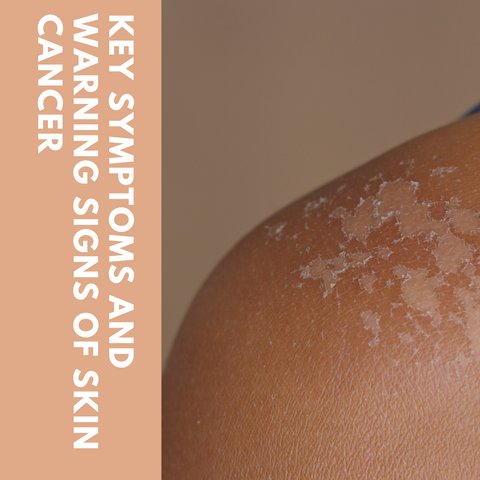
Skin cancer can appear in a variety of ways, and the symptoms vary depending on the type of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma are the three main kinds of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma are some of the primary symptoms and warning signs linked with each form. It's crucial to note that these are only suggestions; not all skin tumors will exhibit the same symptoms. Furthermore, non-cancerous skin diseases can sometimes mimic skin cancer symptoms. For early detection and treatment, regular self-examinations and expert skin exams by a dermatologist are essential. Seek immediate medical assistance if you observe any unusual changes to your skin or have concerns about a mole or lesion. Skin cancer prognosis is greatly improved by early detection and treatment. Remember to use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and prevent excessive UV exposure to protect your skin from the sun.
Understanding the ABCDE Rule
The ABCDE rule is a useful mnemonic for identifying possible melanoma, a kind of skin cancer. It describes the important features to look for while analysing moles or other skin lesions. Each letter represents a distinct trait that may necessitate additional investigation by a healthcare practitioner. Each letter in the ABCDE rule stands for something different, such as Asymmetry, Border Irregularity, Colour Variation, Diameter, and Evolution or Change. The ABCDE rule is a useful tool for self-examination, but it is not a substitute for professional medical evaluation. If you see any moles or skin lesions with these features, or if you have any worries about your skin, you should see a dermatologist or healthcare expert very once. Furthermore, some experts have enlarged the rule to include the letter "E" for "Evolution" to emphasise the importance of any change in a mole or skin lesion over time. Skin self-examinations and professional skin checks are essential for the early diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer.
Identifying Suspicious Moles and Spots
Paying attention to specific traits and changes in your skin will help you identify worrisome moles and patches. Asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, diameter, evolution or change, itching or discomfort, bleeding or seeping, and new or unusual growth are some suggestions to help you recognise probable indicators of skin cancer. It's critical to perform regular self-examinations of your skin, noting any changes in moles, freckles, or other skin lesions. If you observe any suspicious features or unusual symptoms, such as itching, discomfort, or bleeding, you should seek professional medical help right away. A dermatologist can examine you thoroughly and, if required, perform a biopsy to establish whether or not a lesion is malignant. Remember that early detection is critical to successful skin cancer treatment; therefore, it's critical to be aware and proactive about your skin health. If you have a family history of skin cancer or other risk factors, see a dermatologist frequently.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Skin Changes
It's critical to take charge of your skin's health and seek medical assistance if you notice any alarming changes. Changes in moles, new or unusual growths, skin lesions that bleed or ooze, persistent itching or tenderness, changes in freckles or sunspots, wounds that heal, any unexplained skin changes, and personal or family history are some general guidelines for when to seek medical attention for skin changes. If you detect any of the aforementioned symptoms or have concerns about changes in your skin, you should see a healthcare expert or a dermatologist very soon. They can examine you thoroughly, discuss your medical history, and, if necessary, perform additional tests or biopsies to identify the nature of the skin abnormalities. Furthermore, routine skin checks and preventive measures, such as the use of sunscreen and protective clothing, are critical for maintaining overall skin health and lowering the risk of skin cancer. Regular dermatologist visits are especially important if you have risk factors for skin cancer or a family history of the disease.
Prevention and Early Detection Strategies

Prevention and early detection are critical components of managing and reducing the risk of skin cancer. Here are some methods for preventing and detecting skin cancer:
Prevention Strategies:-
Sun Protection: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. Wear protective clothing, such as hats with wide brims, sunglasses, and long sleeves.
-
Seek Shade: Limit direct sun exposure between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If you are going to be outside, look for shade under trees, umbrellas, or other buildings.
-
Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit UV radiation, which increases the risk of developing skin cancer. If you want to get a tan, use sunless tanning products.
-
Protective Clothing: Wear clothing that covers your arms and legs, and look for UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) fabrics.
-
Eye Protection: Protect your eyes and the skin around them by wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays.
-
Regular Skin Self-Exams: Examine your skin on a regular basis to keep track of any changes in moles, freckles, or other skin lesions.
Early Detection Strategies:
-
Know Your Skin: Be aware of your moles, freckles, and other skin features so that you can spot any changes quickly.
-
Apply the ABCDE Rule: To identify suspicious moles, use the ABCDE rule: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Colour variation, Diameter greater than 6mm, and Evolution or change.
-
Professional Skin Exams: See a dermatologist on a regular basis, especially if you have a history of skin cancer or other risk factors.
-
Monitor Changes: Keep an eye out for any changes in your skin, such as new growths, colour changes, or itching.
-
Skin Cancer Screenings: Think about taking part in skin cancer screenings offered in your community or by dermatologists.
-
Seek Professional Advice: Consult a healthcare professional right away if you notice any suspicious changes or have concerns about your skin.
-
Educate Yourself: Keep up to date on skin cancer risks, prevention, and early detection methods.
Remember that early detection increases the likelihood of successful treatment. If you notice any changes in your skin or have any concerns about skin cancer, seek immediate medical attention. Establishing sun-safe habits and being proactive about your skin health is critical for the early prevention and detection of skin cancer.
The Role of Regular Self-Examinations
Regular self-examinations are critical in the early identification of skin cancer because they allow individuals to monitor their skin for any changes that could be suggestive of a problem. Here are some of the reasons why regular self-examinations are essential:
-
Early Detection: Skin cancer, particularly melanoma, is highly treatable if detected early. Regular self-examinations allow people to detect changes in moles or other skin lesions quickly.
-
Increased Awareness: Regular self-examinations raise one's awareness of the normal appearance of one's skin. This makes identifying any deviations or abnormalities that may arise over time easier.
-
Empowerment: Self-examinations give people the ability to actively manage their health. People can be proactive in seeking medical attention if they notice any concerning changes by becoming familiar with their skin and conducting regular checks.
-
Understanding Risk Factors: People who are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer, such as those with fair skin, a history of sunburns, or a family history of skin cancer, can benefit greatly from regular self-examinations. Knowing one's risk factors can increase vigilance and prompt early intervention.
-
Frequent Sun Exposure: People who spend a lot of time outside, especially in sunny or high-altitude environments, may be at a higher risk of developing skin cancer. This population requires regular self-examinations.
How to Conduct a Self-Examination of the Skin:
-
Use Adequate Lighting: Examine in a well-lit room with adequate natural or artificial lighting.
-
Examine All Areas: Examine every part of your body, including areas that are not normally exposed to the sun, like between your fingers and toes, underarms, and the soles of your feet.
-
Use Mirrors: Use mirrors to inspect hard-to-see areas, or ask a partner for help.
-
Follow the ABCDE Rule: Examine moles or spots for asymmetry, irregular borders, colour variations, diameters larger than 6mm, and any evolution or change.
-
Take Notification of Itching or Discomfort: Keep an eye out for any moles or spots that itch, become tender, or cause pain.
-
Photographic Documentation: Consider photographing your skin at regular intervals to monitor changes over time.
-
Regular Schedule: Perform self-exams on a regular basis, such as once a month, to maintain consistency and better identify changes.
If you notice any suspicious changes during a self-exam, or if you have concerns about a mole or spot on your skin, you should see a healthcare professional or dermatologist as soon as possible. They are capable of conducting a thorough examination, performing necessary tests, and providing appropriate guidance based on their findings. Regular professional skin checks are also advised, especially for people who have risk factors for skin cancer.
Scheduling Regular Dermatologist Visits
Regular visits to a dermatologist are essential for maintaining skin health and detecting potential issues, such as skin cancer, in their early stages. Here are some tips for scheduling and attending regular dermatologist appointments:
-
Frequency of Visits: The frequency of dermatologist visits can vary depending on individual risk factors, such as a personal or family history of skin cancer, the presence of numerous moles, a history of sunburns, or other skin conditions. Generally, individuals with a higher risk may need more frequent check-ups.
-
General Recommendations: Even if there are no known risk factors, it is often recommended to have a full-body skin examination by a dermatologist at least once a year.
-
High-Risk Individuals: If you have a history of skin cancer, a family history of melanoma, a large number of moles, or other risk factors, your dermatologist may advise you to visit more frequently, possibly every 3 to 6 months.
-
Self-Examinations: Between dermatologist visits, it is critical to conduct regular self-examinations. Monitor changes in your skin and seek professional help immediately if you notice anything unusual.
-
Annual Check-ups: Schedule your dermatologist appointment around the same time each year to establish a routine.
-
Preventive Measures: Use dermatologist visits not only for detecting potential problems, but also for preventive advice. Dermatologists can advise patients on sun protection, skincare routines, and healthy lifestyle choices.
-
Moles that are new or are changing: If you notice new moles or changes in existing moles between scheduled visits, make an appointment with your dermatologist right away.
-
Communicate Changes: Inform your dermatologist about any changes or concerns you have noticed in your skin since your last appointment. This data is critical for accurate assessments.
-
Full-Body Examination: Ensure that the dermatologist performs a thorough full-body examination, including areas that may not be exposed to the sun on a regular basis.
-
Be Proactive: If you have any concerns about a specific spot on your skin or notice any changes, make an appointment with your dermatologist right away.
Remember that early detection is critical for successful treatment and that visiting a dermatologist on a regular basis can assist. If you are confused about how frequently you should see a dermatologist, talk to your healthcare provider, who can make personalised recommendations based on your unique risk factors and concerns.
Sun Protection and Risk Factor Reduction
Sun protection and risk factor reduction are critical for skin cancer prevention and general skin health. Here are some essential measures for limiting sun exposure and lowering risk factors for skin cancer:
Sun Protection Strategies:
-
Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. Sunscreen should be applied liberally to all exposed skin, especially the face, neck, ears, and hands. Apply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you're swimming or sweating.
-
Clothing: Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats with wide brims. For added sun protection, wear clothing with a UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor).
-
Seek Shade: Limit direct sun exposure during peak hours, which are typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. When you are outside, look for shade under trees, umbrellas, or other structures.
-
Sunglasses: To protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them, wear sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays.
-
Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds emit dangerous UV radiation, increasing the risk of skin cancer. Avoid using them.
Risk Factor Reduction:
-
Regular Self-Exams: Examine your skin on a regular basis to keep track of any changes in moles, freckles, or other skin lesions.
-
Dermatologist Visits: Visit a dermatologist on a regular basis for full-body skin examinations, especially if you have risk factors or a history of skin cancer.
-
Know Your Skin: Be aware of your skin's normal appearance so that you can spot any changes quickly.
-
Protect Children: Children are particularly susceptible to sun damage. Assure that they are adequately protected with sunscreen, clothing, and hats.
-
Avoid Peak Sun Hours: Limit outdoor activities during peak sun hours to avoid being exposed to harmful UV rays.
-
Quit Smoking: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma. Quitting smoking can reduce this risk.
-
Healthy Diet: Adopt a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants, which may contribute to overall skin health.
-
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports skin health and can help prevent sun-related dehydration.
-
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is associated with an increased risk of skin cancer. Limit alcohol intake.
-
Stay Informed: Stay informed about your family's medical history, as genetics can play a role in skin cancer risk.
Implementing these sun protection and risk reduction techniques can greatly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer. It is critical to incorporate these activities practises daily routine and to maintain vigilance over your skin's health. If you detect any changes or have any concerns, consult a dermatologist right away. Early detection and preventative activities are critical for maintaining healthy skin and mitigating the effects of skin cancer.
Navigating Diagnosis and Treatment Options
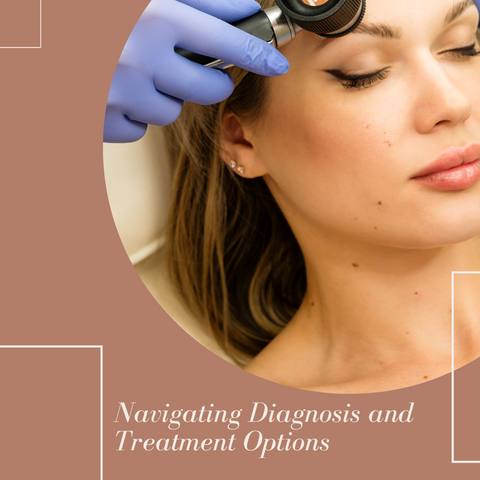
Navigating a skin cancer diagnosis and treatment options can be difficult. If you suspect or have been diagnosed with skin cancer, it is critical to take the following steps: consultation with a healthcare professional, biopsy, pathology report, consultation with a dermatologic surgeon or oncologist, treatment options, second opinion, emotional support, follow-up care, educate yourself, skin health maintenance, clinical trials, insurance, and financial support. Keep in mind that each person's situation is unique, and treatment options are adjusted to criteria such as cancer type and stage, overall health, and personal preferences. Open communication with your healthcare team and a proactive attitude towards your care can help you get the best results possible.
The Process of Skin Biopsies
A skin biopsy is a medical technique that involves removing a tiny sample of skin tissue for examination under a microscope. This method is frequently used to diagnose or rule out skin diseases such as skin cancer. Here's a summary of the skin biopsy process, including clinical examination, discussion, and informed consent; biopsy type selection; local anaesthesia; biopsy procedure; hemostasis (if needed), dressing and care, pathological investigation and results; and follow-up. Complications are uncommon, and the process gives useful information for precise diagnosis and treatment planning. If you have any concerns or questions regarding a skin lesion, you should visit with a healthcare expert who can assess if a biopsy is required and explain the procedure in greater detail.
Interpreting Biopsy Results
The interpretation of biopsy results requires understanding the information provided by a pathologist who has examined the tissue sample under a microscope. The findings will assist in determining if the skin lesion is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). A general guide to interpreting biopsy results such as normal/benign results, atypical or dysplastic cells, pre-cancerous changes, malignant results, margins and depth of invasion, further testing or staging, discussion with a healthcare provider, treatment planning, and follow-up care is provided below. They will walk you through the findings, explain the ramifications, and work with you to develop a complete treatment plan. If you have received biopsy results and have questions or concerns, speak with your healthcare professional for personalised advice.
H3: Latest Advances in Skin Cancer Treatment
There have been continual breakthroughs in the treatment of skin cancer. Remember that medical research is constantly evolving, and new discoveries may have occurred since then. Immunotherapy, targeted therapies, combination therapies, intralesional therapy, adjuvant therapies, genetic profiling, radiation breakthroughs, liquid biopsies, nanotechnology, and clinical trials are some of the most recent advances and trends in skin cancer treatment. Patients diagnosed with skin cancer should consult with their healthcare provider about treatment choices, including potential breakthroughs. The type and stage of cancer, hereditary traits, and overall health all influence therapy options. Always seek the most up-to-date information and personalised advice from a healthcare professional.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself Against Skin Cancer

Skin cancer prevention requires a proactive and informed approach to skin health. Sun protection, regular self-examinations, dermatologist visits, prevention tactics, risk factor reduction, treatment advancements, emotional support, education, early intervention, and complete healthcare are some major lessons to conclude. By implementing these tactics into your daily routine and taking a proactive approach to your skin health, you will be able to fight skin cancer more effectively. Remember that personalised guidance from healthcare professionals is critical, and that regular check-ups are critical to the early detection and successful management of skin cancer. For a brighter and healthier future, be aware, and proactive, and prioritise your skin health.
















