Sweating, often known as perspiration, happens in response to activity, extreme temperatures, or events that cause anxiety or fear. Sweat, which is made up of 99% water and 1% salt and fat, stops your body from overheating by evaporating and cooling you down. However, excessive sweating, or hyperhidrosis, can occur even while you are at rest or in a cool atmosphere. Sweating heavily and uncontrollably can cause physical and emotional distress. What is the good news? There are things you may do to manage your condition. Continue reading to learn about hyperhidrosis' causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The Science of Sweat: Understanding Hyperhidrosis

Hyperhidrosis is indeed fascinating! It's a condition characterized by excessive sweating beyond what's necessary for regulating body temperature. While sweating is a natural bodily function, serving to cool us down when we're hot or stressed, those with hyperhidrosis experience it to an extreme degree.
-
There are two main types of hyperhidrosis: primary focal hyperhidrosis, which typically affects specific areas like the palms, soles, armpits, and face; and secondary generalized hyperhidrosis, which is usually caused by an underlying medical condition or medication.
-
The exact cause of primary focal hyperhidrosis is still somewhat of a mystery, but it's believed to involve overactivity of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls sweating. Factors like genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental triggers may also play a role.
-
Treatment options for hyperhidrosis range from topical treatments like antiperspirants and medications to more invasive procedures like botox injections, iontophoresis (using electrical currents to reduce sweating), and even surgery in severe cases.
-
Understanding the science behind hyperhidrosis is crucial for developing effective treatments and improving the quality of life for those who experience excessive sweating. It's a complex interplay of neurological, hormonal, and environmental factors that researchers are continuously striving to unravel.
Identifying the Symptoms: More Than Just Sweating
Identifying hyperhidrosis requires more than simply recognising excessive sweating; there are several symptoms and signs to consider:
-
Excessive Sweating: This is the hallmark symptom of hyperhidrosis. It goes beyond what is required to regulate body temperature and can occur even when the person is not exercising or in a cool environment.
-
Localised Sweating: Hyperhidrosis usually affects a specific area of the body, known as focal hyperhidrosis. Common locations include the palms, soles, armpits, and face.
-
Interference with Daily Activities: Excessive perspiration can cause embarrassment, discomfort, and even avoidance of certain situations by interfering with social interactions and everyday activities.
-
Skin Changes: Persistent sweating can cause fungal or bacterial infections, an unpleasant odour, and maceration, or the softening and breaking down of the skin.
-
Emotional Impact: If hyperhidrosis interferes with social interactions and self-esteem, it can have a major emotional impact, leading to feelings of anxiety, depression, and self-consciousness.
-
Worsening in Certain Circumstances: People who have hyperhidrosis may experience worsening sweating in response to specific triggers, such as heat, stress, or particular foods or beverages.
-
Family History: There may be a family history of hyperhidrosis, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the condition.
-
Absence of Underlying Medical Condition: In primary focal hyperhidrosis, excessive sweating occurs without an underlying medical condition or medication as the cause. However, if hyperhidrosis is secondary to another medical condition or medication, other symptoms related to that condition may be present.
Causes and Triggers: Why Sweat Happens
Sweating is a normal and necessary bodily function that regulates body temperature and maintains internal balance. However, in hyperhidrosis, this process is exaggerated and occurs even when not required. Understanding the causes and triggers of sweating can help explain why hyperhidrosis occurs:
-
Overactive Sympathetic Nervous System: The sympathetic nervous system controls sweat production. Individuals with hyperhidrosis may have an overactive system that causes excessive sweating even when there is no need to cool the body.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Evidence suggests that hyperhidrosis has a genetic component. It frequently runs in families, suggesting a predisposition to the condition.
-
Hormonal Changes: Sweating patterns can be influenced by hormonal fluctuations such as those experienced during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. Some people may notice an increase in sweating during these times.
-
Environmental Triggers: Some environmental factors can cause or worsen sweating in people with hyperhidrosis. Hot weather, high humidity, physical activity, stress, spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol are all potential triggers.
-
Medical Conditions: Hyperhidrosis can sometimes be caused by an underlying medical condition such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, infections, or hormonal imbalances. Excessive sweating is a possible side effect of medications used to treat these conditions.
-
Neurological Disorders: Neurological conditions such as Parkinson's disease or autonomic neuropathy can disrupt the sympathetic nervous system's normal function, resulting in abnormal sweating patterns.
-
Emotional Factors: Emotional stress and anxiety can stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, triggering sweating in susceptible individuals. This is often observed in situations like public speaking, job interviews, or social interactions.
Eccrine vs. Apocrine: The Glands Behind the Gloss
Understanding the distinction between eccrine and apocrine glands sheds light on the mechanisms of sweating and how hyperhidrosis manifests.
-
Eccrine Glands:
-
Eccrine glands are found all over the body, but they are especially abundant in the palms, soles, forehead, and armpits.
-
These glands are primarily responsible for thermoregulation, which involves secreting sweat onto the skin's surface to help the body cool itself. Eccrine sweat consists primarily of water, electrolytes (such as sodium and chloride), and trace amounts of metabolic waste products.
-
Eccrine glands are activated by changes in body temperature, physical activity, and emotional stimuli (such as stress or anxiety).
-
Apocrine Glands:
-
Apocrine glands are found in areas with dense hair follicles, including the armpits, groyne, and scalp.
-
Unlike eccrine glands, apocrine glands secrete a thicker, odourless mixture of lipids, proteins, and steroids. This secretion is odourless when first released, but it can develop an odour when bacteria on the skin degrade it.
-
Emotional stimuli, such as stress or anxiety, are the primary triggers for apocrine gland activity. They are less involved in thermoregulation and more related to emotional sweating and pheromone production.
In hyperhidrosis, both eccrine and apocrine glands may be overactive, resulting in excessive sweatingHowever, primary focal hyperhidrosis usually affects eccrine glands, causing excessive sweating in specific areas such as the palms, soles, and armpits. Secondary generalised hyperhidrosis, on the other hand, may affect both eccrine and apocrine glands and be caused by underlying medical conditions or medications. Understanding the role of the eccrine and apocrine glands aids in the effective diagnosis and treatment of hyperhidrosis, as various treatment approaches may target specific glandular mechanisms or pathways involved in sweating regulation.
Combating Excessive Sweating: From Natural Remedies to Medical Interventions

Combating excessive sweating, whether due to hyperhidrosis or other causes, often involves a multi-faceted approach that can include natural remedies, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions:
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Wearing breathable, natural fabrics, such as cotton, can help reduce sweating by improving air circulation. Keeping the skin clean and dry can help prevent bacterial growth and reduce the odour associated with sweating. Drinking plenty of water helps maintain hydration levels and can regulate body temperature more effectively. Stress and anxiety can exacerbate sweating, so practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga may help reduce symptoms. Identify and avoid triggers that exacerbate sweating, such as spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and hot environments.
-
Natural Remedies: Over-the-counter antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can help reduce sweating by blocking sweat ducts. Some herbs like sage have natural astringent properties and may help reduce sweating when applied topically or consumed as a tea. Applying diluted apple cider vinegar to the skin may help balance pH levels and reduce bacterial growth, minimizing body odor associated with sweating. Baking soda can absorb moisture and neutralize odors when applied to the skin, making it a useful natural remedy for managing sweating.
-
Medical Interventions: For more severe cases, prescription-strength antiperspirants containing higher concentrations of aluminum chloride may be recommended. Botulinum toxin injections can temporarily block nerve signals to sweat glands, reducing sweating in targeted areas like the armpits, palms, or soles. This non-invasive treatment involves passing a mild electrical current through water to block sweat gland activity temporarily. Oral medications such as anticholinergics or beta-blockers may be prescribed to reduce sweating, although they may have side effects. In severe cases that don't respond to other treatments, surgical options like sympathectomy (nerve surgery) or sweat gland removal may be considered.
Treatment choice depends on the severity of symptoms, individual preferences, and underlying causes of excessive sweating. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the most appropriate approach for managing this condition effectively.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Simple Changes, Big Impact
Lifestyle changes can have a big impact on controlling excessive sweating. Dietary modifications, clothing choices, personal hygiene, stress management, environmental adjustments, foot and hand care, and footwear choices are all easy changes that can have a large impact. Making these lifestyle changes can be used in conjunction with other hyperhidrosis treatments or to manage mild cases independently. It is critical to identify the optimum combination of methods for you and get personalised advice and direction from a healthcare practitioner.
Advanced Treatments: Botox, Medications, and Surgery
If lifestyle changes or other conservative measures do not work, advanced treatments for hyperhidrosis may be required. Here are some advanced treatment alternatives:
-
Botox Injections: Botulinum toxin injections temporarily block the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates sweat glands. This effectively reduces sweating in the treated area. Botox injections are typically administered in targeted areas such as the armpits, palms, or soles. Multiple injections are usually required for optimal results. The effects of Botox injections typically last for several months, after which the procedure may need to be repeated.
-
Prescription Medications: Medications such as glycopyrrolate or oxybutynin may be prescribed to reduce sweating by blocking the action of acetylcholine on sweat glands. However, they can have side effects like dry mouth, blurred vision, and constipation. Beta-blockers like propranolol may help reduce sweating associated with anxiety or stress by blocking the effects of adrenaline. They may be particularly useful for individuals with stress-induced sweating.
-
Iontophoresis: Iontophoresis involves passing a mild electrical current through water to block sweat gland activity temporarily. It's particularly effective for treating excessive sweating of the hands and feet. During iontophoresis treatment, the hands or feet are immersed in a shallow water tray, and a low-voltage electrical current is applied. Treatment sessions typically last 20 to 40 minutes and may need to be repeated several times per week initially, followed by maintenance sessions.
-
Surgery: Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a surgical procedure that involves cutting or clamping the sympathetic nerves that control sweating. It's usually reserved for severe cases of hyperhidrosis that don't respond to other treatments. However, ETS carries risks of compensatory sweating and other potential complications. In some cases, surgical removal of sweat glands may be considered, particularly for focal hyperhidrosis of the armpits. This procedure, known as axillary sweat gland excision, can provide long-lasting relief from excessive sweating.
The Role of Diet and Hydration in Managing Sweat
Diet and hydration are important for sweat management and overall body temperature regulation. Here's how they affect sweating and what you can do to improve them:
-
Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for regulating body temperature through sweating. When you're adequately hydrated, your body can produce sweat more efficiently to cool you down. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially in hot or humid environments or during physical activity. The general recommendation is to consume about 8 glasses (64 ounces) of water per day, but individual needs may vary based on factors like age, weight, activity level, and climate.
-
Diet: Certain foods and beverages can stimulate sweating in some individuals. Spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol are common triggers for sweating. While the exact mechanisms vary, these substances can increase metabolism or stimulate the nervous system, leading to increased sweating. Eating foods with high water content, such as fruits and vegetables, can contribute to hydration and help maintain electrolyte balance, which is important for sweat production and overall body function. Maintaining a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods can support overall health and may indirectly influence sweating. Nutritional deficiencies or imbalances can affect various bodily functions, including temperature regulation.
-
Electrolyte Balance: Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium play essential roles in maintaining hydration levels and regulating muscle function, including sweat gland activity. During periods of heavy sweating, such as during exercise or in hot weather, it's important to replenish electrolytes lost through sweat by consuming electrolyte-rich foods or beverages, such as sports drinks or coconut water.
-
Alcohol and Caffeine: Both alcohol and caffeine have diuretic properties, meaning they can increase urine production and potentially contribute to dehydration if consumed in excess. Dehydration can, in turn, affect sweat production and body temperature regulation. While moderate consumption of alcohol and caffeine is generally considered safe for most people, excessive intake can lead to dehydration and may exacerbate sweating in susceptible individuals.
-
Medical Conditions and Medications: Some medical conditions and medications can affect sweat production and body temperature regulation. For example, certain medications may increase sweating as a side effect, while others may cause dehydration. If you have a medical condition or take medications that affect sweating or hydration, it's important to discuss dietary and hydration strategies with your healthcare provider to ensure they're appropriate for your circumstances.
Beyond the Physical: The Social and Emotional Impact of Hyperhidrosis

The social and emotional consequences of hyperhidrosis can be profound and far-reaching, often going beyond the physical symptoms. Here are some of the social and emotional effects of hyperhidrosis:
-
Hyperhidrosis can cause embarrassment and self-consciousness about visible sweat stains or body odour, causing people to withdraw from social situations to avoid being judged or embarrassed.
-
Hyperhidrosis can have an impact on personal relationships, such as romantic ones, friendships, and family dynamics. Excessive sweating may make people feel self-conscious or anxious about physical contact, such as holding hands or hugging.
-
Sweating excessively at work can be particularly difficult, especially in professional settings where appearance and confidence are valued. Individuals with hyperhidrosis may be concerned about handshakes during interviews or meetings, affecting job performance and advancement.
-
Constant sweating-related worry and anxiety can have a significant negative impact on overall quality of life. Simple activities such as going to the gym, attending social events, or even writing or using electronic devices can cause stress and discomfort.
-
Hyperhidrosis can contribute to psychological issues such as low self-esteem, depression, and anxiety disorders. The constant struggle with sweating and the negative impact on social interactions can take a toll on mental well-being over time.
-
Individuals with hyperhidrosis may experience stigma or discrimination due to misconceptions about sweating being associated with poor hygiene or lack of control. This can further exacerbate feelings of shame and isolation.
-
Excessive sweating can affect body image perception, leading individuals to feel self-conscious about their appearance and less confident in social settings.
-
Managing hyperhidrosis may also impose a financial burden, as individuals may need to invest in specialized clothing, antiperspirants, medical treatments, or therapies to alleviate symptoms.
Navigating Daily Life: Clothing, Social Interactions, and Self-Esteem
Navigating daily life with hyperhidrosis can present unique challenges, but there are strategies and techniques that individuals can use to manage their condition and maintain a positive outlook. Here are some tips for managing clothing choices, social interactions, and self-esteem:
-
Clothing Choices:
-
Opt for loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics like cotton or linen, which allow air circulation and can help minimize sweat buildup.
-
Dark-colored clothing can help conceal sweat stains better than lighter colors.
-
Layering clothing allows for better temperature regulation, so you can remove outer layers if you start to sweat excessively.
-
Consider wearing moisture-wicking fabrics designed specifically to keep you dry, especially during physical activity or in hot weather.
-
Social Interactions:
-
Consider opening up to close friends, family members, or trusted colleagues about your hyperhidrosis. Educating others about your condition can help reduce feelings of isolation and promote understanding and support.
-
Practice positive self-talk and confidence-building exercises to boost self-esteem and resilience in social situations.
-
Redirect your focus away from sweating by engaging in activities or conversations that you enjoy and that help distract you from self-conscious thoughts.
-
Practical Tips:
-
Keep a small bag or pouch with essentials like tissues, handkerchiefs, or antiperspirant wipes to help manage sweat throughout the day.
-
If you're uncomfortable with handshakes due to sweaty palms, consider explaining your situation or politely offering a fist bump or verbal greeting instead.
-
Pay attention to your body language and try to adopt open, confident postures to convey self-assurance, even if you're feeling anxious about sweating.
-
Self-Esteem and Mindset:
-
Remind yourself of your strengths, talents, and accomplishments to cultivate a positive self-image that isn't defined solely by your hyperhidrosis.
-
Consider joining support groups or online communities for individuals with hyperhidrosis to connect with others who understand your experiences and can offer empathy, advice, and encouragement.
-
If you continue to experience low self-esteem or anxiety, talk to a mental health professional about how to cope with the emotional impact of hyperhidrosis.
Coping Mechanisms: Psychological Strategies and Support Networks
Coping with hyperhidrosis frequently entails psychological strategies and support networks to alleviate the emotional impact of the condition. Here are some coping strategies and support resources:
-
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Reduce stress and anxiety by practicing mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation, which can exacerbate sweating. Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine to promote a state of calm and reduce the physiological response to stress.
-
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Consider consulting a qualified mental health professional, such as a psychologist or counsellor, who can offer cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). CBT can help you identify and challenge negative thought patterns associated with hyperhidrosis, learn coping skills for anxiety and self-consciousness, and boost your self-esteem and confidence.
-
Support Groups and Online Communities: Joining support groups or online communities for individuals with hyperhidrosis can provide a sense of belonging and validation, as well as practical tips and advice from others who understand your experiences. Engage with supportive peers who can provide empathy, encouragement, and solidarity as you navigate the challenges of living with hyperhidrosis.
-
Peer Support and Social Connections: Develop supportive relationships with friends, family, or colleagues who understand and accept your hyperhidrosis. Share your thoughts and feelings with trusted people who can offer emotional support and encouragement during difficult times.
-
Positive Self-Talk and Affirmations: Positive self-talk and affirmations can help you overcome negative thoughts and beliefs about yourself and your condition. Remind yourself of your strengths, accomplishments, and worth as an individual beyond your hyperhidrosis.
-
Educational Resources: Educate yourself on hyperhidrosis and its treatment using credible sources such as medical websites, books, or articles written by healthcare professionals. Understanding your condition allows you to advocate for yourself, make informed treatment decisions, and communicate effectively with healthcare providers.
-
Self-Care and Stress Management: Prioritise self-care activities that promote physical and emotional well-being, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, healthy nutrition, and participating in hobbies or activities that you enjoy. Create a personalised stress management plan that includes strategies for dealing with hyperhidrosis-related stressors, such as relaxation techniques, time management, and boundary setting.
Charting Your Path: Navigating Treatment Options and Living with Hyperhidrosis
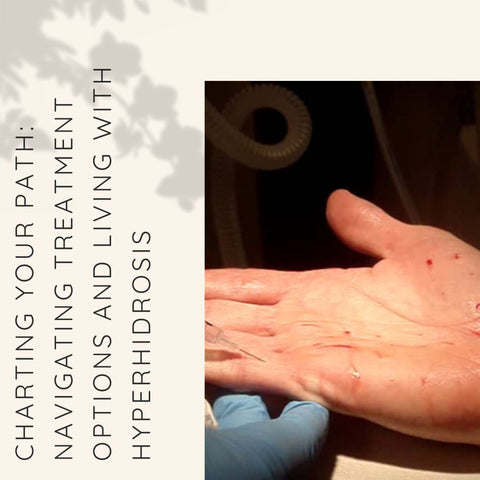
Navigating treatment choices and living with hyperhidrosis necessitates a proactive and holistic approach that addresses both the physical symptoms as well as the social and emotional consequences of the condition. Here are some steps to help you chart your course: educate yourself, consult with healthcare professionals, look into treatment choices, set realistic objectives, build coping techniques, track progress and make adjustments, seek support, and practise self-advocacy. By taking a proactive and holistic approach to controlling hyperhidrosis, you can create a route that prioritises your physical, mental, and social well-being, allowing you to live your life to the fullest despite the difficulties caused by excessive sweating.
When to See a Doctor: Signs It's Time for Professional Help
Knowing when to seek professional care for hyperhidrosis is critical for optimal management of the condition. Excessive sweating, localised sweating, secondary symptoms, failure of over-the-counter medicines, negative impact on daily life, medical history and drug side effects, new-onset sweating, and concerns about complications are all indications that it's time to consult a physician.
Success Stories: Real-Life Triumphs Over Excessive Sweating
These success stories demonstrate the tenacity, determination, and courage of those who have conquered the obstacles of excessive sweating. They have transformed their lives and regained control by getting help, researching treatment alternatives, and being devoted to their well-being. Their experiences serve as encouragement for others suffering similar challenges, reminding them that relief is available and that they are not alone on their road.
Empowering Yourself: A Comprehensive Guide to Managing Hyperhidrosis

This is a comprehensive guide to empowering individuals to manage hyperhidrosis effectively, including understanding the condition, seeking professional help, exploring treatment options, lifestyle changes, topical treatments, advanced medical treatments, self-care strategies, coping mechanisms, tracking progress, seeking support, advocating for yourself, and celebrating successes. You can effectively manage hyperhidrosis and enhance your overall quality of life by educating yourself, getting professional help, researching treatment choices, and applying self-care practices. Remember that you are not alone on your path, and assistance is available to help you negotiate the difficulties of living with excessive sweating.
















