Dehydration is a condition in which the body loses more fluids than it intakes. While many people connect dehydration with minor discomforts like thirst and a dry mouth, the repercussions of dehydration can go well beyond these first symptoms. The importance of water, recognizing dehydration, physical performance, and cognitive function, its effect on mood and emotional well-being, its impact on digestive health, kidney function, urinary health, skin, and long-term effects, and vulnerable populations will be explored in this blog. We may protect ourselves from this quiet threat and maintain good health by recognizing the indications of dehydration and prioritizing appropriate water. Remember that prevention is vital, so make hydration a daily priority.
Understanding Dehydration: Symptoms, Causes, and Beyond

Dehydration is a condition in which the body loses more fluids than it intakes. It has the potential to have a substantial impact on overall health and well-being. In this blog, we will go over the basics of dehydration, including recognizing the symptoms, causes of dehydration, risk factors, complications of dehydration, prevention, and treatment, hydration for special circumstances, and when to seek medical attention. Prioritizing hydration and treating dehydration as soon as it occurs will protect our bodies from the risks and issues that could arise from this condition. Always remember that hydration is essential for a healthy body.
Recognizing the Symptoms: Common Dehydration Signs to Look Out For
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing the body's vital functions to malfunction. Recognizing the symptoms of dehydration is critical for prompt intervention and the avoidance of further complications. In this blog, we will look at the most common signs of dehydration that people should be aware of.
-
Thirst and Dry Mouth: A persistent thirst is one of the first signs of dehydration. When the body is dehydrated, it produces a thirst response to encourage fluid intake. A dry mouth is another common symptom, characterized by a parched sensation and decreased saliva production.
-
Dark Urine: Observing the color of urine can provide useful information about hydration levels. Urine that has been properly hydrated is typically clear or pale yellow. Dehydration, however, causes urine to darken and concentrate more, going from deep yellow to amber.
-
Weakness and Fatigue: Dehydration can make you feel tired and generally weak. The body's cells need enough water to function properly, and when they are dehydrated, their energy levels can fall, resulting in fatigue and a lethargic feeling.
-
Dizziness and Headaches: Both headaches and vertigo can be brought on by dehydration. These symptoms are caused by dehydration, which reduces blood volume and alters blood flow to the brain. It is critical to pay attention to persistent or recurring headaches, especially if they are accompanied by other dehydration-related symptoms.
-
Muscle Spasms and Cramps: Dehydration can cause muscle spasms and cramps, which frequently affect the arms, legs, or abdomen. Electrolyte imbalances brought on by fluid loss can impair muscle performance and cause excruciating cramping.
-
Dry Skin and Lips: The level of internal hydration is reflected in the skin. The skin might look flaky, dry, or rough when it is dehydrated. Lips can become chapped, dry, and cracked. Lack of moisture reduces the elasticity of the skin and can hasten the aging process.
-
Reduced Urination: A decrease in urine production may indicate dehydration. When we are dehydrated, our bodies try to conserve water by producing less urine. It may be a sign of severe dehydration and necessitate immediate medical attention if you notice a marked decrease in urination or a prolonged period without urinating.
-
Other Symptoms: In addition to the ones listed above, dehydration can also show up as a rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, agitation, confusion, sunken eyes, and a lack of tears during crying (especially in babies and young children).
Unraveling the Causes: Factors that Contribute to Dehydration in Daily Life
Dehydration happens when the body loses more fluid than it intakes, resulting in an imbalance that can be harmful to one's health. Understanding the causes of dehydration is critical for identifying potential risk factors and implementing preventative strategies to maintain sufficient hydration. We will investigate the factors that contribute to dehydration in everyday life, such as insufficient fluid intake, physical activity, and sweating; environmental factors; illnesses and health conditions; medications; alcohol, and caffeine consumption, insufficient fluid intake in specific groups, and a lack of access to clean water. People can protect their health and well-being by maintaining ideal hydration levels by being aware of these causes and prioritizing proper hydration.
Dehydration Beyond the Skin: Exploring Its Impact on Overall Health
Dehydration, which is frequently perceived as a minor inconvenience, can have far-reaching repercussions on the body that extend beyond the skin. Adequate hydration is essential for the correct functioning of the body's numerous systems. We will investigate the impact of dehydration on overall health, shedding light on its effects that go beyond the obvious symptoms, such as cardiovascular system, kidney function, digestive system, cognitive function, energy levels and fatigue, joint and muscle health, mood and emotional well-being, and skin health. To maintain maximum health and support the normal functioning of the body's complicated systems, it is critical to prioritize hydration and guarantee appropriate fluid intake throughout the day. Remember that sufficient hydration is essential for overall health.
The Mind-Body Connection: How Dehydration Impacts Your Daily Life

Dehydration can have a significant negative impact on both the physical and mental aspects of our well-being because the two are intricately linked. Hydration is essential for optimal physical and mental performance. We will look at how dehydration can affect your daily life and how it affects different aspects of your mind-body connection.
-
Physical Performance: Dehydration can impair physical performance and athletic abilities. Dehydration impairs the body's ability to regulate temperature and deliver oxygen and nutrients to muscles. This can result in decreased endurance, strength, and overall athletic performance. Staying hydrated is critical for peak physical performance.
-
Cognitive Function: Adequate hydration is essential for optimal cognitive function. Dehydration can impair memory, attention, concentration, and other cognitive abilities. It has the potential to impair decision-making, problem-solving, and overall mental clarity. Maintaining adequate hydration levels is critical for optimal brain function and cognitive performance.
-
Mood and Emotional Well-Being: Dehydration can negatively impact mood and emotional well-being. Mild dehydration has been linked to increased feelings of anxiety, irritability, and fatigue, according to research. It can also have an effect on emotional stability, making stress management more difficult. Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining a stable mood and emotional balance.
-
Energy Levels and Fatigue: Dehydration can result in low energy levels and fatigue. When the body does not have enough fluids, metabolic processes become inefficient, affecting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to cells. This can lead to decreased stamina, decreased productivity, and a constant state of exhaustion. Proper hydration is critical for maintaining optimal energy levels throughout the day.
-
Headaches and Migraines: Dehydration is a common cause of migraines and headaches. When the body is dehydrated, blood vessels in the brain constrict, causing pain and discomfort. Staying hydrated can aid in the prevention or relief of headaches and migraines.
-
Digestive Health: Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Dehydration can exacerbate digestive issues such as constipation and acid reflux. It can also have an effect on nutrient absorption and overall digestive efficiency. Drinking plenty of water aids digestion and alleviates gastrointestinal discomfort.
-
Sleep Quality: Dehydration can have an effect on sleep quality. When the body is dehydrated, it can interfere with normal sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep throughout the night. Inadequate hydration can also contribute to leg cramps at night, which can disrupt sleep.
-
Skin Health and Appearance: Healthy skin requires adequate hydration. Dehydration can cause skin dryness, dullness, and premature ageing. It can also aggravate skin conditions like eczema and acne. Maintaining adequate hydration levels benefits skin health, promotes a radiant complexion, and aids in the prevention of ageing signs.
Mental Performance and Dehydration: The Surprising Effects on Cognitive Function
While many people equate dehydration with physical symptoms, its influence on cognitive function and mental performance is frequently underestimated. Adequate hydration is critical for optimum brain function, and even slight dehydration can impair cognitive ability. We'll look at how dehydration affects cognitive function and mental performance in areas like memory and attention, cognitive processing speed, mood and emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility and creativity, decision-making and risk assessment, mental fatigue and cognitive decline, and performance in high-cognitive-demand tasks. Maintaining optimal brain function, improving mental performance, and promoting overall cognitive well-being all require adequate hydration. Remember to drink water on a regular basis, especially during mentally demanding tasks, and make hydration a priority in your daily routine.
Physical Performance and Dehydration: How It Affect Your Exercise and Fitness
Dehydration has been shown to have a negative impact on physical performance and exercise outcomes. Hydration is essential for peak athletic performance and overall fitness. In this blog, we will look at how dehydration affects physical performance, exercise capacity, and the importance of staying hydrated while exercising.
-
Impaired Cardiovascular Function: Dehydration can strain the cardiovascular system, compromising exercise performance. When you are dehydrated, your blood volume decreases, making it more difficult for your heart to pump oxygen and nutrients to your working muscles. This can lead to an increase in heart rate, a decrease in cardiac output, and a decrease in exercise capacity.
-
Reduced Endurance and Stamina: Maintaining endurance and stamina during exercise requires proper hydration. Dehydration reduces blood volume and impairs the body's ability to regulate temperature. This can result in early fatigue, decreased endurance, and a drop in overall exercise performance.
-
Increased Perceived Exertion: Dehydration can cause an increase in perceived exertion during exercise. When the body is dehydrated, it works harder to maintain performance, resulting in a greater sense of exertion. This can make exercise feel more difficult, resulting in a decreased willingness to continue and motivation.
-
Impaired Temperature Regulation: During exercise, water is essential for regulating body temperature. Dehydration reduces the body's ability to sweat away heat, increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses like heat exhaustion and heatstroke. Proper hydration helps maintain core body temperature and prevents overheating during physical activity.
-
Decreased Muscle Strength and Power: Dehydration can cause a reduction in muscle strength and power output. Water is necessary for muscle contraction and nutrient transport to the muscles. Muscle cells lose water when dehydrated, reducing their efficiency and capacity to generate force. This can lead to diminished strength and power during exercise.
-
Impaired Concentration and Coordination: Dehydration can impair mental concentration and coordination during exercise. Proper hydration is essential for optimal brain function, and even mild dehydration can impair cognition. Impaired focus and coordination can increase the risk of accidents, injuries, and poor exercise performance.
-
Slower recovery and increased injury risk: Dehydration slows the recovery process following exercise. When the body is dehydrated, it loses its ability to repair damaged tissues and replenish glycogen stores. This can lead to increased muscle soreness, slower recovery, and a higher risk of injury.
-
Importance of Hydration Strategies: It is critical to prioritize proper hydration strategies in order to optimize physical performance and exercise outcomes. Adequate fluid intake is essential before, during, and after exercise. It is recommended to drink water on a regular basis, especially during strenuous or prolonged physical activities. Electrolyte-rich beverages can also aid in the replenishment of lost minerals and the maintenance of fluid balance.
Hydration and Mood: Understanding the Link Between Dehydration and Emotional Well-being
Hydration is important for more than just physical health; it also has an impact on mental well-being and mood management. Dehydration can have an impact on many facets of mental health, and knowing the relationship between hydration and mood is critical for achieving optimal emotional well-being. We will look at the relationship between dehydration and emotional health, including how it affects brain function, fatigue, cognitive impairments, anxiety, and irritability, how it affects stress response, headaches, and discomfort, how it affects sleep quality, and how it affects emotional well-being. Individuals can promote a more positive mood state, improve emotional resilience, and support overall mental well-being by prioritizing hydration and ensuring adequate fluid intake. Remember that staying hydrated is not only good for your body but also helps you maintain a healthy and balanced mind.
Dehydration and Your Body Systems: Long-Term Effects and Risks
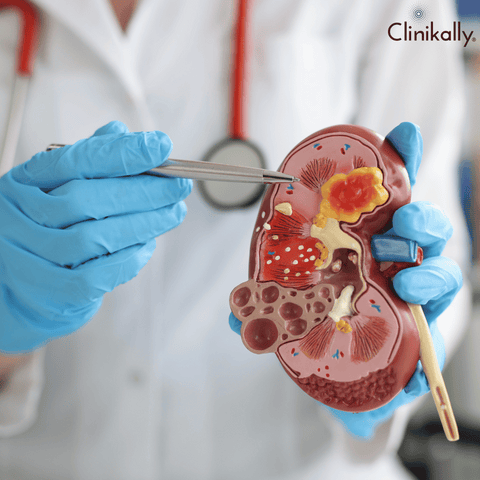
Dehydration is more than just an annoyance; it can have long-term consequences for many body systems. Failure to maintain enough hydration levels over time can endanger one's general health and well-being. We'll look at the long-term impacts and risks of dehydration on various physiological systems.
-
Cardiovascular System: Chronic dehydration can put a strain on the cardiovascular system. It causes decreased blood volume and thickening of the blood, increasing the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and other cardiovascular complications. Prolonged dehydration can lead to long-term heart and blood vessel damage.
-
Kidney Function: The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood as well as maintaining fluid balance. Chronic dehydration can impair kidney function and put you at risk for kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and kidney disease. Long-term dehydration can damage the kidneys and jeopardize overall renal health.
-
Digestive System: Maintaining a healthy digestive system requires adequate hydration. Chronic dehydration can contribute to digestive issues such as constipation, acid reflux, and an increased risk of gastrointestinal disorders. Prolonged dehydration can cause long-term damage to the gastrointestinal tract and negatively impact digestive health overall.
-
Musculoskeletal System: Dehydration can have a variety of effects on the musculoskeletal system. Muscle cramps, weakness, and impaired muscle function can all be caused by dehydration. Chronic dehydration can reduce joint lubrication, potentially increasing the risk of joint problems and musculoskeletal disorders in the long run.
-
Skin Health: Maintaining healthy skin requires adequate hydration. Chronic dehydration can cause skin dryness and flakiness, as well as an increased risk of developing skin disorders like eczema and psoriasis. Prolonged dehydration can hasten skin aging, resulting in wrinkles and fine lines.
-
Cognitive Function: Adequate hydration is essential for optimal cognitive function. Chronic dehydration can impair memory, attention, concentration, and other cognitive abilities. It can contribute to cognitive decline and increase the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's over time.
-
Immune System: The immune system relies on adequate hydration to function properly. Chronic dehydration weakens the immune system, making people more vulnerable to infections, viruses, and other illnesses. Prolonged dehydration can impair immune response and immune system health overall.
-
General Health Risks: Chronic dehydration can increase the risk of a variety of health conditions and complications. It has been linked to kidney disease, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, digestive disorders, and skin problems. Prolonged dehydration can also cause fatigue, impaired physical performance, and an increased susceptibility to other illnesses.
The Cardiovascular Consequences: Dehydration's Impact on Heart Health
Dehydration not only reduces bodily comfort but also puts one's cardiovascular health at risk. Adequate hydration is essential for optimal heart function and cardiovascular health. Reduced blood volume, increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, impaired exercise performance, increased risk of cardiovascular events, impaired blood flow, electrolyte imbalance, and the importance of proper hydration are discussed, as are the cardiovascular consequences of dehydration. Maintaining optimal fluid intake and prioritizing proper hydration are critical for supporting heart health, lowering the risk of cardiovascular problems, and promoting overall cardiovascular well-being. Remember that staying hydrated is an important part of maintaining a healthy heart.
Dehydration and Kidney Function: How Lack of Hydration Can Affect Your Kidneys
Maintaining normal kidney function requires adequate fluids. Dehydration can have a serious influence on the kidneys, impairing their capacity to perform essential tasks. Impaired filtration and waste removal, concentrated urine and urinary tract infections, kidney stone formation, decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery, increased risk of acute kidney injury, electrolyte imbalance, long-term kidney damage, and the importance of proper hydration are all effects of dehydration. Maintaining appropriate fluid balance and prioritizing proper hydration are critical for sustaining kidney health, preventing kidney-related disorders, and boosting general well-being. Remember that staying hydrated is essential for maintaining healthy kidneys.
Joint Health and Dehydration: Understanding the Relationship and Supporting Mobility
Proper hydration is essential for keeping joints healthy and promoting overall joint mobility. Dehydration can have a negative impact on joint health, causing discomfort and decreasing movement. We will look at the connection between joint health and dehydration, as well as measures to support joint mobility with proper hydration.
-
Joint Lubrication: Maintaining joint lubrication requires proper hydration. Synovial fluid, a thick fluid found within joints, serves as a lubricant, reducing friction and allowing for smooth movement. Dehydration can cause a decrease in synovial fluid production, resulting in insufficient joint lubrication and the possibility of joint stiffness and discomfort.
-
Cartilage Health: Cartilage, a firm connective tissue that cushions the joints, is dependent on adequate hydration to maintain its health and function. Dehydration can compromise cartilage integrity, potentially leading to increased wear and tear. This can contribute to joint degeneration, such as osteoarthritis, and limit mobility over time.
-
Impact on Joint Range of Motion: Dehydration can have an impact on the joint range of motion. When joints are dehydrated, they become stiffer and less flexible, resulting in a reduced range of motion. This can make movement difficult and interfere with daily activities and physical performance.
-
Increased Inflammation and Joint Pain: Dehydration increases the risk of joint pain and inflammation. Inadequate hydration can cause toxins and metabolic byproducts to build up in the joints, potentially triggering an inflammatory response. Inflammation can cause joint pain, swelling, and decreased mobility.
-
Joint Injury and Recovery: Proper hydration aids in the prevention and recovery of joint injuries. Dehydration weakens tissues such as ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, making joints more prone to injury. Furthermore, adequate hydration promotes recovery by promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
-
Maintaining Electrolyte Balance: Hydration is crucial for maintaining electrolyte balance, which is essential for optimal joint health. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium help to maintain proper muscle and nerve function, including the muscles and nerves around joints. Electrolyte imbalances caused by dehydration can impair joint function and mobility.
-
Supporting Joint Mobility: Proper hydration is an important part of promoting joint mobility. It is important to hydrate yourself throughout the day by drinking plenty of water and other hydrating liquids. Additionally, eating a diet high in hydrating foods, like fruits and vegetables, can support joint health further.
-
Importance of Long-Term Hydration: Consistently keeping hydrated is essential for the long-term health of your joints. Making drinking water a daily habit ensures the joints receive enough fluid to support their functionality and general mobility. Prioritizing hydration is crucial because fluid loss is greater during physical activity and in hot weather.
Headaches, Sleep, and More: Lesser-Known Effects of Dehydration

Beyond the well-recognized symptoms, dehydration can have a variety of impacts on the body. It has an impact on not just physical health but also on other factors such as headaches and sleep. We will investigate the lesser-known impacts of dehydration and shed light on how it can affect several aspects of our health.
-
Migraines and headaches: Dehydration is a frequent cause of headaches and migraines. The blood vessels in the brain may narrow if you are dehydrated, which can cause pain. In order to prevent and treat headaches brought on by dehydration, proper hydration is essential.
-
Sleep Quality: Dehydration can have an effect on sleep quality. Dehydration can disrupt normal sleep patterns, making it difficult to fall or stay asleep throughout the night. Maintaining adequate hydration promotes improved sleep quality and overall restfulness.
-
Mood and Cognitive Function: Dehydration can have an impact on mood and cognitive function. Mild dehydration, according to research, can increase feelings of anxiety, irritability, and fatigue. It has the potential to impair cognitive abilities like memory, attention, and decision-making. Proper hydration promotes mood stability and cognitive function.
-
Joint and Muscle Pain: Dehydration can contribute to joint and muscle pain. Inadequate hydration can cause muscle cramps and injuries, as well as increased stiffness and flexibility. Proper hydration promotes joint and muscle health, as well as comfort and mobility.
-
Dry Eyes and Mouth: Dehydration can result in dry eyes and mouth. Inadequate fluid intake reduces the production of tears and saliva, resulting in dryness and discomfort. Drinking plenty of water keeps the eyes and mouth moisturized.
-
Digestive Issues: Dehydration can disrupt normal digestion and contribute to digestive issues such as constipation and acid reflux. Water is essential for softening stools and encouraging regular bowel movements. Hydration is essential for a healthy digestive system.
-
Decreased Exercise Performance: Dehydration can have a negative impact on exercise performance. When you are dehydrated, your body's ability to regulate temperature and deliver oxygen and nutrients to your muscles suffers. This can result in decreased endurance, strength, and overall exercise capacity.
-
Skin Issues: Dehydration can contribute to skin issues such as dryness, flakiness, and increased susceptibility to skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. Proper hydration benefits skin health by keeping moisture levels stable and promoting a healthy complexion.
Dehydration and Headaches: Triggers, Prevention, and Relief Strategies
Dehydration frequently serves as an initiator for headaches and migraines. Determining triggers, taking preventative measures, and employing efficient treatment options can all be facilitated by being aware of the connection between dehydration and headaches. We will look into the connection between dehydration and headaches and make recommendations for both prevention and relief.
-
Dehydration as a Headache Trigger: For those who are susceptible, dehydration can cause headaches and migraines. The blood vessels in the brain may close down if the body is dehydrated, which can cause pain and discomfort. Headaches caused by dehydration frequently have a throbbing sensation and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue and dizziness.
-
Prevention through Adequate Hydration: It is important to stay properly hydrated to avoid headaches brought on by dehydration. The general recommendation is to consume two liters of water, or about eight glasses, throughout the day. However, based on variables like activity level, climate, and general health, individual fluid needs may change.
-
Monitoring Fluid Intake: Staying on top of your fluid intake is crucial for avoiding dehydration and the accompanying headaches. Pay attention to your body's thirst cues and increase fluid intake during hot weather, physical activity, and illness. As a reminder to sip water frequently throughout the day, keep a water bottle nearby.
-
Electrolyte Balance: It is crucial to keep your electrolytes in check to stay hydrated and avoid headaches. Include foods and drinks high in electrolytes, such as fruits, vegetables, sports drinks, and coconut water, in addition to water. Electrolytes aid in fluid retention and hydration, which lowers the risk of headaches brought on by dehydration.
-
Avoid Consuming Dehydrating Substances: Some substances can aggravate headaches and raise the risk of dehydration. Diuretic drinks, such as alcohol, caffeinated drinks, and sugary sodas, should be consumed in moderation because they can cause fluid loss. Be cautious when taking medications that could cause diuresis, and speak with your doctor if necessary.
-
Exercise Hydration: Staying properly hydrated while exercising is essential to avoiding headaches brought on by the activity. To keep your fluid levels balanced and avoid becoming dehydrated, drink water before, during, and after physical activity. Depending on the amount of exercise you do, how long it lasts, and the weather, adjust your fluid intake.
-
Techniques for Pain Relief: If you suffer from a headache as a result of dehydration, you may want to consider drinking more water, unwinding, using a cold compress, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers.
-
Seek Medical Attention: It is critical to get medical help if headaches continue despite adequate hydration and self-care efforts or if they significantly interfere with daily life. A medical expert can suggest suitable treatment options and assist in locating potential underlying causes.
Hydration and Quality Sleep: How Dehydration Can Disrupt Your Rest and Recovery
In addition to being important for physical health, proper hydration is also crucial for getting a good night's sleep. Dehydration can interfere with sleep cycles and harm the body's capacity for rest and recovery. We will examine the connection between hydration and sleep and discover how dehydration can interfere with the healing process.
-
Body Temperature Regulation: Proper hydration is essential for regulating body temperature, which is necessary for good sleep. Dehydration reduces the body's ability to dissipate heat through sweat, causing discomfort and making it difficult to achieve and maintain sleep.
-
Sleep Onset and Duration: Dehydration can affect sleep onset and duration. According to studies, dehydration can lengthen the time it takes to fall asleep and result in fragmented sleep patterns. Individuals may wake up more frequently during the night, resulting in shorter overall sleep duration.
-
Sleep Quality and Efficiency: Dehydration can impair sleep quality and efficiency. Dehydrated people tend to have lighter, less restful sleep. This may lead to more sleep disruptions, less time spent in the deep sleep stages, and a higher chance of waking up feeling exhausted.
-
Increased Risk of Snoring and Sleep Apnea: Dehydration can cause snoring and increase the risk of sleep apnea. Inadequate hydration can cause nasal congestion and dryness, making airway passages more susceptible to obstruction while sleeping. This can lead to snoring and disrupted breathing patterns, impairing sleep quality.
-
Daytime Fatigue and Sleepiness: Dehydration can cause daytime fatigue and sleepiness. When sleep is disrupted, people may become excessively sleepy during the day, lose alertness, and have difficulty concentrating. These effects can have a negative impact on daily functioning as well as overall well-being.
-
Impaired Sleep-Related Recovery: Hydration is critical for the body's restorative processes while sleeping. Dehydration can reduce the effectiveness of sleep-related recovery mechanisms by impairing muscle recovery, tissue repair, and hormone regulation. This can result in lower physical performance and slower recovery from physical exertion.
-
Sleep and Cognitive Function: Dehydration can have an effect on cognitive function and memory consolidation, both of which are important aspects of getting enough sleep. Inadequate hydration can impair cognitive abilities like attention, concentration, and problem-solving, making memory formation and retention difficult.
-
Strategies for Hydration and Sleep: To promote quality sleep and improve hydration, consider drinking enough water, limiting diuretic substances, hydrating before bedtime, and monitoring urine color.
Preventing Dehydration: Tips for Staying Hydrated and Nourished

Preventing dehydration is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Proper hydration ensures optimal bodily functions and supports various physiological processes. We will provide valuable tips for staying hydrated and nourished to prevent dehydration and promote optimal hydration levels, including drinking water regularly, hydrating before, during, and after physical activity, consuming hydrating foods, monitoring urine color, limiting diuretic beverages, setting hydration reminders, using electrolyte-rich beverages, and paying attention to hydration during illness. Remember that staying hydrated is an important part of supporting overall health and living a healthy lifestyle.
Hydration Hacks: Simple Strategies to Ensure Proper Hydration Throughout the Day
Proper hydration is critical for overall health and well-being. Simple hydration hacks that you can incorporate into your everyday routine can help you stay appropriately hydrated throughout the day. We will look at simple and practical ways to stay hydrated and support your overall hydration objectives.
-
Drink Water to Start the Day: Start your day with a glass of water as soon as you wake up. This jump-starts your hydration and replenishes fluids lost during the night.
-
Carry a Reusable Water Bottle: Take a reusable water bottle with you wherever you go. It is easier to stay hydrated throughout the day when water is readily available. Choose a bottle that is both convenient and portable so that you can refill it as needed.
-
Set Hydration Goals: Set hydration goals for yourself. Aim to consume a certain amount of water at specific times of the day. Aim to complete a certain number of water bottle refills by lunchtime, mid-afternoon, and evening, for example.
-
Infuse Your Water: Infuse your water with fruits, vegetables, or herbs to add natural flavors. Try pairings like lemon and mint, cucumber and lime, or strawberry and basil.
-
Use Hydration Apps: Use smartphone apps designed to track and remind you to drink water. These apps will send you notifications and reminders to keep you on track with your hydration goals.
-
Consume Hydrating Foods: Include foods high in water content in your diet. Hydrating fruits and vegetables include watermelon, cucumber, oranges, strawberries, celery, and lettuce.
-
Set Reminders: Use your phone or computer to set reminders to drink water throughout the day. Set up periodic reminders to take a few sips or finish a glass of water.
-
Hydrate Before and After Meals: Make drinking water before and after meals a habit. This not only aids hydration, but it can also aid digestion and promote satiety.
-
Make Hydration Stations: Place water dispensers or pitchers filled with infused water in strategic locations throughout your home or workplace. Having hydration stations nearby makes it easier to get water and encourages regular fluid intake.
-
Make Hydration a Habit: Finally, incorporate hydration into your daily routine to make it a habit. Drink a glass of water every time you brush your teeth or take a break at work or school, for example.
Beyond Water: Hydrating Foods and Beverages to Support Your Daily Fluid Intake
Staying hydrated entails not just drinking water but also including hydrating foods and beverages in your diet. These solutions can supplement your normal fluid intake while also providing additional nutrients and flavors. We'll look at some hydrating foods and beverages that can help you meet your hydration objectives.
-
Coconut Water: Coconut water is an electrolyte-rich natural beverage that hydrates and replenishes critical minerals. It is an excellent substitute for sugary sports drinks and can be consumed on its own or as a base for smoothies and refreshing beverages.
-
Herbal Teas: Herbal teas, including chamomile, peppermint, and hibiscus, are both hydrating and caffeine-free. They can be served hot or cold and are a tasty way to remain hydrated throughout the day.
-
Cucumber: Cucumber is a highly hydrating vegetable that contains over 95% water. It can be sliced and added to salads, sandwiches, or infused water for a refreshing twist. Cucumber also contains vitamins and minerals, making it a healthy choice.
-
Watermelon: Watermelon is not only delicious but also hydrating due to its 92% water content. It can be eaten as a snack, blended into smoothies, or frozen into watermelon popsicles for a refreshing and tasty treat.
-
Citrus Fruits: Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruits, and lemons are hydrating and high in vitamin C. They can be eaten whole, juiced, or added to infused water for a flavor and hydration boost.
-
Leafy Greens: Leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and kale have a high water content as well as essential vitamins and minerals. For a hydrating and nutrient-dense meal, mix them into salads, wraps, or green smoothies.
-
Soups and broths: Soups and broths, particularly those made with vegetables or chicken, can be hydrating and comforting. They contain both fluids and electrolytes and can be a nourishing option for hydration, especially during the colder months.
-
Berries: Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, are hydrating fruits high in antioxidants and fibre. Enjoy them as a snack, mix them into yoghurt or smoothies, or toss them into salads for a hydrating and nutritious boost.
-
Aloe Vera Juice: The hydrating properties of aloe vera juice, which is derived from the aloe vera plant, are well known. It is high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
-
Homemade Infused Water: With infused water, you can flavor your hydration. Experiment with different fruit, herb, and vegetable combinations, such as lemon and mint, strawberry and basil, or cucumber and lime. Infused water is a fun and refreshing way to stay hydrated.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Your Well-being Through Optimal Hydration

Maintaining optimal hydration is a critical component of overall well-being. We may take proactive actions to be well-hydrated if we understand the importance of hydration and its far-reaching impacts. We have obtained vital insights into the critical function of hydration in our daily lives by recognizing typical symptoms of dehydration and investigating its impact on numerous body systems, mental performance, and emotional well-being. We can prevent dehydration and its bad repercussions by recognizing the signs of dehydration, knowing its origins and the variables that contribute to it, and investigating its impact on various parts of our health. Let us make hydration a daily practice, ensuring that our bodies get the fluid they need to function properly. We may increase our energy, mental clarity, physical vigor, and overall health by reclaiming our well-being through optimum hydration. Remember that staying hydrated is a simple yet powerful method to nourish our bodies and live a vibrant, balanced existence.
















