Itchy fingers are an irritating and uncomfortable condition that can affect one or both hands. Skin issues, allergies, and other illnesses are just a few of the potential causes of this syndrome. Effective therapy and symptom reduction depend on identifying the root cause of itchy fingertips. We will examine the typical causes, symptoms, and treatment options for itchy fingertips in this response. From mild to severe, itchy fingertips can be a sign of many different diseases. To properly treat the symptoms of itchy fingertips, the underlying cause must be identified. Seek medical attention if symptoms worsen or persist so that you can be properly diagnosed and treated.
Understanding Itchy Fingers
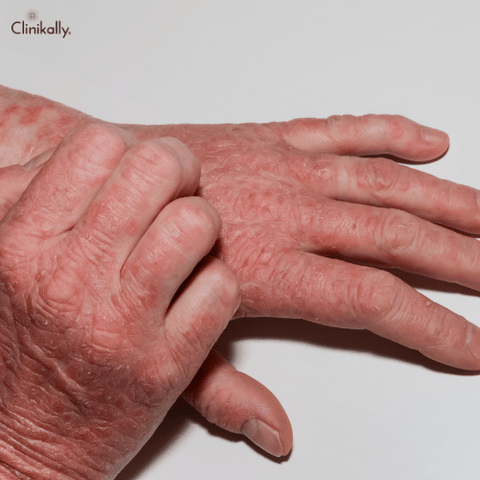
The term "itchy fingers" describes a condition in which a person feels an irritable sensation on the skin of their fingers or nearby. There are many different things that might make you itch, such as skin conditions, infections, allergic reactions, and irritants in the environment. There are occasions when other symptoms, including redness, dryness, scaling, and pimples, might appear along with itchy fingers. The severity of the condition, which can range from mild to severe, can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life.
Skin Irritation and Pruritus
The most frequent causes of itchy fingers are skin irritation and pruritus. There are numerous different skin conditions that can itch and irritate the skin, such as:
-
Eczema: Eczema is a persistent skin ailment that results in itchy, swollen, and red skin. It can happen anywhere on the body, including your fingers.
-
Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune disorder that results in thick, scaly, and itchy skin. It is also capable of causing joint pain and inflammation.
-
Contact dermatitis: When the skin comes into contact with an allergen or irritant, a skin reaction known as contact dermatitis results. It may result in swelling, itching, and redness.
-
Scabies: Tiny mites that burrow into the skin are the cause of the contagious skin condition known as scabies. It is known to cause severe itching and a rash, particularly on the fingers and hands.
-
Dry skin: Particularly during the colder months, dry skin can cause itching and flaking.
-
Allergic reactions: Allergic reactions to food, drugs, or other substances can make the fingers itch and turn red.
-
Insect bites and stings: Itching, swelling, and redness on the fingers can result from insect bites and stings.
Itchy fingers can also be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as liver disease or kidney failure, so it is critical to see a doctor if the itching is severe or persistent.
Common Causes of Itchy Fingers
The following list includes some possible causes of itchy fingers:
-
Dry skin: It can become dry and itchy when it loses moisture, especially on the hands and fingers.
-
Allergies: Exposure to allergens such as poison ivy, detergents, soaps, and cleaning products can result in an allergic reaction and cause itchy fingers.
-
Eczema: Dry, itchy, and inflamed skin are symptoms of the chronic skin condition eczema. It can happen anywhere on the body, including your fingers.
-
Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a long-lasting autoimmune condition that results in scaly, itchy patches on the skin, including the fingers.
-
Fungal infections: Fungal infections, like ringworm, can make your fingers itchy and red.
-
Insect bites: Bites from fleas or mosquitoes, for example, can result in itchy, swollen fingers.
-
Stress and anxiety: These two conditions can itch and irritate the skin.
Specific Conditions and Causes
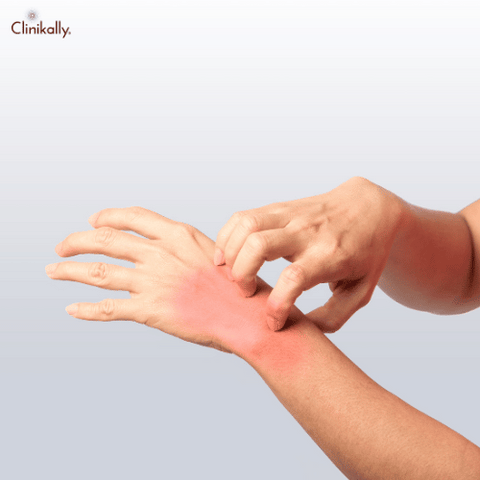
Some specific ailments and factors that contribute to itchy fingers include:
-
Allergic reactions: Itching and redness in the fingers can result from allergic reactions to substances that come into contact with the skin, such as detergents, soaps, lotions, or metals.
-
Eczema: Eczema is a chronic skin condition that can affect the hands and fingers and causes itching and redness of the skin.
-
Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune disorder that results in thick, scaly patches of skin that can be itchy and painful.
-
Scabies: A skin infestation known as scabies is brought on by microscopic mites that burrow into the skin, resulting in severe itching and tiny, red bumps.
-
Dyshidrotic eczema: This type of eczema causes tiny, itchy blisters on the fingers, palms, and soles of the feet.
-
Fungal infections: The skin on the fingers may become itchy, red, and scaly due to fungal infections of the skin, such as ringworm or athlete's foot.
-
Dry skin: In dry climates or during the winter, dry skin can cause itching and flaking of the skin, especially on the fingers.
-
Raynaud's disease: This condition causes the blood vessels in the fingers to constrict, decreasing blood flow and resulting in pain, numbness, and itching in the fingers.
-
Hormonal changes: Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy or menopause can make the skin itchy and dry, including the fingers.
-
Medication: As a side effect, some medications, such as antibiotics, antifungal drugs, and drugs used to treat high blood pressure or cholesterol, can cause itching and skin irritation.
In order to effectively treat and manage the symptoms, it is crucial to determine the underlying cause of itchy fingers. A dermatologist can identify the underlying issue and suggest the best course of action for treatment.
Contact Dermatitis and Allergic Reactions
When the skin comes into contact with an allergen or an irritant, contact dermatitis develops. It can cause a wide range of symptoms, including redness, itching, and swelling. When the immune system responds to an allergen or other foreign substance in the body, allergic reactions take place. Allergic reactions and contact dermatitis are common causes of itchy fingers. Exposure to a variety of things, including metals like nickel, perfumes, chemicals, and soaps, can result in contact dermatitis. Numerous allergens, including pet dander, pollen, foods, and medications, can trigger allergic reactions. Both times, blisters, redness, and edema may also be present in addition to uncomfortable fingers. To prevent further exposure to the allergen or irritant, it is critical to pinpoint the precise origin of the allergic reaction or contact dermatitis.
Eczema, Psoriasis, and Dry Skin
Itchy fingers are a common symptom of psoriasis, eczema, and dry skin.
-
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that impairs the barrier function of the skin. The skin becomes dry, itchy, and scaly as a result of the condition. Itchy fingers are a common eczema symptom, and the itching can be intense, causing skin damage and infection.
-
Psoriasis is another chronic inflammatory skin condition that can cause itchy fingers. The condition is distinguished by red, scaly patches of skin that are itchy and painful. Psoriasis can manifest itself in any part of the body, including the fingers and nails.
-
Itchy fingers can also be caused by dry skin. When skin dries out, it can become itchy, crack, and peel. Low humidity, cold weather, and excessive washing or exposure to water can aggravate this.
Itchy fingers may occasionally be a sign of an underlying medical illness, such as thyroid issues, diabetes, or liver or kidney disease. Additionally, some medications' side effects can cause itchy fingers. You should see a doctor if your itchy fingers persist or are accompanied by other symptoms.
Fungal Infections and Insect Bites
Itchy fingers can also result from fungal diseases and insect bites. Ringworm and other fungal diseases can produce red, scaly areas of skin on the fingers that are extremely itchy. Similar to how itchy, red, and swollen they can be, insect bites on the fingers can be Mosquitoes, ticks, fleas, and bedbugs are examples of common insects that can bite you on your fingers. Scabies, a highly contagious skin infestation caused by microscopic mites that burrow into the skin, can cause itchy fingers in rare cases.
Home Remedies and Topical Treatments

Depending on the underlying cause, there are a number of home remedies and topical treatments that can soothe itchy fingers. Here are a few possibilities:
-
Applying a cool compress to the area can help lessen itching and inflammation. A wet washcloth works well.
-
Moisturizing the skin with a fragrance-free lotion or cream can help prevent itching caused by dry skin.
-
Over-the-counter (OTC) creams and ointments with hydrocortisone, pramoxine, or lidocaine can help relieve itching and discomfort caused by skin irritations and insect bites.
-
If the itching is caused by a fungal infection, an antifungal cream can help relieve symptoms.
-
Taking a warm bath with oatmeal can help relieve itchy skin brought on by eczema or dry skin.
-
Diluted apple cider vinegar can aid in easing the itching brought on by allergic reactions or insect bites.
-
Tea tree oil and lavender oil are two examples of essential oils that have anti-inflammatory and calming properties that can help with itching.
It's important to remember that while these treatments may offer brief relief, they might not get to the root of the itch. The itching should be evaluated by a healthcare professional for a diagnosis and the best course of action if it lasts or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Hydrocortisone Cream and Antihistamines
The two types of medications that can be used to treat itchy fingers are hydrocortisone cream and antihistamines.
-
Topical steroids like hydrocortisone cream can help to lessen itching and inflammation. It is offered in a range of strengths, with lower strengths being available without a prescription and higher strengths requiring one. Hydrocortisone cream can be applied directly to the affected area on the fingers.
-
Antihistamines are drugs that assist in lessening itching brought on by allergic reactions. They function by obstructing the effects of histamine, a substance the body releases in response to an allergen. Antihistamines can be taken orally or applied topically in the form of creams or lotions. They are sold over-the-counter and on prescription.
It is important to keep in mind that while some medications may soothe scratchy fingertips, they may not be appropriate for all users or itching conditions. It is essential to consult a healthcare provider before beginning these treatments, especially if the itching is severe or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Moisturizing and Skin Protection
Additionally, protecting and moisturizing the skin can ease itchy hands. Itching can be avoided by keeping the skin well-hydrated, which can help prevent dryness and cracking. The following advice can help you moisturize and safeguard your skin:
-
Utilize a moisturizer: After washing your hands, moisturize your hands frequently. In order to avoid irritating your skin, pick a moisturizer without any fragrances.
-
Wear gloves: Wear gloves when doing tasks that involve exposure to water or chemicals, such as washing dishes or cleaning. This can help protect your hands from irritation.
-
Avoid using hot water: Hot water can strip the skin's natural oils, causing dryness and irritation. Instead, use lukewarm water to wash your hands.
-
Use gentle soaps: When washing your hands, use a gentle, fragrance-free soap. Harsh soaps can irritate the skin and make itchy skin worse.
-
Apply sunscreen: If you spend a lot of time outside, use broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect your hands from the sun's harmful UV rays.
-
Avoid triggers: If you know what causes your itchy fingers, try to avoid those situations. If you are allergic to nickel, for example, avoid wearing jewellery containing this metal.
-
Keep your nails short: Keeping your nails short can help you avoid scratching your skin, which can aggravate itching and lead to infections.
If your itchy fingers persist despite these measures, see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
When to Consult a Medical Professional

If you've tried over-the-counter medications and home remedies and the itching on your fingers persists, or if you experience other troubling symptoms such as a rash or swelling, you should consult a doctor. A dermatologist can assist in determining the underlying cause of your itchy fingers and offer you a personalized treatment plan. To find the source of the itching, it may occasionally be necessary to use prescription drugs or additional tests. If you suspect that your itchy fingers may be brought on by an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or a thyroid disorder, you should consult your primary care physician or an endocrinologist for additional evaluation.
Persistent Itch or Worsening Symptoms
It could be necessary to see a doctor if your symptoms are getting worse or you endure chronic itching despite taking over-the-counter medications or home cures. Itching that lasts longer than two weeks or that is accompanied by other symptoms like pain, redness, or swelling may be an indication that a medical condition needs to be treated. Additionally, it's crucial to seek medical attention if you believe an allergy or infection may be the source of your itchy fingers. A medical professional can assess your symptoms and suggest the best course of action, which may include prescription medication or more testing, if necessary.
Seeking Proper Diagnosis and Treatment
You should see a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment if your symptoms are getting worse or you have persistent itching despite using over-the-counter medicines and home remedies. Your hands and fingers can be examined by a dermatologist, who can also identify the underlying source of your problems. To assist in the diagnosis, they might also run a few tests, such as an allergy test or skin biopsy. The dermatologist can suggest the best course of action after the source of the itching is found. Depending on the underlying reason for the itch, this can involve prescription-strength topical medicines, oral medications, or other therapy. It is crucial to carefully follow the dermatologist's instructions and to show up for follow-up sessions so that your condition may be monitored and the course of therapy can be changed as needed.
Preventive Measures and Skin Care Tips

By keeping your hands clean and taking care of your skin, you can avoid having itchy fingers. To keep your hands healthy and itch-free, try these preventative measures and skin care advice:
-
Keep your hands clean: Wash your hands frequently with mild soap and warm water, especially after using the restroom, before eating, and after touching germ-infested surfaces.
-
Moisturize your skin: Keeping your skin hydrated and moisturized can help prevent itching and dryness. After washing your hands, apply a fragrance-free and gentle moisturizer.
-
Wear gloves: If you work with chemicals or harsh detergents, wear protective gloves to avoid direct contact with your skin. To prevent your skin from drying out and cracking in the cold, wear gloves as well.
-
Avoid triggers: If you have allergies to certain things, try to limit your exposure to them. This might include everyday irritants like detergents, soaps, and particular fabrics.
-
Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your body hydrated, which can help prevent dry skin.
-
Use gentle soaps: If you have sensitive skin, look for gentle, fragrance-free soaps. Detergents and soaps with abrasive ingredients can itch and irritate the skin.
-
Avoid using hot water: lukewarm water is preferable, as hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils and lead to dryness.
-
Pat dry: Use a clean towel to gently pat your hands dry after washing them. Rub your skin sparingly because doing so can irritate and itch your skin.
-
Avoid scratching: If your fingers are itchy, do not scratch them as this may aggravate the itching and increase the risk of infection.
-
Consult a dermatologist: if your symptoms persist or worsen despite home remedies and over-the-counter medications.
You can keep your hands healthy and itchy by following these preventive measures and skincare tips.
Avoiding Triggers and Irritants
Itchy fingers can be prevented by avoiding triggers and irritants. The following advice:
-
Avoid using harsh soaps or hot water, as these can strip the skin of its natural oils, causing dryness and itchiness.
-
Wear gloves when working with chemicals or doing household chores to protect your skin.
-
Apply a fragrance-free moisturizer on a regular basis to your hands to prevent dryness.
-
If you have an allergy to something, try to stay away from it as much as you can.
-
Wear gloves made of cotton or other soft, breathable fabrics to prevent irritation by choosing skin-friendly materials.
-
Reducing stress is important because it can exacerbate or cause skin conditions. Use stress-reduction strategies like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
-
A healthy diet and regular exercise can help you maintain healthy skin and ward off skin issues.
-
Keep your hands clean by regularly washing them with soap and water to avoid the accumulation of bacteria or other skin irritants.
Consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment if your symptoms are severe or persistent.
Maintaining Healthy Skin Care Practices
The prevention and relief of itchy fingers can be achieved by maintaining healthy skin care routines. Here are a few advices:
-
Keep your hands clean: To get rid of irritants and germs, wash them frequently with mild soap and warm water.
-
Hand moisturizer: After washing your hands, or as needed throughout the day, moisturize your hands. Pick a moisturizer that is non-comedogenic, hypoallergenic, and fragrance-free.
-
Protect your hands: Wear gloves when doing household chores or working with chemicals to protect your hands from irritants and allergens.
-
Avoid hot water: When washing your hands or taking a shower, use lukewarm water because hot water can strip your skin of its natural oils, causing dryness and itching.
-
Use gentle soaps: For washing your hands, body, and face, choose mild, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic soaps. Use gentle soaps that will not irritate or dry out your skin.
-
Stay hydrated: To keep your skin hydrated and healthy, drink plenty of water and eat a well-balanced diet.
-
Avoid scratching: Scratching or rubbing the affected area can aggravate and damage your skin.
-
Wear comfortable clothing: To prevent skin irritation and friction, choose loose-fitting, breathable clothing made of soft materials like cotton.
-
Manage your stress: Stress can cause eczema and psoriasis flare-ups or make them worse. To keep stress under control, practice stress-management methods like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
-
Consult a dermatologist: If your itchy fingers don't go away or get worse despite home remedies, consult a dermatologist who can determine the underlying cause and suggest the best course of action.








































