A chronic skin ailment called Prurigo Nodularis causes itching and raised pimples to appear on the skin. Although they can appear anywhere on the body, the arms, legs, and trunk tend to be the most frequently affected areas. For people who have the illness, it can be extremely unpleasant and quite distressing. The affected areas should not be scratched or rubbed as much as possible because doing so can cause further irritation and nodule growth. Regular skin moisturising can also aid in easing irritation and itching. A dermatologist should be consulted if you have Prurigo Nodularis symptoms in order to decide the best course of action for your particular situation.
What is Prurigo Nodularis?
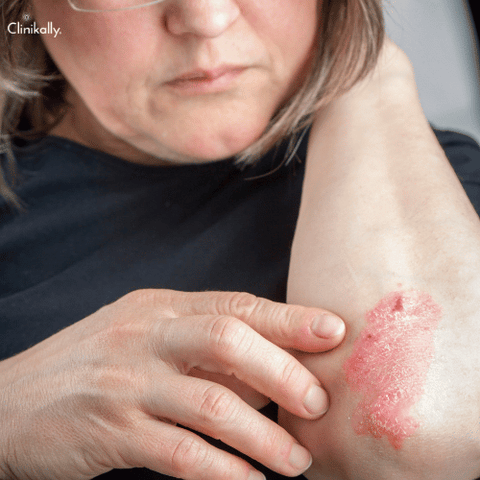
The development of extremely itchy, raised lumps or nodules on the skin is the hallmark of the skin condition known as prurigo nodularis. These nodules can develop anywhere on the body, although they usually develop on the arms, legs, back, or torso. They can be red, brown, or pink in colour and have a diameter that varies from a few millimetres to several centimetres. The illness may be chronic, with flare-ups and remissions. Although the precise cause of Prurigo Nodularis is unknown, it is believed to be linked to an abnormal immune response or nervous system dysfunction. Prurigo Nodularis can be treated with topical creams and ointments, oral drugs, phototherapy, and surgery.
Overview of the Skin Condition
The skin, the biggest organ in the body, acts as a partition between the internal organs of the body and the outside world. It is essential for the body's defence against harm, infection, and dehydration, as well as for controlling body temperature and generating vitamin D. However, a number of ailments and diseases can also have an impact on the skin. Skin disorders come in a variety of forms and severity levels, from moderate to severe. Infections, allergies, autoimmune diseases, environmental factors, and hereditary factors can all contribute to the development of these problems. Acne, eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, rosacea, and skin cancer are a few prevalent skin diseases.
A persistent skin ailment called Prurigo Nodularis causes elevated, itchy nodules to form on the skin. As the exact cause is not fully understood, treating it can be difficult. Scratching the nodules might cause greater irritation and the growth of additional nodules. The nodules can be extremely irritating and unpleasant. Prurigo Nodularis can be treated with topical creams and ointments, oral drugs, phototherapy, and surgery. If you detect any changes or irregularities, it's crucial to take good care of your skin and have it checked out by a doctor. A dermatologist should perform routine skin checks to help identify skin issues early and increase the likelihood that therapy will be effective.
Prevalence and Impact on Quality of Life
Prurigo Nodularis is frequently misdiagnosed and underdiagnosed, hence, its prevalence is not well known. It is thought to affect 0.1% to 0.5% of the general population, with older adults and people with underlying medical disorders like HIV or chronic kidney disease having a higher incidence. A person's quality of life may be significantly impacted by Prurigo Nodularis. The severe scratching and discomfort can make it difficult to sleep, lead to despair and worry, and interfere with daily activities. The nodules' appearance can also be upsetting and harm someone's self-esteem. In extreme circumstances, the illness can cause social isolation and a reduction in everyday function. Because Prurigo Nodularis is a chronic condition, managing it can be challenging, and those who are afflicted by it may feel frustrated and hopeless. However, many people with Prurigo Nodularis are able to relieve their symptoms and enhance their quality of life with the right diagnosis and care. It's critical for those who experience the signs and symptoms of Prurigo Nodularis to get medical help and engage with a dermatologist to create a personalised treatment plan.
Symptoms of Prurigo Nodularis
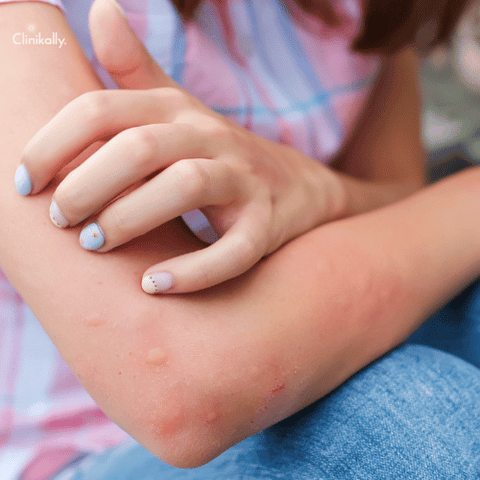

The development of itchy, raised nodules on the skin is a hallmark of the skin condition prurigo nodularis. Prurigo Nodularis symptoms can vary from person to person, but they commonly include:
-
Itchy nodules: The presence of raised, itchy nodules on the skin is the most common symptom of Prurigo Nodularis. These nodules can vary in size, colour, and shape, and additional symptoms like redness, scaling, and crusting may also be present.
-
Chronic itching: Prurigo Nodularis can cause chronic itching that is severe, persistent, and may be worse at night. Scratching can exacerbate the cycle of itching and scratching, which can lead to new nodules and irritation.
-
Thickened skin: Over time, Prurigo Nodularis-related scratching can result in the thickening and discoloration of the skin. This process, called lichenification, can cause more itching and discomfort.
-
Emotional distress: The persistent nature of Prurigo Nodularis, along with the excruciating itching and discomfort, can result in significant emotional distress. For those who have this condition, anxiety, depression, and social isolation are frequent symptoms.
If you have Prurigo Nodularis symptoms, it is critical that you seek medical attention and collaborate with a dermatologist to develop an individualised treatment plan.
Recognizing the Itchy Nodules
Prurigo Nodules or tiny, irritating lumps on the skin, are the most common manifestation of nodularis. These nodules can form clusters and are frequently grouped together. They can be flesh-coloured, red, brown, or black and range in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter. The nodules are frequently associated with severe itching, which can be exacerbated at night and by specific triggers such as heat or stress. Scratching can be so severe that it interferes with sleep and daily activities. Scratching the nodules may aggravate the itch and promote the growth of additional nodules, starting a vicious cycle of scratching and itching. Prurigo Nodularis can also result in other skin abnormalities such as scaling, crusting, and skin thickening in addition to the nodules. Due to frequent scratching, the affected skin may appear rough, dry, or scaly and may also be discoloured or hyperpigmented. If you notice any painful nodules on your skin, consult a dermatologist immediately, especially if they are accompanied by persistent itching. Although Prurigo Nodularis can be challenging to diagnose and manage, many people can find symptom relief and an improvement in their quality of life with the right care and management.
Commonly Affected Areas
Prurigo Nodularis can infect any part of the body, but since the arms, legs, and back are the easiest to scratch, these areas are more commonly affected. The head, neck, and trunk may also be affected. The body may be significantly affected by the lesions, or only a small piece of it. There may be nodules and itching in the groyne, pubic region, or vulva as a result of Prurigo Nodularis on occasion. This can be quite upsetting for those who are affected because it can block daily duties and make them feel ashamed. It is significant to note that each individual may have a different location and distribution of Prurigo Nodularis. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist for treatment if your skin is developing nodules and you are suffering from constant itching. They can do a comprehensive evaluation and provide a personalised treatment plan to control your symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors

Although the precise causes of Prurigo Nodularis are unknown, it is believed that persistent scratching and itching are contributing factors. The skin can become damaged and inflamed from frequent scratching, which can result in nodules and thicker skin. In other situations, the itching may be brought on by a skin condition like atopic dermatitis or psoriasis, or by an underlying medical condition like renal illness or HIV. Prurigo Nodularis can affect everyone, but some things may make it more likely that you'll get it. These consist of:
-
Age: People over 60 years old have the highest incidence of the disease Prurigo Nodularis, which is more prevalent in older adults.
-
Gender: Prurigo Nodularis is more likely to affect women than men.
-
Skin conditions: Prurigo Nodularis may be more likely to develop in people with other skin conditions like atopic dermatitis or psoriasis.
-
Chronic kidney disease: People with chronic kidney disease may be more likely to develop Prurigo Nodularis, though the exact relationship is unknown.
-
HIV: People living with HIV are at a higher risk of developing Prurigo Nodularis, particularly in the advanced stages of the disease.
-
Mental health conditions: Prurigo Nodularis can be associated with anxiety, depression, and other mental health conditions, which may increase the risk of developing the condition.
If you are more likely to develop Prurigo Nodularis, it is imperative that you keep an eye out for the development of nodules and persistent itching on your skin. If you notice any changes in your skin, you should seek treatment from a dermatologist right away. They can perform a thorough evaluation and offer a tailored treatment plan to manage your symptoms.
Aetiology of Prurigo Nodularis
It is unclear exactly what causes Prurigo Nodularis, or its aetiology. However, it is believed that the condition is connected to persistent scratching, which can harm the skin and result in nodules. Prurigo Nodularis could occur as a result of a number of circumstances, including:
-
Dysfunction of the skin barrier: A breakdown in the skin barrier can leave the skin more susceptible to allergens and irritants, which can cause itching and scratching.
-
Neurogenic inflammation: When nerve signals cause inflammation, histamine and other inflammatory mediators may be released, causing itching and scratching.
-
An abnormal immune response: Although the exact mechanisms are unknown, an abnormal immune response may play a role in the development of Prurigo Nodularis.
-
Underlying medical conditions: Prurigo Nodularis can be associated with underlying medical conditions such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, chronic kidney disease, and HIV, which may contribute to the condition's development.
-
Psychological factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression can all aggravate itching and scratching, which may contribute to the development of Prurigo Nodularis.
It is significant to remember that Prurigo Nodularis has a complicated and multivariate aetiology that might differ from person to person. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist for treatment if your skin is developing nodules and you are suffering from constant itching. They can do a comprehensive evaluation and provide a personalised treatment plan to control your symptoms.
Associated Health Conditions
Prurigo Nodularis has been linked to a number of underlying health issues, including:
-
Atopic dermatitis: Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by itching and dry, scaly skin. People who have atopic dermatitis are more likely to develop Prurigo Nodularis.
-
Psoriasis: This autoimmune skin condition causes the skin's cells to grow rapidly, resulting in the appearance of thick, scaly patches on the skin. The risk of developing Prurigo Nodularis may be higher in people with psoriasis.
-
Chronic kidney disease: People with chronic kidney disease may be more likely to develop Prurigo Nodularis, though the exact relationship is unknown.
-
HIV: People living with HIV are at a higher risk of developing Prurigo Nodularis, particularly in the advanced stages of the disease.
-
Hepatitis C: This viral infection causes liver damage. Prurigo Nodularis may be more dangerous to people who have hepatitis C.
-
Anaemia due to iron deficiency: Prurigo Nodularis development has been linked to anaemia due to iron deficiency.
-
Neurological disorders: Prurigo Nodularis has been linked to a number of neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, and spinal cord injuries.
Not everyone with these underlying health issues will experience the development of Prurigo Nodularis, and the connection between these issues and the onset of Prurigo Nodularis is complicated and poorly understood. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist for treatment if your skin is developing nodules and you are suffering from constant itching. They can do a comprehensive evaluation and provide a personalised treatment plan to control your symptoms.
Diagnosing Prurigo Nodularis
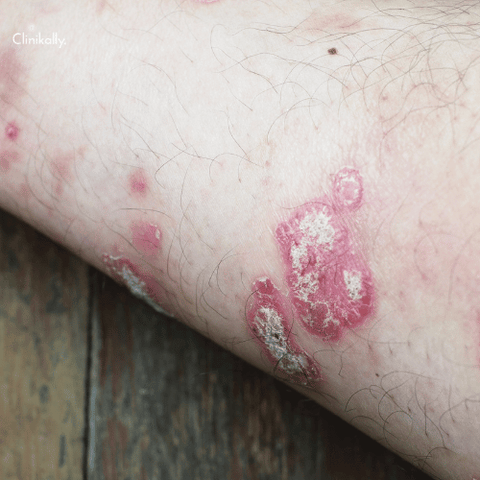
Due to the lack of a single diagnostic test for Prurigo Nodularis, diagnosis can be difficult. Skin biopsy, clinical examination, and medical history are frequently used to make diagnoses. A dermatologist will check the affected skin areas during a clinical examination, looking for distinctive nodules and any evidence of scratching or scarring. They might also inquire about any symptoms you may be having, such as itchiness or soreness, as well as any underlying medical conditions you may be dealing with. A skin biopsy could also confirm the diagnosis. During a skin biopsy, a small sample of skin tissue is removed and examined under a microscope. This can establish the presence of Prurigo Nodularis and help rule out any other skin disorders. It is significant to note that determining the precise diagnosis of Prurigo Nodularis can be difficult and may require multiple consultations with a dermatologist. It is crucial to consult a dermatologist for treatment if your skin is developing nodules and you are suffering from constant itching. They can do a comprehensive evaluation and provide a personalised treatment plan to control your symptoms.
Physical Examination
A dermatologist will closely inspect the skin's afflicted areas during a physical examination for Prurigo Nodularis. They will search for distinctive nodules as well as scratches or scars. The evaluation could consist of:
-
Examining the skin: The dermatologist will examine your skin for any elevated, hard, or irritating nodules. These nodules can be small (a few millimetres) or large (a few centimetres), and they can be red, brown, or black in colour.
-
Skin palpation: The dermatologist may gently press on the nodules and surrounding skin with their fingers. This can aid in determining the firmness and texture of the nodules as well as any underlying inflammation.
-
Itching assessment: The dermatologist may inquire about any itching or discomfort you are experiencing in the affected areas. They may also inquire about any triggers that appear to aggravate your itching.
-
Scarring evaluation: The dermatologist may look for signs of scarring or other skin damage caused by scratching or rubbing the affected areas.
-
Examination of additional body parts: The dermatologist may check additional body parts for any indications of skin conditions or underlying health issues that might be influencing the emergence of Prurigo Nodularis.
It is significant to note that determining the precise diagnosis of Prurigo Nodularis can be difficult and may require multiple consultations with a dermatologist. If you are experiencing persistent itching and the formation of nodules on your skin, you should consult a dermatologist. They can conduct a comprehensive evaluation and create an individualised treatment plan to manage your symptoms.
Histopathological Analysis
Prurigo Nodularis can be identified via histopathological investigation, which is a diagnostic tool. A pathologist does this analysis by taking a tiny sample of skin tissue from the affected area and examining it under a microscope. The pathologist will examine the skin tissue for distinctive alterations connected to Prurigo Nodularis. These alterations include lymphocytic infiltration, acanthosis, and hyperkeratosis. Acanthosis refers to a rise in the thickness of the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, whereas hyperkeratosis refers to an overgrowth of the outermost layer of skin cells. Lymphocyte infiltration is the term used to describe the presence of immune cells in the skin tissue.
Histopathological evaluation can help rule out other skin disorders like eczema or psoriasis in addition to helping confirm the diagnosis of Prurigo Nodularis. It is important to remember that diagnosing Prurigo Nodularis may not necessarily require a skin sample and histological examination. In certain circumstances, a diagnosis can be made solely on the basis of a clinical examination and medical history. Depending on your particular circumstances, your dermatologist will decide whether a skin biopsy is required.
Treatment Options for Prurigo Nodularis
The goals of treatment for Prurigo Nodularis are symptom relief, itching relief, and halting the growth of new nodules. A combination of behavioural therapy, oral medicines, and topical drugs may be used as treatment options.
-
Topical medications: Topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors may be prescribed to relieve itching and inflammation in affected areas of the skin.
-
Oral medications: Antihistamines or tricyclic antidepressants may be prescribed to alleviate itching and improve sleep. Immunosuppressive drugs like methotrexate or cyclosporine may occasionally be prescribed to treat inflammation and stop the growth of new nodules.
-
Behavioural therapies: Patients who need to learn new behaviours and strategies to manage itching and scratching may benefit from behavioural therapies like cognitive-behavioural therapy or habit reversal training.
-
Phototherapy: Phototherapy, or light therapy, can also be used to treat Prurigo Nodularis. This involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light in order to reduce inflammation and itching.
-
Surgery: Surgical removal of nodules may be required in some cases. This is usually reserved for large, persistent nodules that have failed to respond to other treatments.
It is important to remember that Prurigo Nodularis has the potential to be a chronic condition and that symptoms may not improve for several months after starting treatment. Based on the severity of your symptoms and your unique condition, your dermatologist will collaborate with you to create a customised treatment plan.
Topical Corticosteroids and Antihistamines
Topical corticosteroids and antihistamines are two medications that are commonly used to treat Prurigo Nodularis.
-
Topical corticosteroids: These medications work by reducing inflammation and itching when applied directly to the affected skin. They come in a variety of strengths and formulations, and your dermatologist will choose the best one for you based on the severity of your symptoms and the location of the nodules. Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids can result in side effects such as skin thinning and an increased risk of infection, so it's critical to use them as directed.
-
Antihistamines: These medications are frequently used to relieve itching and improve sleep in patients with Prurigo Nodularis. They work by preventing the release of histamine, a chemical in the body that causes itching and inflammation. Antihistamines can cause drowsiness and a dry mouth, so use them as directed and avoid activities that require alertness.
The fundamental cause of Prurigo Nodularis cannot be treated with topical corticosteroids or antihistamines, despite the fact that they can be beneficial in lowering symptoms. To control symptoms and stop the growth of new nodules, it may occasionally be essential to use additional treatments such behavioural therapy or immune-suppressing drugs. Together, you and your dermatologist will create a personalised treatment plan that takes your unique symptoms and concerns into account.
Phototherapy and Immunosuppressive Therapy
Phototherapy and immunosuppressive therapy are two additional treatment options for Prurigo Nodularis.
-
Phototherapy: To lessen inflammation and itching, phototherapy, commonly referred to as light therapy, involves exposing the skin to particular light wavelengths. Prurigo Nodularis has been treated with phototherapy using narrowband UVB (NB-UVB) and UVA1. The most typical form of phototherapy for Prurigo Nodularis is NB-UVB, which has been proven to be beneficial in minimising itching and enhancing nodule appearance. But not all patients may benefit from phototherapy, and it may have adverse effects like sunburn, itching, and a higher risk of skin cancer.
-
Immunosuppressive therapy: Prurigo Nodularis can be treated with immunosuppressive drugs such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and mycophenolate mofetil. These drugs function by lowering inflammation in the skin's afflicted areas and inhibiting the immune system. Patients with severe or persistent symptoms who do not respond to other treatments may require immunosuppressive therapy. These medications can, however, have serious side effects, including an increased risk of infections, damage to the liver and kidneys, and an increased risk of developing specific types of cancer. While taking these medications, you must be closely monitored by a medical professional.
It is important to remember that, in comparison to topical medications and antihistamines, phototherapy and immunosuppressive therapy are more invasive treatments with a higher risk of side effects. Your dermatologist and you will decide together which treatment options are best for your specific needs and concerns.
Lifestyle Changes and Stress Management
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and stress management can help with Prurigo Nodularis management. Here are some suggestions:
-
Avoid triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers that can worsen symptoms, such as stress, certain fabrics, and certain foods, can aid in the management of Prurigo Nodularis.
-
Moisturise the skin: Dry skin can aggravate itching and inflammation. Applying a fragrance-free moisturiser to the skin can help keep it hydrated and relieve symptoms.
-
Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight clothing can irritate the skin and aggravate symptoms. Itching and irritation can be lessened by donning comfortable, loose-fitting clothing.
-
Practice stress management techniques: Stress can worsen symptoms of Prurigo Nodularis. Meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga are all stress management techniques that can help reduce stress and improve symptoms.
-
Seek help: Living with a chronic skin condition such as Prurigo Nodularis can be difficult. Seeking help from family, friends, and support groups can aid in stress management and overall well-being.
It's important to remember that lifestyle changes and stress-reduction techniques aren't a replacement for medical treatment. It's important to work with a healthcare professional to develop an individualised treatment plan that addresses both the medical and lifestyle aspects of managing Prurigo Nodularis.
Tips for Living with Prurigo Nodularis
Living with Prurigo Nodularis can be difficult, but there are some suggestions that can make the situation more bearable:
-
Learn everything you can about the condition and its treatments. Self-education can assist you in better understanding the condition and making informed decisions about your treatment plan.
-
To effectively manage Prurigo Nodularis, close collaboration with your dermatologist is essential. Be forthright and honest about your symptoms, worries, and preferred course of treatment. For the benefit of your conversations with your healthcare provider, keep a record of your symptoms, triggers, and treatments.
-
Cleanse and moisturise it gently every day to help reduce itching and inflammation. Avoid using harsh soaps and fragranced products on your skin.
-
Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of Prurigo Nodularis. Stress management techniques, such as practising relaxation techniques, can help reduce symptoms.
-
Living with a chronic skin condition can be difficult. Seeking help from family, friends, and support groups can aid in stress management and overall well-being.
-
Make time for yourself and engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation. Practising self-care can help improve your overall well-being and reduce stress.
Keep in mind that Prurigo Nodularis requires continuing therapy because it is a chronic illness. In order to create an individualised treatment plan and make lifestyle adjustments that will enhance your symptoms and quality of life, it's critical to engage closely with your healthcare professional.









































