Atrophic scars form when the skin's underlying tissues are destroyed, resulting in a depressed or sunken look. Acne, surgery, or accident can all lead to the formation of these scars. While atrophic scars pose no health dangers, they can have a negative influence on a person's self-esteem and confidence. Fortunately, there are a number of successful treatments for atrophic scars. It should be noted that the efficiency of various therapies varies depending on the individual and the degree of the scar. It is essential to get the advice of a dermatologist or other experienced healthcare professional who can assess your situation and provide the best treatment choices for your atrophic scars.
Understanding Atrophic Scars: Types, Causes, and Characteristics
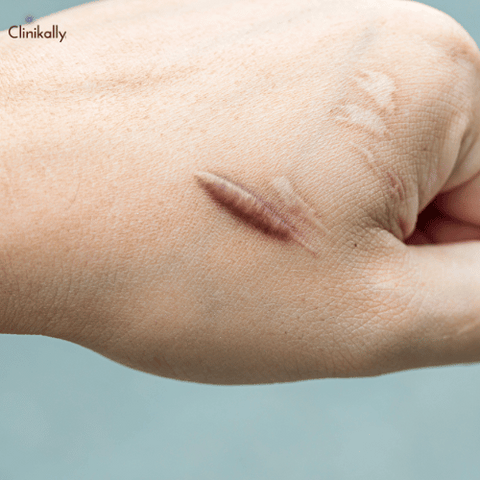
Understanding the many forms, causes, and characteristics of atrophic scars can help guide appropriate treatment options. Here is a breakdown of these factors:
Types of atrophic scars: Acne scars, surgical scars, traumatic or injury scars, and chickenpox scars are examples of atrophic scars.
Causes of Atrophic Scars:
-
Loss of Collagen: Atrophic scars develop when there is a shortage of collagen, a protein that keeps the skin's elasticity and structure in place. Depressed or sunken scars can result from wound healing that damages the collagen fibres.
-
Poor Wound Healing: Poor wound healing, which can include delayed closure, infection, or excessive inflammation, can result in atrophic scarring.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Atrophic scar formation may be a genetic predisposition in some people. Skin tone, ethnicity, and family history are a few variables that may have an impact on scar formation.
Characteristics of Atrophic Scars:
-
Sunken or depressed appearance: Atrophic scars have this appearance because the scar tissue is below the level of the surrounding skin.
-
Smooth or Irregular Texture: The texture of an atrophic scar can be smooth or irregular, with uneven or wavy contours, depending on its severity and type.
-
Discoloration: Atrophic scars may differ in pigmentation from the skin around them. They might look lighter or darker than the tissue around them.
-
The surface that is Pitted or Indented: Atrophic scars frequently have a pitted or indented surface, looking like tiny craters or divots in the skin.
-
Emotional Impact: Aside from physical characteristics, atrophic scars can have a psychological impact, affecting an individual's self-esteem and confidence.
It's crucial to note that everyone's experience with atrophic scars is unique, and scar severity can range from minor to severe. A dermatologist or healthcare professional should be consulted to properly examine your unique situation and decide the best treatment options.
Decoding Atrophic Scars: Exploring Different Types and Their Features
Let us delve deeper into the various atrophic scar types and their distinctive characteristics:
- Ice Pick Scars:
-
Description: Ice pick scars are narrow, deep, and have a V-shaped appearance.
-
Features:
-
Size: These scars are usually less than 2mm in diameter.
-
Depth: They penetrate deeply into the skin, giving it an "ice pick" or pitted appearance.
-
Shape: The scars frequently have steep edges and narrow openings.
-
Texture: Ice-pick scars can be either smooth or rough.
- Boxcar Scars:
-
Description: Boxcar scars are broader depressions with well-defined edges.
-
Features:
-
Size: These scars are larger than ice pick scars, ranging in diameter from 1 to 4mm.
-
Depth: They are shallower than ice-pick scars but still appear depressed.
-
Shape: Boxcar scars have a box-like appearance with sharp edges.
-
Texture: The skin within these scars may be rough or uneven.
- Scars on the Roll:
-
Description: Rolling scars have a wave-like or undulating appearance on the skin.
-
Features:
-
Size: These scars are broader and larger in diameter than ice-pick scars.
-
Depth: Rather than deep depressions, they are typically shallow, with a gradual slope.
-
Shape: Rolling scars resemble wavy or rolling hills and lack clearly defined edges.
-
Texture: The skin within these scars may be smooth or slightly uneven.
- Hypertrophic Scars:
-
Description: Hypertrophic scars are raised and thickened, often with a red or pink coloration.
-
Features:
-
Size: The raised tissue on these scars can range in size from small to large.
-
Elevation: Scars with hypertrophy stick out from the skin's surface.
-
Colour: They may be darker than the surrounding skin or appear red, pink, or both.
-
Texture: Hypertrophic scars have a firm or hard texture to the touch.
- Scars with Keloid:
-
Description: Keloid scars are similar to hypertrophic scars but extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound.
-
Features:
-
Size: Keloids can be larger than the site of the initial injury or incision.
-
Elevation: They are elevated and extend beyond the scar's borders.
-
Colour: Keloids can be red, pink, or darker than the surrounding skin.
-
Texture: Keloid scars have a firm or rubbery texture.
It is worth noting that atrophic scars can be a mix of these types or vary in severity within a single scar. A dermatologist's or healthcare professional's proper diagnosis and evaluation are critical for determining the specific type of atrophic scar and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Unveiling the Origins: What Causes Atrophic Scars to Form?
Atrophic scars form as a result of injury or disturbance of the skin's underlying tissues during the wound healing process. There are numerous factors that can lead to atrophic scarring. The main reasons are as follows:
-
Loss of Collagen: The protein collagen gives the skin its strength, structure, and elasticity. The normal production and arrangement of collagen may be disturbed when the skin is injured or experiences trauma, such as acne, surgery, or injury. Atrophic scars can be caused by either insufficient or excessive collagen synthesis.
-
Poor Wound Healing: Scar formation is heavily influenced by how a wound heals. Atrophic scars may form if the wound-healing process is hampered or interfered with. Infection, poor blood flow to the wound site, protracted inflammation, and improper wound closure are all factors that can affect how well a wound heals.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Atrophic scarring may be a genetic predisposition in some people. Genetics can affect how the body responds to skin damage, controls the synthesis of collagen, and manages inflammation. These scars may be more likely to appear in people with a family history of atrophic scarring.
-
Skin Type: Atrophic scarring is more common in some skin types. Atrophic scars are more likely to form on people with naturally thinner skin because they have less collagen and underlying support. Additionally, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin) within atrophic scars may be more common in people with darker skin tones.
-
Injury severity: The type and extent of scarring can vary depending on how badly the skin was damaged initially. Atrophic scars are more likely to develop after deeper wounds, such as deep acne cysts, surgical incisions that go through multiple layers of skin, or traumatic injuries that harm deeper tissue layers.
It is important to remember that unique circumstances and factors can also have an impact on scar formation. Atrophic scar formation and appearance can be reduced with proper wound care, early intervention, and the right treatment options. For a thorough assessment of your unique situation and advice on scar prevention and management, speaking with a dermatologist or healthcare professional is advised.
Examining the Impact: How Atrophic Scars Affect Skin Appearance
Atrophic scars can have a dramatic impact on the appearance of the skin, producing self-consciousness and lowering confidence. Atrophic scars can have the following effects on skin appearance:
-
Sunken or Depressed Appearance: Atrophic scars cause indentations or depressions in the skin, giving it a sunken or uneven appearance. These scars may alter the skin's uniformly smooth surface.
-
Texture irregularities: The skin texture may become uneven or rough within and around the scarred area, depending on the type and severity of the atrophic scar. This may result in an uneven surface that is distinct from the skin around it.
-
Colour variations: Due to changes in pigmentation, atrophic scars may appear lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. It is possible that the scarred area has a different color, which is especially obvious in people with lighter or darker skin tones.
-
Disruption of Skin Continuity: Atrophic scars can disrupt the skin's natural flow and continuity. They may leave visible boundaries or edges, especially if the scar is on an exposed or prominent area of the body.
-
Emotional and psychological impact: Atrophic scars can have a significant emotional impact on a person. They can make you feel insecure, self-conscious, and have low self-esteem. These scars can interfere with social interactions and limit participation in activities that require the exposed areas to be exposed.
The psychological impact of atrophic scars, as well as the potential need for emotional support, must be recognized. Individuals who are dealing with the emotional consequences of their scars may benefit from professional help, such as therapy or counselling. Various treatment options for atrophic scars can help enhance their look and reduce their detrimental influence on skin aesthetics. A dermatologist or other healthcare professional can provide important advice on appropriate treatment options based on specific circumstances and scar types.
Expert-Backed Treatments for Atrophic Scars: Techniques, Tips, and Results
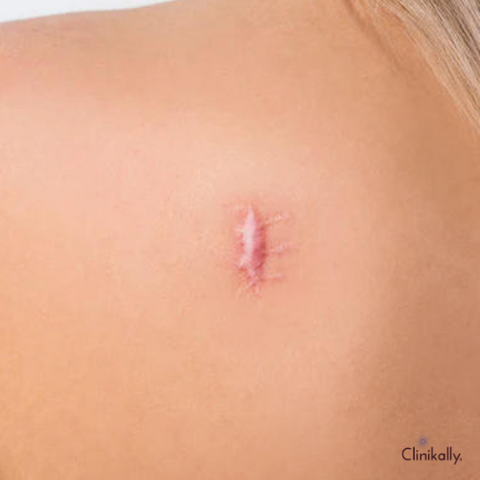
Here are some expert-recommended treatments for atrophic scars, along with the techniques, tips, and potential outcomes associated with each method:
- Dermal Fillers:
-
Technique: Dermal fillers, such as those based on hyaluronic acid, are injected into atrophic scars to lift the depressed areas and restore volume.
-
Tips: Have the injections performed by an experienced dermatologist or healthcare professional. Multiple treatment sessions spaced several weeks apart may be required for optimal results.
-
Results: Depending on the product used, dermal fillers provide immediate improvement in the appearance of atrophic scars, with results lasting several months to a year.
- Microneedling:
-
Technique: To produce controlled micro-injuries in the skin, micro-needling involves using a device with tiny needles. This procedure encourages skin remodelling and stimulates the production of collagen.
-
Tips: A skilled expert should do micro-needling. Multiple sessions are usually required for best results, and post-treatment care, such as sun protection and gentle skincare, is essential.
-
Results: Microneedling can improve the texture and overall appearance of atrophic scars over time, with visible results typically becoming apparent after a few treatments.
- Chemical Peels:
-
Technique: During chemical peels, the top layers of the skin are controlled and exfoliated by putting a chemical solution on the skin. This promotes skin cell renewal and boosts collagen production.
-
Tips: Only trained professionals should perform chemical peels. The depth of the peel can be altered based on how severe the scars are. Use of sun protection and appropriate aftercare are essential.
-
Results: Chemical peels can improve the overall appearance of atrophic scars by improving their texture, color, and appearance. The best results might require multiple sessions.
- Laser Therapy:
-
Technique: Laser treatments, like fractional laser resurfacing, stimulate collagen production, encourage skin regeneration, and lessen the appearance of atrophic scars by using targeted laser energy.
-
Tips: A trained dermatologist or healthcare practitioner should perform laser therapy. Multiple sessions may be necessary, and post-treatment maintenance, such as sun protection and gentle skincare, is essential.
-
Results: Laser therapy can effectively reduce the depth and visibility of atrophic scars. Results are typically gradual and may continue to improve over time.
- Subcision:
-
Technique: Subcision is a minor surgical procedure in which a needle is inserted beneath the scar to break up the fibrous bands that bind the scar to the skin. underlying tissue. This raises the depressed scar to the level of the surrounding skin.
-
Tips: A qualified dermatologist or plastic surgeon should perform subcision. Compression after the procedure and appropriate wound care are crucial for optimum healing.
-
Results: By releasing scar tissue and levelling the skin surface, subcision can significantly improve the appearance of atrophic scars. Results frequently last a long time.
It is important to remember that each person's reactions to treatments may differ and that for more severe or intricate atrophic scars, a combination of methods may be required. A dermatologist or other healthcare provider should be consulted to determine the best course of action based on each patient's unique situation and scar characteristics.
Dermatologist-Recommended Solutions: Effective Treatments for Atrophic Scars
Here are some recommendations from dermatologists for treating atrophic scars successfully:
-
Fractional Laser Resurfacing: Using laser technology, controlled microscopic injuries to the skin are produced in fractional laser resurfacing. This prompts skin remodelling and stimulates the production of collagen. It can enhance the atrophic scars' depth, texture, and appearance. Depending on the strength of the laser being used, multiple treatment sessions may be required, and recovery time may vary.
-
Microneedling with radiofrequency: This procedure applies radiofrequency energy to the skin while also microneedling the tissue. Microneedles cause microscopic wounds, whereas radiofrequency energy warms the deeper layers of the skin, promoting the synthesis of collagen. This combination effectively improves the appearance of atrophic scars. For the best results, multiple sessions are typically necessary.
-
Dermal Fillers: Atrophic scars can be raised and given a better appearance by injecting dermal fillers, such as those based on hyaluronic acid, into the depressed areas. The effects start to show right away and, depending on the product used, can last anywhere from a few months to a year. It is a non-surgical choice that necessitates knowledge of injection methods.
-
Chemical Peels: A chemical solution is applied to the skin during a chemical peel to exfoliate the top layers and encourage skin regeneration. This can help atrophic scars look better in terms of texture and colour. The number of treatments necessary to achieve the best results depends on the severity of the scars and the depth of the peel.
-
Subcision: Subcision is a minor surgical procedure in which the fibrous bands holding the scar to the underlying tissue are cut with a needle or blade inserted beneath the scar. This allows the depressed scar to rise to the level of the surrounding skin, which is what causes it to be released. Subcision can be combined with other treatments for enhanced results.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: In PRP therapy, concentrated platelet-rich plasma is injected into atrophic scars after being isolated and extracted from the patient's blood. Growth factors found in PRP encourage collagen synthesis and advance tissue regeneration. It can help atrophic scars look better and encourage skin renewal in general.
-
Silicone Gel or Sheets: To hydrate the skin and create an occlusive barrier, silicone gel or sheets are applied over atrophic scars. This helps to flatten and soften the scars over time. Silicone-based products can be used in conjunction with other scar management techniques.
It is important to remember that factors like scar type, severity, location, and personal patient characteristics influence the type of treatment selected. The best treatment option for your particular needs and goals must be determined in consultation with a dermatologist or other healthcare specialist.
Collagen Induction Therapy: Stimulating Skin Repair for Atrophic Scars
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, is a popular treatment for accelerating skin healing and reducing the appearance of atrophic scars. The following is how collagen induction treatment works:
-
Technique: During collagen induction therapy, a device with fine needles known as a micro-needling pen or roller is used to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. The needles puncture the skin's surface, causing the body's natural healing response to be triggered.
-
Collagen Production: The micro-injuries caused by the microneedles cause growth factors to be released and to stimulate the production of collagen, a protein crucial to the flexibility and structure of the skin. Collagen production is increased, which fills in atrophic scars and improves skin texture and look.
-
Skin Remodelling: The skin undergoes remodelling as collagen is produced. The new collagen fibres form a more organised and uniform pattern, thereby replacing damaged scar tissue and promoting a smoother skin surface.
-
Treatment Sessions: To achieve optimal results, collagen induction therapy usually necessitates multiple treatment sessions spaced several weeks apart. The severity of the atrophic scars and the patient's response to treatment determine the necessary number of sessions.
-
Professional Care: A licensed dermatologist or skincare expert should administer collagen induction therapy. They will determine the proper needle depth and tailor the treatment to address specific areas of concern.
-
Post-Treatment Care: Following collagen induction therapy, it is critical to follow proper post-treatment care. This may include avoiding sun exposure, following a gentle skincare routine, and using recommended post-treatment products to promote healing and protect the skin.
-
Results: Collagen induction therapy can lead to a gradual improvement in the appearance of atrophic scars over time. The number of sessions completed, the severity of the scars, and the individual's response to treatment all influence the outcome. It is important to have reasonable expectations and recognize that total scar removal might not always be possible.
Collagen induction therapy is usually regarded as safe and appropriate for a wide range of skin types. However, if you have any underlying skin disorders or concerns, you should speak with a dermatologist or skin care professional to see if this is the right treatment option for you. They may evaluate your specific condition, make personalised recommendations, and guarantee that the treatment is carried out safely and successfully.
Microdermabrasion: Smoothing the Path to Atrophic Scar Improvement
Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive skin rejuvenation method that can help make atrophic scars look better. It entails exfoliating the skin's outermost layer with a device that emits fine crystals or a diamond-tipped wand. Here's how microdermabrasion works and what it could do for atrophic scars:
-
Exfoliation: The device uses gentle exfoliation to remove dead skin cells and encourage cell renewal during the procedure. This exfoliation procedure aids in reducing skin roughness and enhancing the general appearance of atrophic scars.
-
Production of Collagen Stimulated: Collagen is a protein that supports the structure and elasticity of the skin, and microdermabrasion stimulates its production. The gentle abrasion of the skin prompts the body's natural healing response, which boosts collagen synthesis and might fill in atrophic scars.
-
Improved Product Penetration: Microdermabrasion improves the penetration of topical products that are applied after the procedure by removing the outer layer of dead skin cells. This makes it possible for skincare ingredients to be absorbed more effectively, which can further enhance the appearance of atrophic scars.
-
Minimal recovery time and non-invasiveness: Microdermabrasion is a non-invasive procedure that frequently does not call for anaesthesia. The majority of people tolerate it well, and recovery time is short. The majority of patients return to their regular activities right away after the procedure.
-
Multiple Sessions: It typically takes several microdermabrasion sessions to noticeably improve atrophic scars. The number of treatments needed depends on the severity of the scars and the desired results. Sessions are usually spaced several weeks apart to allow for proper healing and collagen regeneration.
-
Suitable for a Wide Range of Skin Types: Microdermabrasion is appropriate for a wide range of skin types and tones. It can be used on the face, neck, chest, and other areas where atrophic scars have formed.
-
Additional Considerations: Because microdermabrasion primarily targets the superficial layers of the skin, it may not be appropriate for deep or severe atrophic scars. Other treatments, such as laser therapy or dermal fillers, may be more effective in such cases.
Chemical Peels and Topical Treatments: Nourishing Skin and Reducing Atrophic Scars
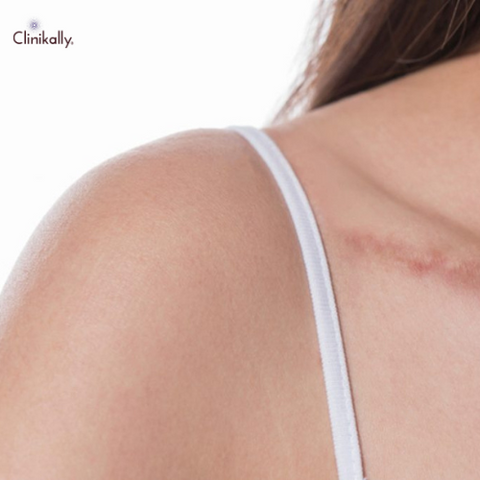

Chemical Peels: A chemical solution is applied to the skin to exfoliate the outer layers and promote skin renewal. They are classified into three levels based on their depth: superficial, medium, and deep.
-
Superficial Peels: These peels target the skin's outermost layer (epidermis) and are generally well-tolerated. They have the ability to improve skin texture, reduce mild scarring, and increase overall skin radiance. Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), such as glycolic acid or lactic acid, are frequently used in superficial peels.
-
Peels of a Medium Intensity: Peels of a Medium Intensity penetrate the dermis, the middle layer of skin, more deeply. They can effectively increase collagen production and reduce the visibility of mild atrophic scars. For medium-depth peels, trichloroacetic acid (TCA) is frequently employed.
-
Deep peels: The most pronounced results are achieved with deep peels because they penetrate the dermis's deeper layers. They require longer recovery times but can significantly lessen the visibility of severe atrophic scars. A common ingredient for deep peels is phenol.
Topical therapies: Topical therapies may be applied alone or in combination with other scar management methods. They can hydrate the skin, encourage the production of collagen, and improve the appearance of atrophic scars. Several popular topical remedies include:
-
Retinoids: Topical retinoids, such as retinol or tretinoin, promote collagen production and quicken skin cell turnover. They can improve the look of atrophic scars and improve the condition of the skin as a whole.
-
Silicone Gel or Sheets: Products made of silicone, such as gels or sheets, form a barrier of protection over the scarred area. They can assist with skin hydration, scar flattening, and texture and colour improvement.
-
Vitamin C serums: Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant that can brighten the skin and encourage the synthesis of collagen. Topical vitamin C serums can enhance the look of atrophic scars and offer further antioxidant advantages.
-
Scar Creams: A variety of over-the-counter scar creams and ointments are offered; these products frequently include hyaluronic acid, onion extract, or allantoin. These goods are designed to hydrate skin, lessen inflammation, and lessen visible scars.
Revealing Radiance: Chemical Peels for Atrophic Scar Reduction
Chemical peels can help reduce the appearance of atrophic scars and reveal a more luminous complexion. Here's a closer look at how chemical peels operate and the benefits they provide for reducing atrophic scars:
-
Exfoliation and Skin Renewal: Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, causing the outer layers to exfoliate in a controlled manner. This procedure aids in the removal of dead skin cells, the unclogging of pores, and the stimulation of skin cell turnover.
-
Collagen Production Stimulation: Chemical peels can increase the synthesis of collagen, a protein that gives the skin structure and support. Increased collagen production reduces the appearance of atrophic scars and enhances the texture and firmness of the skin.
-
Scar Smoothing: Chemical peels' exfoliating action helps to smooth the skin's surface, which makes atrophic scars less visible. In order to achieve a more even skin tone and texture, the outer, damaged layers of skin must be removed.
-
Selection of Peel Depth: Depending on how severe the atrophic scars are, the chemical peel's depth can be changed. For milder scars, superficial peels like those with alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid or lactic acid work well. Scars of moderate depth can be treated with medium-depth peels using substances like trichloroacetic acid (TCA). For scarring that is more severe, deep peels, which typically use phenol, are used.
-
Customization and Expertise: Chemical peels should only be performed by a qualified dermatologist or skin care professional who can assess the state of your skin and create a customised treatment plan for you. They will determine the best peel depth, concentration, and duration to achieve the best results while minimising complications.
-
Gradual and Progressive Results: Chemical peels for atrophic scar reduction typically necessitate a series of treatments to achieve the desired result. The severity of the scars and the kind of peel employed determine the number of sessions necessary. The appearance of atrophic scars can improve over time as the skin heals and rejuvenates.
-
Post-Treatment Care: After a chemical peel, it is critical to adhere to your dermatologist's post-treatment care recommendations. This might entail avoiding exposure to the sun, using gentle skincare products, and regularly applying sunscreen to guard newly exposed skin.
The Power of Topicals: Enhancing Atrophic Scar Healing with Skincare
Topical skincare products have a noticeable positive impact on the healing and appearance of atrophic scars. Here are some essential components and advice for using topicals to accelerate the healing of atrophic scars:
-
Products made of silicone: Silicone gel or sheets are frequently used to make atrophic scars look better in terms of texture and colour. Silicone forms a barrier of defence over the scar, retaining moisture and lowering redness and inflammation. To get the most out of silicone gel or sheets, use them as your dermatologist instructs.
-
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives known as retinoids, such as tretinoin or retinol, can improve the texture and appearance of atrophic scars. They function by boosting collagen production, boosting cell turnover, and reducing scar pigmentation. Retinoids should only be used as directed by your dermatologist because they may need to be introduced gradually and can lead to skin sensitivity.
-
Vitamin C: Topical vitamin C is well-known for its anti-inflammatory and skin-brightening effects. Additionally, it can support collagen synthesis, which is good for atrophic scar healing. In serums or creams, look for stable forms of vitamin C like ascorbic acid or sodium ascorbyl phosphate.
-
Hyaluronic Acid: By hydrating the skin and plumping the surrounding tissue, hyaluronic acid can improve the overall appearance of atrophic scars. To hydrate the skin and enhance its texture, look for hyaluronic acid serums or creams.
-
Peptides: Peptides are short chains of amino acids that can increase the production of collagen and enhance the firmness and texture of the skin. Look for peptides in serums or creams designed especially for scar healing, such as copper peptides or palmitoyl pentapeptide-4.
-
Sun protection: It is important for scars to heal to be shielded from the sun's UV rays. Scars may become darker and more obvious after exposure to UV light. Even on cloudy days, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and reapply every two hours when exposed to the sun.
-
Consistency and Patience: Topical treatments for atrophic scars need to be used consistently and over time in order to show noticeable results. Results may vary based on the depth of the scars and each person's skin's reaction. Be patient and adhere to your dermatologist's advice regarding how long to use a product for.
Before beginning any new topical treatment, consult a dermatologist or skincare specialist. They can assess your individual requirements, recommend appropriate items, and advise you on how to utilise them properly. They may also help you track your progress and make any required changes to your skincare routine for the best scar healing results.
Advanced Approaches: Laser Treatments, Microneedling, and Injectable Fillers
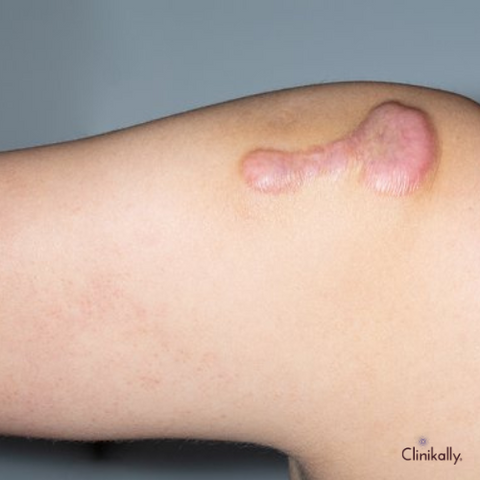
There are several efficient options available for treating atrophic scars using cutting-edge methods. Injectable fillers, microneedling, and laser treatments are frequently used to make atrophic scars look better. Let us investigate each of these methods:
-
Laser Treatments: Atrophic scars can be targeted and treated with laser treatments, which use concentrated beams of light. There are various kinds of lasers in use, including fractional CO2 lasers, erbium YAG lasers and pulsed dye lasers.
-
Microneedling: Microneedling, also referred to as collagen induction therapy, is a procedure in which controlled micro-injuries are made to the skin using a device with fine needles. This procedure encourages skin remodelling and collagen production, which improves atrophic scars. A dermaroller or a microneedling pen can be used to perform microneedling. The skin is rolled or pressed against the device, which causes minute punctures that start the body's healing process. For best results, multiple sessions are typically necessary.
-
Injectable Fillers: Hyaluronic acid-based fillers, for example, can be used to temporarily fill in atrophic scars and improve their appearance. The filler is injected directly into the scar, bringing it up to the same level as the surrounding skin. This technique smoothes the skin's surface and reduces the visibility of the scar.
Injectable fillers produce instant results that can endure for several months, but they are only temporary. Typically, multiple treatments are required to maintain the intended effect. Only experienced medical experts with experience in cosmetic operations should use injectable fillers. To identify the most appropriate advanced technique for your unique form of atrophic scars, speak with a dermatologist or cosmetic specialist. They will examine your scars, discuss the benefits and dangers of each treatment option, and recommend the best course of action based on your specific needs and goals.
Targeted Precision: Laser Treatments for Atrophic Scars
Laser treatments cure atrophic scars in a precise and focused manner. They employ concentrated light beams to encourage collagen synthesis, renew the skin, and diminish scar visibility. Here's a look at how laser treatments for atrophic scars can be beneficial:
-
Fractional CO2 lasers: Atrophic scars are frequently treated with fractional CO2 lasers. These lasers damage the skin by spewing high-intensity light beams in a fractional pattern. The micro-injuries start the body's normal healing process, causing collagen to be produced and the skin to remodel.
-
Erbium YAG lasers: These lasers are another kind that can be used to treat atrophic scars. These lasers, like fractional CO2 lasers, remove the top layers of the skin. However, when compared to CO2 lasers, Erbium YAG lasers have less downtime and a faster recovery.
-
Pulsed Dye Lasers: These lasers are designed specifically to target blood vessels in the skin. They produce concentrated light beams that are absorbed by haemoglobin in blood vessels, causing them to shrink and reducing the redness associated with atrophic scars.
-
Treatment Customization: The type and severity of the atrophic scars, the individual's skin type, and the desired outcomes all influence the choice of laser treatment. A dermatologist or cosmetic specialist will assess your unique situation and recommend the best laser treatment option for you.
Microneedling Marvel: Harnessing Skin's Healing Potential for Atrophic Scars
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, is a common treatment for atrophic scars that takes advantage of the skin's natural healing ability. It entails utilizing a device with fine needles to create regulated micro-injuries in the skin, boost collagen formation, and promote scar remodelling. Here's how microneedling can help atrophic scars look better:
-
Collagen Stimulation: Microneedling stimulates the skin's natural wound healing response. The tiny punctures made by the needles stimulate the production of collagen, a protein that provides structural support to the skin. Increased collagen production aids in the rebuilding and strengthening of the skin, resulting in smoother and more even skin texture.
-
Enhanced Topical Product Absorption: Microneedling creates microchannels in the skin, which improves the absorption of topical skincare products. This allows for more effective delivery of active ingredients such as vitamin C, hyaluronic acid, and growth factors into the skin's deeper layers. These ingredients can boost collagen production, increase hydration, and speed up the healing process.
-
Scar Remodelling: Scar remodelling occurs as a result of repeated microneedling sessions. As collagen is produced and distributed, it aids in the breakdown of scar tissue and the replacement of it with new, healthy skin cells. This remodelling process gradually improves the texture, colour, and overall appearance of atrophic scars.
-
Individual Scar Customization: Microneedling can be tailored to the type and severity of atrophic scars. The needle depth can be adjusted to target different layers of skin, allowing for more precise treatment. Deeper scars may necessitate longer needles, whereas shallow scars may require shorter needles. Your dermatologist or other skincare expert will determine the best settings for your unique scar characteristics.
-
Minimal Recovery Time: Microneedling is a minimally invasive procedure that requires little recovery time. The skin may feel mildly sensitive and appear slightly red after the treatment, much like a sunburn. However, these side effects usually disappear after a few days, and redness can be covered up with makeup. The length of time it takes to recover varies depending on the severity of the treatment and the sensitivity of the patient's skin.
-
Cumulative and Gradual Results: It is important to remember that microneedling does not produce results right away. Atrophic scars typically require multiple treatment sessions to see any improvement. To allow for proper healing and collagen remodelling, sessions are typically spaced several weeks apart. The scars' texture and appearance gradually get better as new collagen is produced over time.
Injectable Fillers: Temporary Solutions for Atrophic Scar Correction
Injectable fillers are temporary remedies that can be used to improve the appearance of atrophic scars. These filters are often made of hyaluronic acid, collagen, or polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). Injectable fillers can aid with atrophic scar repair in the following ways:
-
Filling Depressions: Atrophic scars leave depressions that can be filled with injectable fillers to raise the scar tissue to the same level as the surrounding skin. The skin surface becomes smoother and more even as a result, which lessens the scar's visibility.
-
Restoring Volume: Atrophic scars can cause the area to lose volume and look sunken in. By boosting the scar tissue's volume and providing support, injectable fillers can restore volume. This enhances the skin's general texture and contour.
-
Instantaneous Results: One benefit of injectable fillers is that they produce results right away. Right after the procedure, the appearance of atrophic scars has clearly improved. As a result, people looking for quick and obvious results frequently choose injectable fillers.
-
Customised Approach: Correcting atrophic scars can be done using a customised strategy thanks to injectable fillers. The kind of filler used and the quantity applied can be customised to meet the individual's needs and the particulars of their scar. Your scars will be evaluated by a qualified dermatologist or cosmetic specialist who will choose the best filler type, concentration, and injection technique for them.
-
Temporary Effects: It is important to remember that injectable fillers only have a short-term effect. The duration of the effect varies depending on the type of filler used, but it usually lasts several months to a year. The filler gradually restores the scar's original appearance as it is naturally metabolised and absorbed by the body over time. To keep the desired effect, repeated treatments are frequently necessary.
-
Minimal Downtime: Atrophic scar treatments with injectable fillers typically involve very little downtime. There might be a little redness, swelling, or bruising where the injections were made, but these side effects are transient and usually go away in a few days. You can hide any side effects from treatment with makeup.
Comprehensive Care: Strategies for Post-Treatment and Scar Management
Following atrophic scar therapy, it is critical to follow adequate post-treatment care and scar management measures. Here are some detailed care suggestions to help you achieve the best results and encourage effective scar healing:
-
After-Treatment Instructions to Follow: Your dermatologist or skincare specialist will give you post-treatment instructions that are specific to the treatment you received. To ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of complications, carefully follow these instructions. This may include cleansing, moisturising, sun protection, and any activity limitations.
-
Protect Your Skin from the Sun: Sun exposure can impede healing and make scars appear worse. Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, wear protective clothing, and seek shade when the sun is at its hottest. This is especially important during the early stages of scar healing, when the skin is more susceptible to UV radiation.
-
Avoid Picking or Scratching: Refrain from picking, scratching, or peeling at the treated area or the healing scar. This can interfere with the healing process, increase the risk of infection, and result in additional scarring or complications. Allow the skin to heal naturally by keeping your hands away from the treated area.
-
Maintain a Healthy Skincare Routine: Maintaining a consistent and gentle skincare routine can aid in the healing process and promote overall skin health. Cleanse your skin with gentle, non-irritating cleansers, moisturise on a regular basis to keep it hydrated, and use skincare products that are appropriate for your skin type. Avoid using abrasive scrubs or harsh chemicals that could irritate the treated area.
-
Consider the following Scar Massage Techniques: Massage can help break down adhesions, improve blood circulation, and promote collagen remodelling in scar tissue. However, you must wait until your healthcare provider gives you the all-clear to begin scar massage, as timing may vary depending on the type of treatment you received. Use gentle, circular motions with clean hands or a scar massage product that has been recommended.
-
Optimise Wound Healing Through Nutrition: Proper nutrition is essential for wound healing. Consume a well-balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and essential nutrients. Adequate hydration is also essential for skin health. For personalised dietary recommendations, speak with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian.
-
Manage Your Expectations and Give It Time: Scar healing is a gradual process, and it may take some time to see significant improvements. Be patient and set realistic expectations. Multiple treatment sessions and consistent scar management strategies may be required to achieve the desired results, depending on the type and severity of the scars.
-
Communicate with Your Medical Professional: Throughout your scar treatment journey, keep in touch with your dermatologist or skin care professional. They can keep track of your progress, address any concerns or questions you may have, and make changes to your treatment plan as needed. During the healing process, your healthcare provider is your best resource for guidance and support.
Post-Treatment Guidance: Nurturing Skin After Atrophic Scar Procedures
Caring for your skin after atrophic scar surgery is critical for optimal healing and outcomes. The following post-treatment recommendations will assist you in taking good care of your skin RE Follow your dermatologist's advice, keep the treated area clean, moisturise on a regular basis, protect your skin from the sun, and avoid irritant products and procedures. Be gentle with the treated area, stay hydrated, and follow a healthy lifestyle. Appointments for additional follow-up: Remember that each person's healing process is unique, and major changes may take time. Maintain your post-treatment care routine with patience and consistency. If you have any concerns or questions about the healing process, please contact your dermatologist or a skincare specialist for advice and support.
Emotional Well-being: Addressing Psychological Aspects of Atrophic Scars
Taking care of the psychological aspects of atrophic scars is an important part of overall health. Here are some methods for dealing with the emotional impact of atrophic scars:
-
Seek Emotional Support: Talk about your feelings and concerns with friends, family, or support groups. Sharing your experiences with others who may be going through similar difficulties can provide emotional support and understanding.
-
Consider Consulting a Mental Health Professional: Seek professional assistance from a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counsellor. They can provide a safe environment for you to explore your emotions, develop coping strategies, and address any underlying psychological issues associated with your scars.
-
Self-Compassion: Be gentle and kind to yourself. Recognize that your worth is not based on how you look and that scars are a normal part of the healing process. Treat yourself with kindness and focus on your strengths and accomplishments.
-
Negative Thoughts Should Be Challenged: Atrophic scars can sometimes lead to a negative self-perception and self-criticism. Recognize and challenge negative thoughts by replacing them with positive, realistic ones. Concentrate on your abilities, accomplishments, and the characteristics that distinguish you.
-
Engage in Confidence-Building Activities: Engage in activities that make you feel good about yourself and boost your confidence. Hobbies, exercise, self-care, and other enjoyable activities can help you shift your focus away from your scars and improve your overall well-being.
-
Educate Yourself: Learn more about atrophic scars, their causes, and the treatment options available to you. Self-education can help you understand your condition better, reduce anxiety, and make informed decisions about your treatment and self-care routines.
-
Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: To help manage stress, anxiety, and negative emotions, try mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or relaxation techniques. These practices can promote relaxation, increase self-awareness, and improve overall well-being.
-
Investigate Scar Camouflage Techniques: If you are self-conscious about your scars, look into makeup techniques or scar camouflage products that can help conceal their appearance. These techniques can help you deal with your scars temporarily while you work on accepting and embracing them.
-
Set realistic expectations: Recognize that scar reduction or improvement takes time and that scars may not be completely eliminated. Set realistic goals for your treatment and concentrate on progress rather than perfection.
-
Celebrate Your Resilience: Keep in mind that your scars are evidence of both your body's capacity for healing and your own resiliency. Honour your fortitude and the struggles you have overcome. Accept your scars as an integral part of your personal history and the person you have evolved into.
The emotional effects of atrophic scars must be addressed, and this may require time and support. Be gentle with yourself, and don't be afraid to seek professional assistance if necessary. Self-care, emotional support, and expert counselling can all assist you in navigating the psychological aspects of living with atrophic scars.

















1 comment
Stephen Pritchard
I thought silicone gel stops collagen ? So wouldn’t it be bad for indented scars?
I thought silicone gel stops collagen ? So wouldn’t it be bad for indented scars?