Fungal infections are a widespread issue that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. They can occur on different parts of the body, such as the skin, nails, scalp, and feet. Tinea infections, also known as ringworm, are a type of fungal infection caused by dermatophytes that can lead to red, itchy, and scaly skin.
There are several different types of tinea infections, and each one has specific symptoms and affected areas. For example, tinea corporis can occur on any part of the body except for the scalp, beard, and feet, while tinea cruris affects the groin area. Tinea pedis, also known as athlete's foot, affects the feet, and tinea capitis affects the scalp and hair.
The symptoms of tinea infections may vary depending on the type of infection and the affected area. However, common symptoms of tinea infections include itching, burning, redness, and scaling of the skin. In severe cases, tinea infections can lead to secondary bacterial infections and cellulitis.
Fortunately, there are effective treatments available for tinea infections. Antifungal medications, both topical and oral, can help eliminate the fungus and alleviate symptoms. Additionally, home remedies and supportive care measures can provide relief and promote healing.
Overall, understanding the different types of tinea infections, their symptoms, and available treatments is essential for managing these common fungal infections. With proper care and treatment, most tinea infections can be easily treated and resolved.
Common Types of Tinea and Their Symptoms
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm)
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection affecting the scalp and hair. It is more common in children, but it can also affect adults. Symptoms of tinea capitis include:
-
Red, scaly patches on the scalp
-
Hair loss in the affected area
-
Itching and discomfort
Tinea Corporis (Body Ringworm)
Tinea corporis is a fungal infection that affects the skin on the body. It is characterized by circular, red, scaly patches that can be itchy or painful. Other symptoms of tinea corporis include:
-
Raised edges around the patches
-
Clearer skin in the middle of the patch
-
Skin that is dry or flaky
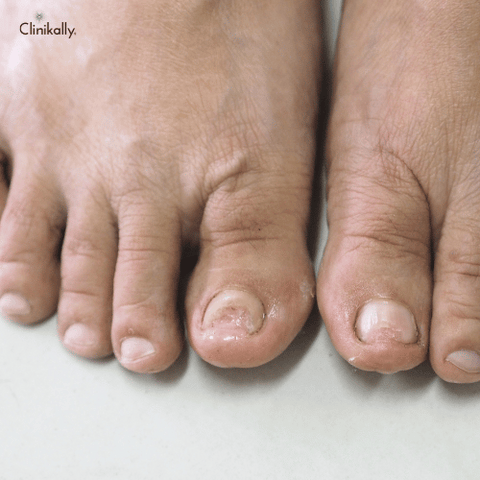
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot)
Tinea pedis, commonly known as athlete's foot, is a fungal infection that affects the feet. It is characterized by red, itchy, and scaly skin between the toes or on the soles of the feet. Other symptoms of tinea pedis include:
-
Blisters that ooze fluid
-
Peeling or cracking skin
-
Dry skin on the soles or sides of the feet
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
Tinea cruris, also known as jock itch, is a fungal infection that affects the groin area. It is characterized by red, itchy, and scaly skin in the groin, inner thighs, or buttocks. Other symptoms of tinea cruris include:
-
Burning sensation in the affected area
-
Flaking or peeling skin
-
Rash that worsens with sweating or activity
Tinea Versicolor (Pityriasis Versicolor)
Tinea versicolor is a fungal infection that affects the skin, usually on the chest, back, or upper arms. It is characterized by small, discoloured patches that can be either lighter or darker than the surrounding skin. Other symptoms of tinea versicolor include:
-
Patches that may be scaly or itchy
-
Patches that may appear white, pink, brown, or red
-
Skin that may become darker or lighter than usual
Effective Treatments for Tinea Infections

Topical Antifungal Medications
Topical antifungal medications are usually the first line of treatment for tinea infections. They are available over-the-counter or by prescription, depending on the severity of the infection. Examples of topical antifungal medications include:
-
Clotrimazole
-
Miconazole
-
Terbinafine
Oral Antifungal Medications
Oral antifungal medications are usually prescribed for severe or recurring tinea infections. These medications can be effective, but they may also have side effects. Examples of oral antifungal medications include:
-
Terbinafine
-
Fluconazole
-
Itraconazole
In addition to antifungal medications, there are also several home remedies and hygiene practices that can help prevent and treat tinea infections. These include:
-
Keeping the affected area clean and dry
-
Avoiding tight-fitting
Dermatologist-Recommended Treatment Plans
If you suspect that you have a tinea infection, it is important to see a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. A dermatologist can prescribe the most effective treatment plan based on the type and severity of the infection. They may also recommend follow-up appointments to ensure that the infection is fully treated.
Prevention and Management of Tinea Infections
Maintaining good hygiene practices one of the most important ways to prevent tinea infections is to maintain good hygiene practices. This includes:
-
Washing your hands regularly, especially after touching pets or other animals
-
Keeping your skin clean and dry
-
Wearing clean, breathable clothing
-
Avoiding sharing personal items such as towels, combs, and hairbrushes
Addressing Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as humidity and temperature can contribute to the growth of fungi that cause tinea infections. To prevent these infections, it is important to:
-
Keep your living spaces clean and dry
-
Avoid wearing damp clothing or shoes for prolonged periods of time
-
Avoid walking barefoot in public places such as locker rooms, showers, and swimming pools
Home Remedies and Supportive Care
Tinea infections are a common problem that can cause a lot of discomfort and irritation. While medical treatments are often necessary to completely eliminate the infection, there are several home remedies and supportive care measures that can be used to alleviate symptoms and improve overall comfort.
One of the most effective supportive care measures is applying cool compresses to the affected area. This can help reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and provide a soothing sensation to the skin. To make a cool compress, simply soak a clean cloth in cold water and apply it to the affected area for 10-15 minutes at a time. This can be repeated several times a day as needed.
Over-the-counter antifungal creams and powders can also be used to treat tinea infections. These products contain ingredients that can help kill the fungus and prevent it from spreading. Some common over-the-counter antifungal products include clotrimazole, miconazole, and terbinafine. It's important to carefully follow the instructions on the product label and continue using the product for the recommended amount of time to ensure the infection is fully treated.
Natural remedies such as tea tree oil, coconut oil, and apple cider vinegar have also been shown to alleviate the symptoms of tinea infections. Tea tree oil has natural antifungal properties and can be applied directly to the affected area with a cotton swab or mixed with a carrier oil such as coconut oil. Coconut oil can also be used on its own to soothe the skin and provide some relief from itching and discomfort. Apple cider vinegar can be diluted with water and applied to the affected area to help balance the pH of the skin and reduce inflammation.
It's important to note that while home remedies and supportive care measures can help alleviate the symptoms of tinea infections, they are not a substitute for medical treatment. If symptoms persist or worsen despite these measures, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion: Overcoming Tinea and Maintaining Healthy Skin
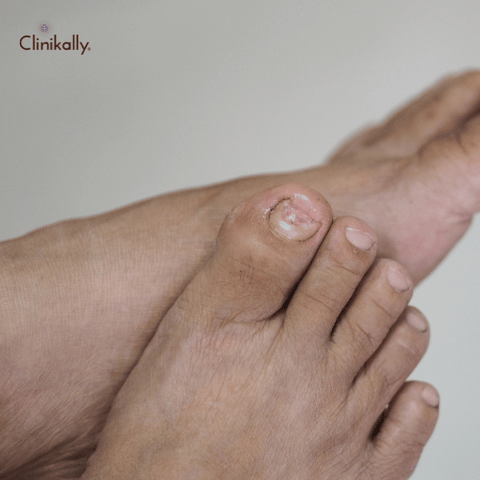
Tinea infections can be uncomfortable and unsightly, but they are treatable. By following good hygiene practices and seeking medical treatment when necessary, you can prevent and manage tinea infections. If you experience symptoms of a fungal infection, it is important to see a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right care and attention, you can overcome tinea and maintain healthy, beautiful skin.
















