Skin lesions are a common occurrence, and most people will develop some form of skin marking throughout their lifetime. Moles, birthmarks, and other types of skin lesions are often benign and harmless. However, there are some types of skin lesions that require close attention and monitoring, such as congenital nevi.
Congenital nevi are a type of mole that are present at birth or develop shortly after birth. These types of moles are typically larger than other types of moles and have a distinct appearance. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the origins, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of congenital nevi.
Understanding Congenital Nevi
Congenital nevi, also known as birthmarks, are pigmented skin lesions that are present at birth or develop shortly after. These marks can vary in size, shape, and color, and can be found anywhere on the body. While most congenital nevi are harmless, some may be associated with an increased risk of developing skin cancer later in life. Understanding the different types of congenital nevi, their potential risks, and available treatment options is important for individuals who have these marks and their healthcare providers.
Defining Congenital Nevi and Their Origins
Congenital nevi are a type of mole that are present at birth or develop within the first few months of life. These types of moles are caused by an overgrowth of melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in the skin. Congenital nevi are typically larger than other types of moles and can vary in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
The cause of congenital nevi is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to genetics. Congenital nevi can be inherited, but they can also occur spontaneously. Studies have found that mutations in the NRAS and BRAF genes, which are involved in regulating melanocyte growth, may play a role in the development of congenital nevi.
Appearance and Characteristics of Congenital Nevi
Congenital nevi can have a wide range of appearances, but they typically have some common characteristics. These moles are usually larger than other types of moles, and they can be flat or raised. The color of congenital nevi can vary from light brown to dark brown, and they may have irregular borders. Some congenital nevi may also have hair growing from them.
The size and appearance of congenital nevi can change over time. They may become darker or more raised, and they may develop hair growth. In some cases, congenital nevi may also become cancerous.
Diagnosing and Monitoring Congenital Nevi
Diagnosing and monitoring congenital nevi is crucial for identifying potential risks and ensuring proper treatment is provided. Congenital nevi, which are pigmented skin lesions present at birth or shortly after, can vary in size and color and may be associated with an increased risk of developing skin cancer later in life. Therefore, regular monitoring and evaluation of these marks are necessary to detect any changes or abnormal growth patterns.
Dermatoscopy and Biopsy for Nevus Diagnosis
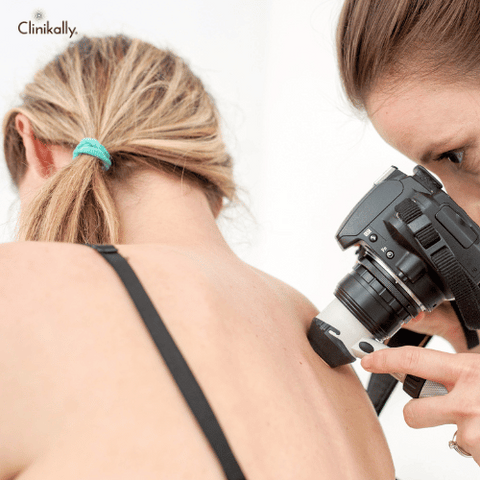
Congenital nevi are typically diagnosed based on their appearance. However, in some cases, a dermatologist may use dermatoscopy to examine the mole more closely. Dermatoscopy is a non-invasive imaging technique that allows a dermatologist to see the mole's internal structure and evaluate any irregularities.
If a dermatologist suspects that a congenital nevus may be cancerous, they may recommend a biopsy. A biopsy involves removing a small sample of tissue from the mole and examining it under a microscope for signs of cancer.
The Importance of Skin Self-Examinations and Check-ups
Regular skin self-examinations and check-ups with a dermatologist are essential for monitoring congenital nevi. It is recommended that individuals perform skin self-examinations once a month to check for any changes in the appearance of their moles or other skin lesions.
During a skin check-up, a dermatologist will examine the individual's skin for any changes or irregularities. They may also use dermatoscopy to examine any moles or skin lesions more closely.
Treatment and Removal Options for Congenital Nevi
While most congenital nevi are benign, some may be associated with an increased risk of developing skin cancer later in life. Therefore, treatment and removal options for congenital nevi are often considered to reduce the potential risks and improve the appearance of the skin. These pigmented skin lesions can vary in size and color, and treatment options depend on factors such as location, size, and potential risks. In this article, we will explore the various treatment and removal options available for congenital nevi, including surgical excision, laser therapy, and topical treatments, among others. We will also discuss the benefits and risks associated with each option and how to decide which treatment is best for your individual situation.
Surgical Excision and Skin Grafting
In some cases, a dermatologist may recommend the surgical excision of a congenital nevus. Surgical excision involves removing the entire mole and a margin of surrounding skin. The area where the mole was removed may be closed with sutures or a skin graft.
Skin grafting involves taking skin from another area of the body and using it to cover the area where the mole was removed. This is often used when a large area of skin has been removed.
Laser Treatment and Other Removal Methods
Laser treatment may also be used to remove congenital nevi. This method involves using a laser to destroy the pigment-producing cells in the mole. Laser treatment is often used for smaller moles, and multiple sessions may be required to achieve the desired results.
Other removal methods for congenital nevi include cryotherapy, which involves freezing the mole with liquid nitrogen, and electrocautery, which involves burning the mole with an electric current. These methods are typically used for smaller moles and may not be effective for larger congenital nevi.
It is important to note that removal of a congenital nevus is not always necessary, and the decision to remove a mole should be made in consultation with a dermatologist.
Skin Care and Cancer Prevention for Congenital Nevi
Individuals with congenital nevi, or birthmarks, may have an increased risk of developing skin cancer later in life. Therefore, proper skin care and cancer prevention measures are essential to reduce this risk and maintain healthy skin. Congenital nevi can vary in size and color, and may require specific care and attention to ensure optimal skin health.
Essential Skin Care Tips for Nevi Management
Proper skin care is essential for managing congenital nevi and preventing skin cancer. It is recommended that individuals protect their skin from the sun by wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Individuals with congenital nevi should also avoid tanning beds and limit their exposure to direct sunlight during peak hours. It is important to monitor the appearance of moles and seek medical attention if there are any changes.
Education and Awareness on Skin Cancer Prevention
Education and awareness are key to preventing skin cancer. It is important to educate individuals about the dangers of UV radiation and the importance of sun protection. Regular skin check-ups with a dermatologist are also important for monitoring the skin and detecting any changes or irregularities.
When to Seek Professional Help for Nevi Concerns
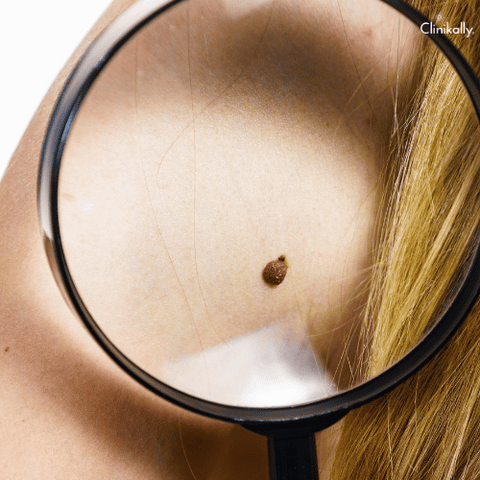

Nevi, also known as moles or birthmarks, are common skin lesions that typically pose no serious health risks. However, in some cases, nevi may become a cause for concern and may require professional help. These pigmented skin lesions can vary in size, shape, and color, and changes in these characteristics may signal an underlying issue.
Identifying Potentially Suspicious Skin Lesions
It is important to be able to identify potentially suspicious skin lesions, as early detection is key to preventing skin cancer. The ABCDE rule can be used as a guide for identifying potentially cancerous moles:
A: Asymmetry - one half of the mole does not match the other half.
B: Border - the edges of the mole are irregular, ragged, or blurred.
C: Color - the mole has varying shades of brown, black, or other colours.
D: Diameter - the mole is larger than 6mm or the size of a pencil eraser.
E: Evolution - the mole is changing in size, shape, color, or texture.
If a mole or skin lesion exhibits any of these characteristics, it is important to seek professional medical attention.
Finding the Right Dermatologist for Your Skin Needs
Finding the right dermatologist is essential for the proper diagnosis and treatment of skin lesions. It is recommended that individuals research dermatologists in their area and read reviews from other patients. It is also important to choose a dermatologist who specializes in the treatment of skin cancer and has experience treating congenital nevi.
The Future of Nevi Research and Dermatology
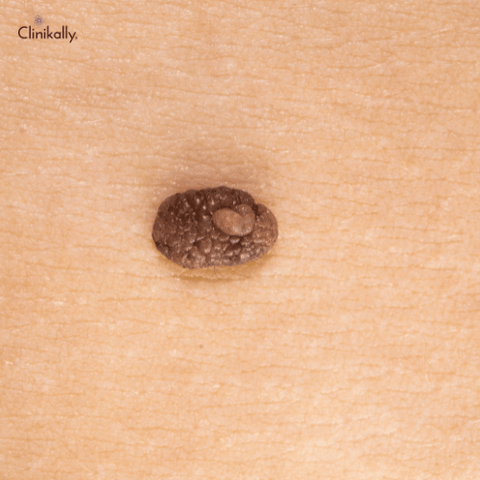

The study of congenital nevi and other types of skin lesions is an ongoing area of research. Researchers are working to better understand the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the development of skin lesions and to develop more effective treatments for skin cancer.
Advances in technology, such as the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, are also changing the way dermatologists diagnose and treat skin lesions. These tools have the potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of skin lesion diagnosis and monitoring.
In conclusion, congenital nevi are a type of skin lesion that are present at birth or appear shortly thereafter. They are caused by an overgrowth of melanocytes, the cells that produce pigment in the skin, and can vary in size, shape, and color. While most congenital nevi are harmless, some may develop into skin cancer, such as melanoma, later in life.
Diagnosis and monitoring of congenital nevi may involve dermatoscopy, biopsy, and regular skin self-examinations. Treatment options for congenital nevi include surgical excision, laser treatment, and skin grafting. Proper skin care and education on skin cancer prevention are essential for managing congenital nevi and preventing skin cancer.
If you notice any changes or irregularities in a mole or skin lesion, it is important to seek professional medical attention. By being aware of the appearance and characteristics of congenital nevi and taking steps to prevent skin cancer, individuals can better manage their skin health and reduce their risk of developing skin cancer.