In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the harmful effects of UV radiation on the skin, and its contribution to the aging process. Photoaging is a term used to describe the changes that occur in the skin as a result of chronic exposure to UV radiation. Unlike natural aging, which is largely a result of the passage of time and genetics, photoaging is preventable and can be exacerbated by lifestyle factors such as smoking and poor diet. With the prevalence of UV radiation in our environment, it is important to understand how it affects our skin and what steps can be taken to protect against its damaging effects. This essay will explore the causes and effects of photoaging, as well as strategies for preventing and treating this common skin concern.
The Role of UV Radiation in Photoaging
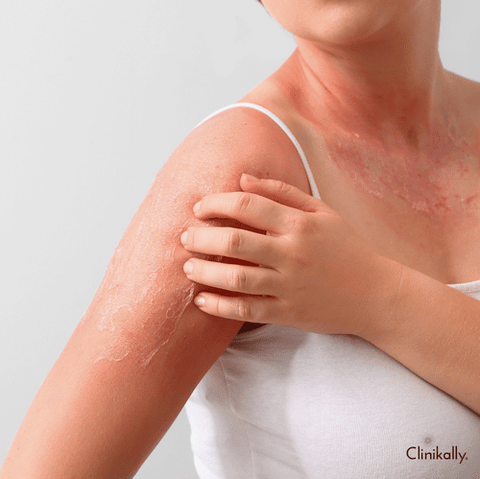
UV radiation is a common environmental factor that can have a significant impact on the health and appearance of the skin. While many people are aware of the dangers of excessive sun exposure, fewer may realize that UV radiation can also contribute to a process known as photoaging. This process can cause changes in the skin such as wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, and can also increase the risk of skin cancer. In this context, it is important to understand the role of UV radiation in photoaging and how it can be prevented or minimized. This essay will explore the science behind UV radiation and photoaging, as well as strategies for protecting the skin from its damaging effects.
Understanding UVA and UVB Rays
UV radiation is divided into two main categories: UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays are longer wavelength rays that penetrate deeper into the skin, causing damage to collagen and elastin, proteins responsible for maintaining skin structure and elasticity. UVB rays, on the other hand, are shorter wavelength rays that primarily damage the outermost layer of the skin, leading to sunburn and skin cancer. Both types of rays contribute to photoaging and can lead to a variety of skin issues, including wrinkles, sagging, and pigmentation changes.
How UV Radiation Damages Your Skin
When UV radiation penetrates the skin, it causes the production of free radicals. These unstable molecules damage the skin's cellular structures, including collagen and elastin fibers. As a result, the skin loses its elasticity and firmness, leading to the formation of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging. Additionally, UV radiation can stimulate the overproduction of melanin, resulting in uneven pigmentation and dark spots.
Signs and Symptoms of Photoaging
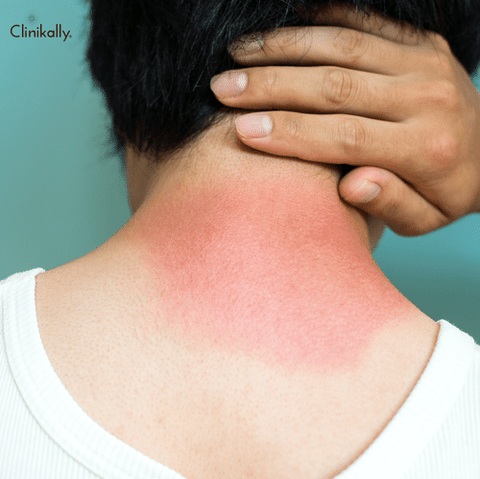
Photoaging is a natural process that occurs in the skin as a result of long-term exposure to UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources such as tanning beds. Over time, this exposure can lead to a variety of changes in the skin, ranging from subtle to more pronounced. These changes may include wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, uneven skin tone, and a loss of elasticity. While some of these changes may be purely cosmetic, others can have more serious health implications, such as an increased risk of skin cancer. Understanding the signs and symptoms of photoaging is an important step in protecting the skin from further damage and maintaining its overall health and appearance. This essay will explore the various ways in which photoaging can manifest in the skin, as well as strategies for identifying and preventing these changes.
Wrinkles, Fine Lines, and Sagging Skin
One of the most visible signs of photoaging is the development of wrinkles and fine lines. As UV radiation damages the skin's collagen and elastin, the skin loses its ability to bounce back and maintain its structure. This leads to the formation of wrinkles and fine lines, particularly around the eyes, mouth, and forehead. Sagging skin is another common sign of photoaging, as the loss of elasticity causes the skin to lose its firmness and tone.
Hyperpigmentation and Dark Spots
UV exposure can also lead to hyperpigmentation and dark spots, which are caused by the overproduction of melanin. These pigmentation changes can appear as age spots, freckles, or melasma and are typically more prevalent in sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, hands, and chest.
Treating and Preventing Photoaging
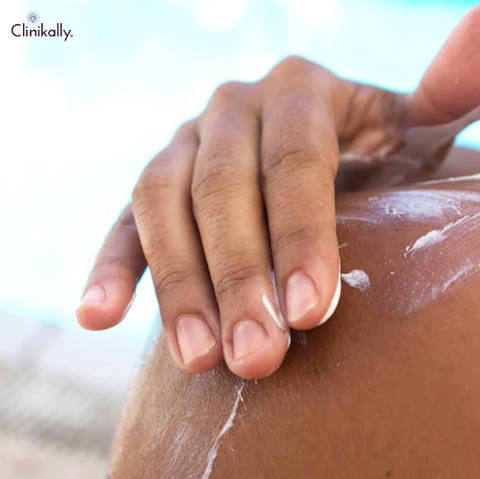

Photoaging is a common concern among those seeking to maintain youthful, healthy-looking skin. While the effects of long-term exposure to UV radiation can be difficult to reverse, there are a variety of treatments and preventative measures that can help to mitigate its impact. These may include a range of topical products, such as moisturizers, sunscreen, and retinoids, as well as more invasive procedures like chemical peels, laser resurfacing, and injectables. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise can also play a role in the prevention and treatment of photoaging. Understanding the various options available for treating and preventing photoaging is an important step in developing a comprehensive skin care routine that can help to maintain the health and appearance of the skin over time. This essay will explore some of the most common strategies for treating and preventing photoaging, as well as their potential benefits and drawbacks.
The Importance of Sun Protection
One of the most effective ways to prevent photoaging is by protecting your skin from harmful UV radiation. Sun protection methods include wearing sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of at least 30, wearing protective clothing and accessories like sunglasses and wide-brimmed hats, and seeking shade during peak sun hours.
Using Antioxidants to Protect Your Skin
Antioxidants are powerful compounds that neutralize free radicals and help protect your skin from UV damage. Some commonly used antioxidants in skincare products include vitamins C and E, niacinamide, and green tea extract. Incorporating these ingredients into your daily skincare routine can help boost your skin's natural defenses against photoaging.
Skincare Treatments for Photoaging
Retinoids and Exfoliants
Topical retinoids, such as retinol and prescription-strength tretinoin, are proven to be effective in reducing the signs of photoaging. They work by increasing cell turnover and collagen production, helping to improve skin texture, tone, and elasticity. Additionally, using exfoliants, such as alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) and beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), can help remove dead skin cells and reveal a brighter, more even complexion.
Collagen-Boosting Treatments
Collagen-boosting treatments, such as microneedling, radiofrequency, and ultrasound therapy, can help stimulate collagen production and improve the appearance of photoaged skin. These treatments work by triggering the skin's natural repair process, which results in increased collagen and elastin production, leading to firmer, smoother skin.
Laser and Light Therapies
Laser and light therapies, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) and fractional laser resurfacing, are effective treatments for addressing various signs of photoaging, including pigmentation issues, wrinkles, and uneven skin texture. These therapies work by targeting the damaged skin cells and stimulating the production of new, healthy skin cells, resulting in a more youthful, radiant complexion.
Photoaging vs. Natural Aging: What's the Difference?
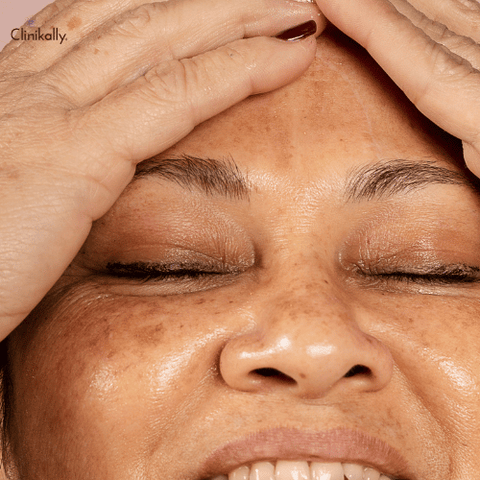

As we age, our skin undergoes a number of changes, both natural and environmental. While the effects of natural aging can be largely attributed to genetics and the passage of time, environmental factors like UV radiation from the sun can also play a significant role in the aging process. This can lead to a phenomenon known as photoaging, which differs from natural aging in a number of ways. While both types of aging can cause similar changes in the skin, such as wrinkles and loss of elasticity, photoaging can also result in additional effects such as age spots and uneven skin tone. Understanding the differences between photoaging and natural aging is important for developing a comprehensive skin care plan that takes into account the unique needs of each individual. This essay will explore the characteristics of both photoaging and natural aging, as well as strategies for addressing each type of aging in a targeted and effective manner.
Understanding the Role of Genetics in Aging
While photoaging is primarily caused by external factors like UV radiation, natural aging is influenced by genetic factors. Your genes determine how quickly your skin ages, and this process is largely out of your control. However, by understanding the differences between photoaging and natural aging, you can take steps to minimize the impact of external factors on your skin's appearance.
Lifestyle Factors that Contribute to Premature Aging
In addition to sun exposure, other lifestyle factors can contribute to premature aging, such as smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise. By adopting a healthier lifestyle and being mindful of the impact of these factors on your skin, you can slow down the aging process and maintain a youthful appearance.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Skin from Photoaging
In conclusion, photoaging is a preventable and treatable process that can have a significant impact on the health and appearance of your skin. By taking a proactive approach to skin care and incorporating strategies to protect against UV radiation and other environmental stressors, you can help to maintain a healthy and youthful complexion. While photoaging may be an inevitable part of the aging process, it is important to remember that there are many options available for minimizing its impact and promoting healthy, radiant skin. With a little effort and attention, you can help to keep your skin looking and feeling its best, no matter what your age.
















