Psoriasis and eczema are long-term skin disorders that cause flaky, irritated, and sometimes inflammatory skin. Although there isn't a treatment, there are several professional techniques that can help control flare-ups and offer relief. We look at some advice for treating psoriasis and eczema in this blog.
Introduction: Understanding Eczema and Psoriasis Flare-Ups
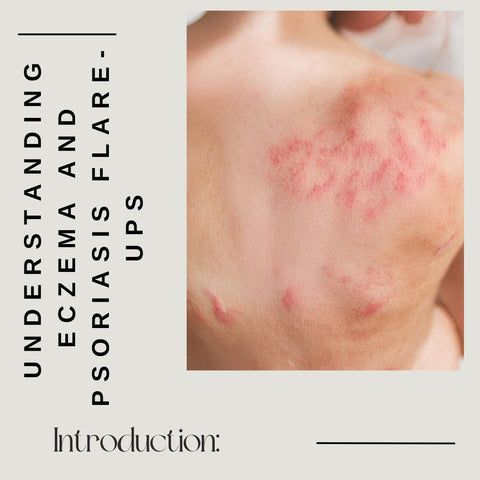
Eczema and psoriasis are chronic skin conditions that affect millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort, inflammation, and constant itching. While there is no cure for these conditions, effectively managing flare-ups is critical for improving the quality of life for people who have eczema or psoriasis.
-
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition characterised by red, itchy rashes that can appear all over the body. It usually starts in childhood but can continue into adulthood. Eczema flare-ups are caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, with allergens, stress, and irritants playing significant roles.
-
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell growth, resulting in thick, red patches with silvery scales. It can affect any part of the body and is frequently linked to joint pain (psoriatic arthritis). The exact cause is unknown, but genetics and the immune system are thought to be involved. Psoriasis flare-ups can be triggered by stress, infections, or certain medications.
-
Eczema and psoriasis both go through periods of remission followed by flare-ups. Flare-ups are sudden worsening of symptoms, such as increased redness, itching, and inflammation. Individuals suffering from these skin conditions must understand the triggers and implement management strategies to prevent flare-ups.
What Causes Eczema and Psoriasis to Flare Up?
Many things can cause flare-ups of psoriasis and eczema, and knowing what these things are is essential to managing the condition effectively. While the precise causes of various skin disorders are still unknown, some recognised factors have been linked to flare-ups. An overview of frequent causes of flare-ups for psoriasis and eczema can be found in this blog.
Key Factors Influencing Flare-Ups and Effective Management Strategies

Eczema and psoriasis flare-ups can be caused by a variety of factors, and effective management necessitates targeting these triggers. The following are key factors that influence flare-ups and the corresponding management strategies for eczema and psoriasis:
-
Irritants and Allergens:
-
Eczema: Use skincare products that are gentle and fragrance-free. Select hypoallergenic detergents and soaps. Identify and avoid personal allergens by testing.
-
Psoriasis: Choose mild soaps and detergents. Be aware of potential skin irritants. Manage your allergies to reduce triggers.
2. Environmental Factors:
-
Eczema: Moisturise frequently to prevent dryness. Use a humidifier in dry weather. Dress in breathable materials.
-
Psoriasis: Moisturise to prevent skin dryness. Avoid adverse weather conditions. In cold weather, you should protect your skin.
3. Stress:
-
Eczema: Practice stress-reduction techniques (such as meditation and yoga). Prioritise self-care and relaxation. Identify and address stressors.
-
Psoriasis: Engage in stress-management activities. Consider counselling or therapy. Develop a healthy work-life balance.
4. Infections:
-
Eczema: Maintain proper hygiene practices. Any skin infections should be treated promptly. Exercise caution in crowded or unsanitary environments.
-
Psoriasis: Take precautionary measures to avoid infection. Infections should be treated promptly. Maintain a healthy lifestyle to strengthen your immune system.
5. Scratching and Skin Trauma:
-
Eczema: Keep your nails short to prevent skin damage. Use anti-scratch mittens on infants. Apply cool compresses to relieve itching.
-
Psoriasis: Moisturise gently to reduce scaling. Avoid excessive scratching. Protect your skin from trauma and injury.
6. Hormonal Changes:
-
Eczema: Adapt your skincare routine to hormonal changes. Consult with a healthcare provider for advice.
-
Psoriasis: Hormone fluctuations should be monitored and managed. Consult your healthcare provider for personalised advice.
7. Medications:
-
Eczema: Be cautious when taking new medications. Inform your healthcare provider about your skin condition.
-
Psoriasis: Discuss potential triggers with your healthcare provider. Notify me about psoriasis when beginning a new prescription.
8. Lifestyle Habits:
-
Eczema: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption. Keep up a nutritious diet. Continue your physical activity.
-
Psoriasis: Adopt a healthy lifestyle. Limit your alcohol intake and quit smoking. Eat a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet.
9. Dietary Factors:
-
Eczema: Identify and avoid trigger foods. Consider an elimination diet under professional guidance.
-
Psoriasis: Explore an anti-inflammatory diet. Monitor how certain foods affect symptoms. Consult with a dietitian for personalised advice.
10. Regular Monitoring and Adaptability: Regularly assess the skin's condition and adapt the skincare routine. Keep a diary of potential triggers and responses to different interventions. Consult with healthcare providers for ongoing guidance.
11. Professional Guidance: Work closely with dermatologists or healthcare providers. Explore advanced treatment options under professional supervision. Regular check-ups and discussions about treatment efficacy are crucial.
The Role of Skin Barrier Function in Eczema and Psoriasis
The skin barrier is critical to the development and progression of both eczema (atopic dermatitis) and psoriasis. A healthy skin barrier serves as a protective shield, preventing irritants, allergens, and pathogens from entering the skin. When the skin barrier is compromised, it can contribute to the development and progression of these skin conditions.
Skin Barrier Function in Eczema:
-
Impaired Barrier Function: Eczema patients typically have a compromised skin barrier, making them more vulnerable to irritants, allergens, and infections.
-
Reduced Moisture Retention: Skin with eczema typically has a dry texture and is not able to hold onto moisture well. Inadequate hydration leads to skin sensitivity and irritation.
-
Inflammation and Itching: The hallmark signs of eczema, such as inflammation, redness, and severe itching, can result from compromised skin barrier function. Scratching exacerbates the damage to the skin barrier, setting off a vicious cycle of irritation and redness.
-
Genetic Factors: In people who are prone to eczema, genetic factors may have an impact on the integrity of the skin barrier. Skin barrier protein-related gene mutations may be a factor in barrier dysfunction.
-
Microbiome Imbalance: Eczema is linked to changes in the skin's microbiome, which is a community of microorganisms. Disruptions in the microbiome can impact the skin barrier and contribute to inflammation.
Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis:
-
Altered Epidermal Proliferation: In psoriasis, there is an accelerated rate of skin cell turnover, leading to the formation of thick, scaly plaques. This altered proliferation disrupts the normal skin barrier function.
-
Increased Permeability: Psoriatic skin exhibits increased permeability, allowing for easier penetration of irritants and allergens. The compromised barrier contributes to the inflammatory response seen in psoriasis.
-
Immune System Activation: Psoriasis is characterised by a compromised skin barrier, which activates the immune system. Inflammatory cytokines are released, causing redness and scaling.
-
Genetic Factors: Psoriasis development is influenced by genetic factors, specifically immune-related gene changes. Genetic factors affect the skin barrier and immune response.
-
Microbiome Influence: Psoriasis is associated with changes in the skin microbiome. Changes in microbiome composition can affect the skin barrier and immune system.
Understanding the role of the skin barrier in eczema and psoriasis emphasises the importance of taking a holistic approach to skincare. By focusing on barrier repair, hydration, and minimising triggers, individuals can work towards managing these chronic skin conditions effectively with the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Anti-Inflammatory Approaches to Alleviate Symptoms
Anti-inflammatory treatments are essential for relieving the symptoms of chronic skin conditions such as eczema and psoriasis. Both conditions result in inflammatory processes that cause skin irritation, redness, and discomfort. Here are some effective anti-inflammatory strategies for managing symptoms:
-
Topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, emollients and moisturisers, wet wrap therapy, bathing practices, dietary changes, anti-inflammatory supplements, and identifying and avoiding triggers are all treatments for eczema (atopic dermatitis).
-
Topical corticosteroids, topical retinoids, calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy (light therapy), systemic medications, salicylic acid, coal tar preparations, dietary changes, stress management, and abstaining from alcohol and smoking are all options for Psoriasis treatment.
It is critical to collaborate closely with healthcare providers, including dermatologists, to determine the most appropriate anti-inflammatory approaches for each patient. A personalised and comprehensive treatment plan typically includes a combination of topical treatments, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, systemic medications. Regular monitoring and changes to the treatment plan may be required to effectively manage symptoms.
Expert-Endorsed Treatments and Skincare Practices

Expert-approved treatments and skincare practices are essential for effectively managing chronic skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis. Dermatologists, skincare professionals, and healthcare Providers can offer advice based on individual needs and the severity of the symptoms. Here are expert-approved treatments and skincare practices:
Expert-Endorsed Treatments for Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis):
-
Topical Corticosteroids: Dermatologists often prescribe anti-inflammatory creams or ointments to alleviate redness and itching during flare-ups. Strengths vary depending on the severity of symptoms.
-
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are non-steroidal creams that reduce inflammation in sensitive areas, such as the face.
-
Dupilumab (a biologic medication): This injectable treatment targets specific immune response pathways. It treats moderate to severe eczema that does not respond to other treatments.
-
Wet Wrap Therapy: A healthcare professional administers wet wrap therapy, which involves applying a damp layer over emollients or medications to soothe and hydrate the skin during severe flare-ups.
-
Phototherapy (Light Therapy): Controlled UVB light exposure under medical supervision may benefit some individuals. It reduces inflammation and promotes skin healing.
-
Emollients and Moisturizers: Regular use of fragrance-free and hypoallergenic moisturisers is essential for maintaining skin hydration and strengthening the skin barrier.
Expert-Endorsed Treatments for Psoriasis:
-
Topical Corticosteroids: These are commonly used as the first treatment for mild to moderate psoriasis, as they reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell turnover.
-
Topical Retinoids: Tazarotene, a topical retinoid, aids in the management of psoriasis plaques and promotes normal skin cell turnover.
-
Calcineurin Inhibitors: Under medical supervision, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus can be used to treat psoriasis, particularly in sensitive areas.
-
Phototherapy (Light Therapy): To slow down skin cell turnover, medical professionals may recommend UVB phototherapy or PUVA (psoralen plus UVA).
-
Systemic Medications: For severe cases, systemic medications like methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics may be prescribed. Biologics, in particular, target specific aspects of the immune system involved in psoriasis.
-
Salicylic Acid: Over-the-counter or prescription-strength salicylic acid helps remove scales and facilitate the effectiveness of other treatments.
-
Coal Tar Preparations: Coal tar has anti-inflammatory properties and is available in various formulations to help slow down skin cell turnover.
-
Moisturizers and Emollients: Regular use of moisturizers is important to alleviate dryness and support the skin barrier.
Getting expert advice is essential for efficient administration. Dermatologists can create individualised treatment programmes that take into consideration each patient's unique demands and skin condition features. Successful long-term management of psoriasis and eczema depends on routine examinations and honest discussions with medical professionals.
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids and Beyond
The mainstay of treating skin diseases like psoriasis and eczema is topical therapy. In addition to corticosteroids, several other topical medications are essential for symptom relief and preserving skin health. It's crucial to remember that the exact ailment, its severity, and individual circumstances all play a role in the therapy decision. The following list of topical medications includes corticosteroids among others:
-
Corticosteroids: How They Work: Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications that help alleviate the redness, itching, and inflammation associated with eczema and psoriasis. Types: Available in a variety of strengths (from mild to potent) based on the severity of the symptoms and the affected area. Considerations: Short-term use is generally safe, but long-term use may cause side effects such as skin thinning. Dermatologists prescribe the appropriate strength based on the patient's individual needs.
-
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: How They Work: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are nonsteroidal drugs that suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. Uses: Especially useful in sensitive areas such as the face and neck, where corticosteroids should be avoided. Considerations: Long-term safety is still being investigated, and their use may be restricted in certain populations. They are frequently reserved for individuals who do not respond well to other treatments.
-
Topical Retinoids: How They Work: Tazarotene is a topical retinoid that regulates skin cell turnover, which reduces scaling and inflammation in psoriasis. Uses: Effective in treating psoriasis plaques and improving overall skin health. Considerations: Skin irritation may occur, and they are generally not recommended for use during pregnancy.
-
Coal Tar Preparations: How They Work: Coal tar has anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative properties, which slow the rapid growth of skin cells. Uses: Available in a variety of psoriasis formulations such as creams, ointments, and shampoos. Considerations: The odour may be strong, and clothing staining is possible. Regular use can help you manage your symptoms.
-
Calcipotriene (Vitamin D Analog): How It Works: Calcipotriene is a synthetic form of vitamin D that regulates skin cell production. Uses: Effective in treating mild to moderate psoriasis. Considerations: Can irritate, and excessive use should be avoided.
-
Salicylic Acid: How It Works: Salicylic acid helps soften psoriasis plaques, making it easier for other medications to penetrate. Uses: Often included in over-the-counter and prescription preparations for psoriasis. Considerations: It can cause skin irritation and should be used under professional guidance.
-
Antibiotics: How They Work: Antibiotics may be prescribed to address bacterial infections that can exacerbate eczema. Uses: Applied topically to infected areas. Considerations: Used as part of a treatment plan when a bacterial infection is present.
-
Moisturisers and Emollients: How They Work: Regular use helps maintain skin hydration, support the skin barrier, and reduce symptoms. Uses: Essential for daily skincare routines in managing both eczema and psoriasis. Considerations: Choose products without fragrances or irritants.
-
Wet Wrap Therapy: How It Works: It involves applying a damp layer over moisturisers or medications to soothe and hydrate the skin during severe flare-ups. Uses: Particularly beneficial in managing acute eczema flare-ups. Considerations: Usually done under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
Moisturizing Solutions for Hydrated and Healthy Skin
Keeping your skin hydrated is essential for overall skin health, especially if you have eczema or psoriasis. Choosing the right moisturising solutions can help soothe dryness, alleviate symptoms, and support the skin barrier. Here are some moisturising solutions for hydrated and healthy skin:
-
Emollients: Emollients are thick, lipid-rich moisturisers that help to lock moisture into the skin and prevent water loss. They are beneficial to people with dry and sensitive skin, such as those who have eczema or psoriasis. Creams, ointments, and balms with ingredients like shea butter, cocoa butter, and ceramides are good examples.
-
Hyaluronic Acid Serums: Hyaluronic acid is a hydrating ingredient that can store a lot of water. Hyaluronic acid-containing serums help to hydrate the skin, leaving it plump and moisturised. Suitable for all skin types, including those with eczema and psoriasis.
-
Occlusive Agents: Occlusive agents form a barrier on the skin's surface to prevent water loss. Petroleum jelly (petrolatum) and mineral oil are effective occlusive agents for dry areas. These are especially useful for people with extremely dry skin.
-
Ceramide-Enriched Products: Ceramides are naturally occurring components of the skin's barrier that help retain moisture. Moisturisers containing ceramides help replenish and strengthen the skin barrier. Suitable for individuals with compromised skin barriers, such as those with eczema.
-
Aloe Vera Gel: Aloe vera has both soothing and moisturising properties. Applying pure aloe vera gel or using aloe vera-containing skincare products can soothe irritated or sunburned skin.
-
Glycerin-Based Moisturizers: Glycerin is a humectant, which draws water to the skin and promotes hydration. Glycerin-based moisturisers are lightweight and ideal for daily use.
-
Coconut Oil: Coconut oil is a natural moisturiser that contains anti-inflammatory properties. It can be used directly on the skin or mixed into skincare products.
-
Jojoba Oil: Jojoba oil is suitable for most skin types and has properties similar to natural sebum. It regulates and nourishes the skin.
-
Colloidal Oatmeal Creams: Colloidal oatmeal has both soothing and anti-inflammatory properties. Creams containing colloidal oatmeal can relieve itching and irritation associated with eczema.
-
Shea Butter: Shea butter is a rich, nourishing moisturiser that aids in moisture retention. It is commonly found in creams, lotions, and body butter.
-
Water-Based Moisturizers: Water-based moisturisers can hydrate skin without feeling greasy for those who like lighter textures. Seek for formulas with glycerin and hyaluronic acid.
-
Probiotic Skincare: Some skincare products contain probiotics, which can help to maintain the skin's natural barrier function. Moisturisers with probiotics may be beneficial for people who have sensitive or compromised skin.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailoring Care to Individual Needs
Developing customised treatment regimens is crucial to the successful management of skin diseases, including psoriasis and eczema. Since each person has a different sort of skin condition, its severity, lifestyle, and skin sensitivity should all be taken into account. To customise care to meet each patient's needs, dermatologists and other medical professionals are essential. The following are essential components of customised treatment programmes:
-
Detailed Skin Assessment: Dermatologists examine the skin thoroughly, taking into account things like the kind of ailment, how severe it is, and any accompanying symptoms. Determining particular traits facilitates customising care to meet each patient's demands.
-
Understanding Triggers: Effective management requires the identification of triggers that exacerbate symptoms. Dermatologists assist patients in identifying dietary, behavioural, and environmental variables that may exacerbate flare-ups.
-
Individualised Skincare Regimen: Customising skincare regimens to meet each person's requirements and preferences is essential. Depending on the kind and condition of the skin, recommendations may include particular cleansers, moisturisers, and topical treatments.
-
Assessment of Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle factors, including food habits, sleep patterns, and stress levels, should be taken into account. It might be advised to modify one's lifestyle to promote general skin health.
-
Severity-Based Treatment: The severity of the skin condition determines how treatment plans are modified. More severe cases may need systemic medications or advanced therapies; milder cases can be managed with topical treatments and lifestyle changes.
-
Regular Follow-Ups: Regular follow-up appointments allow dermatologists to assess the progress of the treatment plan. Adjustments can be made based on the skin's reaction and any changes in symptoms.
-
Educational Support: Providing education on a specific skin condition allows people to better understand their condition and the reasoning behind recommended treatments. Dermatologists advise on skincare techniques, trigger avoidance, and lifestyle changes.
-
Customised Topical Treatments: Topical treatments such as corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and other medications are prescribed based on the individual's needs. Formulations can be tailored to skin sensitivity and application area.
-
Phototherapy Options: Dermatologists may recommend phototherapy for psoriasis, depending on the type and location of the plaques. Individual factors, such as skin type and light sensitivity, influence the choice of phototherapy.
-
Biologic Medications: In cases of severe psoriasis or eczema, dermatologists may prescribe biologic medications. Selection is based on factors like the individual's overall health, response to previous treatments, and preferences.
-
Incorporating Integrative Approaches: Individual preferences may dictate the use of integrative approaches such as stress management techniques, dietary adjustments, or complementary therapies.
-
Patient-Centred Decision-Making: Dermatologists consult with patients before making decisions, taking into account their preferences, lifestyle, and treatment goals. Open communication promotes a collaborative approach to care.
-
Adjustments for Aging Skin: As people age, their skincare needs change. Dermatologists may modify treatment regimens to address age-related changes in skin health and elasticity.
-
Monitoring for Side Effects: Regular monitoring aids in the identification and management of potential side effects of medications or treatments. Adjustments are made to reduce side effects while still ensuring effective management.
-
Educating on Long-Term Management: Dermatologists recommend long-term management strategies to maintain skin health. Individuals are empowered to actively manage their condition.
A customised treatment plan takes the patient's needs into account holistically, acknowledging that a variety of factors affect skin health. Dermatologists collaborate with patients to customise therapy, guaranteeing the most efficient and long-lasting method of treating psoriasis and eczema. Sustaining the treatment plan over time requires consistent follow-ups and communication to make necessary adjustments.
Lifestyle and Holistic Approaches to Managing Eczema and Psoriasis

Lifestyle changes and holistic therapies are just as important as medications for chronic skin disorders such as psoriasis and eczema. To support the skin, these methods emphasise general well-being, dealing with possible stressors, and encouraging a healthy lifestyle. Here are some holistic and lifestyle approaches to consider: journaling, hydrotherapy, mind-body connection, balanced living, aromatherapy, skincare routines, sun protection, complementary therapies, altered nutrition, journaling, social support, and expert advice. It's crucial to remember that although lifestyle and holistic methods might support medical care, they shouldn't take the place of recommended drugs or therapies. Patients should collaborate closely with their dermatologists and other medical professionals to incorporate these tactics into a thorough and unique treatment regimen. Holistic management combines medical, lifestyle, and self-care strategies to promote long-term skin health and well-being.
Stress Management: Understanding the Mind-Skin Connection
Stress management is a vital element of maintaining skin health, especially for people living with chronic skin problems like eczema and psoriasis. The mind-skin connection emphasises the delicate relationship between psychological well-being and skin health. Prolonged stress can worsen skin disorders and trigger flare-ups. To implement stress management techniques that work, it is imperative to comprehend this relationship. Below is a summary of the mind-skin connection:
-
Impact of Stress on the Skin: The body releases the hormones cortisol and adrenaline, which can have an impact on the skin, while under stress. Long-term stress can aggravate pre-existing skin disorders, raise inflammation, and interfere with the skin's natural healing mechanisms.
-
Skin Conditions Affected by Stress:
-
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Stress can cause or exacerbate eczema flare-ups. It may worsen itching and inflammation, making treatment more difficult.
-
Psoriasis: Stress is known to cause psoriasis flare-ups. Individuals with psoriasis may experience more severe symptoms during times of high stress.
-
Acne and Rosacea: Stress can affect the severity of acne and rosacea. It may cause increased oil production, inflammation, and breakouts.
-
Hives and Allergic Reactions: Stress may contribute to the development of hives and exacerbate allergic reactions.
-
Inflammatory Response: Stress activates the body's inflammatory response, which can impair skin barrier function. Disruptions in the skin barrier can increase sensitivity and vulnerability to environmental irritants.
-
Itch-Scratch Cycle: Stress can intensify the itch-scratch cycle common to many skin conditions. Continuous scratching can cause skin damage and prolonged healing.
Implementing Natural Remedies and Home Care Techniques
Complementing medical treatments, natural remedies, and home care approaches can help control chronic skin disorders like psoriasis and eczema overall. These methods can be included in a comprehensive skincare regimen, even though they might not take the place of prescription drugs. Before attempting any new treatments, it is crucial to speak with a dermatologist, particularly for those with sensitive skin or particular skin disorders. Oatmeal baths, coconut oil, cold compress, apple cider vinegar soaks, aloe vera gel, chamomile tea compress, diluted tea tree oil, honey masks, probiotics, wet wrap therapy, green tea compress, evening primrose oil, omega-3 fatty acids, witch hazel, and sunflower seed oil are a few natural remedies and home care techniques to think about. However, different people may find them to be more or less effective. It is important to approach these treatments knowing what your skin needs specifically, and to seek the advice of medical professionals for individualised treatment plans. Skin health can be improved by combining medical treatments with natural remedies and using a holistic approach to skincare.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself with Knowledge and Expert Guidance
Handling skin care issues such as psoriasis and eczema demands a customised approach, professional advice, and an understanding of the intricacies of skincare. You can create a skincare regimen that encourages lifetime radiance by learning about the changing demands of your skin over time, investigating substances specifically designed for each age group, and examining the science behind age-specific skincare. A young appearance is mostly dependent on collagen, the essential protein for skin suppleness and strength. As protectors, antioxidants shield your skin from the elements and advance the general health of your skin. Including substances recommended by experts for each age group guarantees that your skincare regimen takes into account the particular needs and problems that each age group's skin presents. Building a solid foundation in your 20s, addressing early indications of ageing in your 30s, stepping up hydration and repair in your 40s, and caring for mature skin with specific formulas in your 50s are important turning points in your skincare journey. These phases necessitate a customised strategy to preserve skin vigour and health. But skincare also includes holistic approaches in addition to topical treatments. Resolving flare-ups of skin disorders such as psoriasis and eczema requires knowledge of triggers, maintenance of the skin barrier function, and application of anti-inflammatory methods. Effective therapies, such as topical corticosteroids and other therapies, are essential for symptom relief and skin health maintenance.
















