Acne treatment with glycolic acid can be successful. Pick the appropriate product, clean your skin, conduct a patch test, apply to the concerned areas, adhere to the directions, moisturise after, and use sunscreen. These are the applications for glycolic acid and how it treats acne. Glycolic acid exfoliates the skin, clears clogged pores, and speeds up cell renewal. It assists in removing dead skin cells, lowering oil and debris build-up, and fading acne scars and hyperpigmentation. It also possesses anti-inflammatory qualities that can aid in lowering the redness and inflammation brought on by acne breakouts. It is advised to see a dermatologist if you have severe or persistent acne so they can make tailored suggestions and offer advice based on your unique skin condition.
The Truth About Glycolic Acid and Sensitive Skin: Is It Safe to Use?
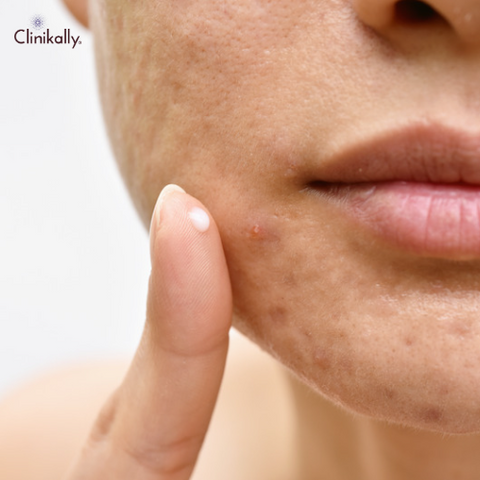
Popular skincare ingredients include glycolic acid, which is used mostly in chemical peels and exfoliants. It is a member of the alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) family, which is well-known for its capacity to exfoliate dead skin cells and enhance the texture, tone, and general appearance of skin. However, caution is advised when dealing with sensitive skin. Sensitive skin is more likely to irritate, get red, and experience pain when exposed to specific chemicals. Although glycolic acid has a number of positive properties, if applied incorrectly or in excessive quantities, it has the potential to harm delicate skin. The following are some crucial considerations:
-
Start with low concentrations: It's best to start with products that contain lower concentrations of glycolic acid (between 5% and 8%) if you have sensitive skin. This enables the ingredient to be absorbed into your skin gradually without overpowering it.
-
Patch test: Before using any glycolic acid products on your face, test them out on a small patch of skin. A small amount of the product should be applied, and any unfavourable reactions like redness, itching, or burning should be watched for. It's best to steer clear of using the product if you feel any discomfort.
-
Observe directions: The glycolic acid product's directions should be carefully read and followed. Pay close attention to the recommended application time and frequency. The likelihood of irritation can be increased by overusing a product or using it for longer than recommended.
-
Consider pH levels: A product's ability to irritate can be influenced by its pH level. Lower pH values (nearer to 2) increase acidity and may irritate sensitive skin more. In order to find a formulation that is more gentle, look for products with a pH that is closer to the skin's natural pH (between 4.5 and 5.5).
-
Protect and moisturise: Sensitive skin typically benefits from a well-maintained moisture barrier. After using products containing glycolic acid, moisturise your skin to replenish moisture and lower the chance of dryness or sensitivity. Additionally, because glycolic acid can make skin more sensitive to the sun, applying sunscreen during the day is essential for protecting your skin from potential sun damage.
-
Speak with a dermatologist: A dermatologist should always be consulted if you have any concerns about using glycolic acid or any other skincare ingredient because of your sensitive skin. They can assess the particular requirements of your skin and suggest appropriate products or less irritating substitutes.
While using glycolic acid on sensitive skin can have negative effects, it can also improve skin structure and look. Prioritise moisturising and sun protection, start with low concentrations, conduct a patch test, and adhere to instructions. Consult a dermatologist for help if you're unsure.
What Is Glycolic Acid and How Does It Work?

A form of alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) generated from sugar cane is glycolic acid. Due to its exfoliating and skin-renewing qualities, this crystalline solid, which is colourless and odourless, is frequently used in skincare products. This is how glycolic acid functions:
-
Exfoliation: Glycolic acid, a tiny molecule, can pierce the stratum corneum, or top layer of skin. It functions by loosening the bonds that hold dead skin cells together, making it easier for them to slough off. This exfoliating process aids in removing the skin's outer, rough, and dull layer to reveal the smoother, younger-looking skin beneath.
-
Skin cell replacement: The natural process of shedding old skin cells and replacing them with new ones is called cell turnover, and glycolic acid promotes this process. Glycolic acid helps to rejuvenate the skin's appearance and improve its texture by promoting cell renewal. Additionally, it can aid in the fading of sun damage symptoms like hyperpigmentation and acne scars.
-
Pore cleaning: Glycolic acid's exfoliating properties can help to unclog pores by removing debris and dead skin cells that can build up and cause the development of blackheads and whiteheads. Acne breakouts can be reduced by using glycolic acid to keep the pores clear.
-
Moisture retention: Glycolic acid has a humectant property, which means it can attract and retain moisture in the skin. This may hydrate the skin and enhance the balance of moisture in it. It is important to note, however, that glycolic acid can cause dryness or irritation in some people, especially when used in high concentrations or on sensitive skin.
There are several skincare products that include glycolic acid, including cleansers, toners, serums, masks, and chemical peels. These products can contain glycolic acid at levels ranging from low (about 5% to 8%) to high (up to 30% or more). It's crucial to remember that while glycolic acid can have many advantages, not everyone may benefit from its use. When using glycolic acid, people with sensitive skin or those with particular skin conditions may face irritation or unfavourable reactions. Before using glycolic acid products on your entire face, it is advised to conduct a patch test and carefully follow the directions included with each product. It's always a good idea to speak with a dermatologist if you have any questions or unique skin disorders, so they can offer you individualised advice and direction based on your specific requirements.
The Benefits of Glycolic Acid for All Skin Types
When applied properly, glycolic acid has various advantages for all skin types. The following are a few benefits of glycolic acid:
-
Glycolic acid is a potent exfoliant that can remove dead skin cells and unclog pores with ease. This exfoliating process encourages cell renewal and smoother, more radiant skin by enhancing skin texture.
-
Glycolic acid can help brighten the complexion and improve the overall appearance of the skin by removing the outer layer of dull and damaged skin cells. It can also aid in the removal of hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone caused by sun damage, acne scarring, or age spots.
-
Glycolic acid can help reduce the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and other ageing signs. Its exfoliating properties and stimulation of collagen production can help improve skin elasticity and firmness, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
-
Glycolic acid is an effective acne treatment because of its ability to unclog pores and reduce the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads). It can also help reduce the inflammation and redness associated with acne breakouts.
-
Glycolic Acid Benefits for People with Rough or Uneven Skin Smoother Texture: Regular glycolic acid use may result in smoother skin texture.
-
Glycolic acid can aid in enhancing the penetration and absorption of other skincare products. Removing the top layer of dead skin cells, it allows subsequent products, such as serums and moisturisers, to penetrate more deeply and deliver their active ingredients effectively.
It's important to keep in mind that while glycolic acid can benefit all skin types, some people may benefit more from it than others. Those with sensitive skin should use glycolic acid with caution and start with lower doses to reduce the risk of irritation. To ensure safe and efficient outcomes, it's also crucial to adhere to the product's recommendations, including the frequency and length of application. Consult a dermatologist or other skincare expert if you have specific skin issues or conditions, so they can evaluate your skin type and make tailored suggestions for how to incorporate glycolic acid into your skincare regimen.
Why Glycolic Acid Can Be Problematic for Sensitive Skin
While many people can benefit from glycolic acid, those with sensitive skin may experience problems. Here are a few explanations:
-
Potential Irritation: Glycolic acid is one of the chemicals that sensitive skin sometimes reacts to more severely. In particular, when applied in high concentrations or if the skin's barrier function is weakened, its exfoliating activities may result in irritation, redness, stinging, or burning sensations. Skin types with sensitive characteristics may be more susceptible to these harmful effects.
-
Barrier Disruption: Glycolic acid can damage the skin's natural moisture barrier, increasing sensitivity and dryness. The exfoliating action of glycolic acid can further erode the thin barrier that protects sensitive skin, increasing sensitivity and possibly causing discomfort.
-
Skin Sensitivity to UV Rays: Glycolic acid can make the skin more sensitive to the sun's harmful UV rays. Sensitive skin is already prone to sun sensitivity, and using glycolic acid can exacerbate the problem. It becomes crucial to apply broad-spectrum sunscreen when using glycolic acid and to take extra precautions to protect the skin from sun exposure.
-
Risk of Over-Exfoliation: Sensitive skin usually reacts poorly to frequent or vigorous exfoliation. If used too frequently or in high concentrations, glycolic acid's exfoliating properties can result in over-exfoliation, which can dry out the skin, make it red, and make it more sensitive.
Glycolic acid might not be ideal for people with sensitive skin, but that doesn't imply it can never be used. The following considerations should be made when using glycolic acid on sensitive skin:
-
Begin with low concentrations: To reduce the risk of irritation, start with products containing lower concentrations of glycolic acid (around 5% to 8%). Before applying the product to your entire face, test it on a small patch of skin.
-
Patch test: Before using any new glycolic acid product, perform a patch test by applying a small amount to a hidden area of your skin. Keep an eye out for any negative reactions such as redness, itching, or burning. If you experience any discomfort, stop using the product.
-
Gradual introduction: If your skin tolerates glycolic acid well after patch testing, ease it into your skincare routine gradually. Start with less frequent applications—every other day or a couple of times per week—and watch how your skin reacts. According to your skin's tolerance, adjust the frequency.
-
Protect and moisturise: Sensitive skin needs enough moisture to maintain its barrier function. After using glycolic acid, apply a light moisturiser to replenish and hydrate the skin. In addition, use sunscreen during the day to protect your skin from sun damage.
-
Consult a dermatologist: If you are concerned about using glycolic acid or any other skincare ingredient on your sensitive skin, you should consult a dermatologist. They can assess your skin's specific requirements and make personalised recommendations.
Keep in mind that every individual has a different type of skin, so what suits one person may not suit another. Glycolic acid may not be good for delicate skin, but there are other chemicals and gentler exfoliation techniques that can offer the same advantages without aggravating the skin.
Tips for Using Glycolic Acid on Sensitive Skin

Here are some suggestions to help you use glycolic acid safely and successfully if you have sensitive skin and want to incorporate it into your beauty routine:
-
Patch test: Perform a patch test on a small area of skin before using glycolic acid on your entire face. The inner arm or the area behind the ear are good places to discreetly apply a small amount of the product. After 24 hours, check for any unfavourable side effects, such as redness, itching, or irritation. The product should not be applied to your face if you feel any discomfort.
-
Select Low Concentrations: Begin with glycolic acid-containing products designed specifically for sensitive skin that have lower concentrations (between 5% and 8%). This enables the ingredient to be introduced to your skin gradually without overpowering it.
-
Frequency of Use: Begin by using glycolic acid products sparingly, such as once or twice a week. Consider how your skin responds before gradually increasing the frequency. Make any necessary adjustments if you notice any sensitivity or irritation in your skin.
-
Shorter Contact Time: Consider using glycolic acid as a wash-off treatment if you find that it irritates your skin when applied for an extended period of time. Apply the solution to your skin, let it sit for a brief period of time (a few minutes, for example), and then wash it off with water.
-
Application Technique: Use gentle pressure when applying glycolic acid to your skin. Avoid vigorously rubbing or scrubbing, as this can make the area more sensitive. Use gentle, circular motions as an alternative and let the product do the work. Additionally, refrain from using any other products that might irritate you at the same time, such as abrasive scrubs or exfoliants.
-
Hydrate and moisten your skin: Sensitive skin is more likely to become dry and irritated. Apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturiser right after using glycolic acid to calm and hydrate your skin. This supports the skin's barrier function and restores moisture to the skin.
-
Sun Protection: Because glycolic acid makes skin more sensitive to the sun's rays, it's critical to shield your skin from these dangerous UV rays. Even on cloudy days, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF of 30 or higher during the day. Think about taking additional safety precautions, such as donning a hat with a wide brim and finding cover when necessary.
-
Consider your skin: Pay close attention to how glycolic acid affects your skin. If you continue to experience persistent redness, itchiness, or discomfort, stop using the product and seek additional advice from a dermatologist.
-
Professional Advice: It's always a good idea to speak with a dermatologist if you have questions about using glycolic acid or concerns about your sensitive skin. They are able to assess the particular requirements of your skin and offer tailored suggestions or substitutes.
Understanding pH Levels and Concentrations
When using specific chemicals in skincare products, it's critical to understand pH levels and concentrations. An outline of these ideas is provided below:
- pH levels: On a scale from 0 to 14, pH determines how acidic or alkaline a substance is. The pH scale goes from 0 to 14, with 14 being neutral, acidic, and alkaline respectively. A pH of 7 is regarded as neutral. The skin's surface typically has a pH of 5.5, which is a mildly acidic level.
Why does pH matter for skincare? The pH of skincare products can have an effect on the skin's natural barrier function and general health. A product's ability to maintain the skin's protective acid layer is enhanced when its pH matches that of the skin. The pH balance of the skin might be off, which can result in problems including dryness, irritation, or greater susceptibility to bacteria.
- Concentrations: A product's concentration is the amount of a specific ingredient. It is typically expressed as a ratio or a percentage.
The importance of concentrations in skincare: why? An ingredient's potency and risk of negative effects depend on its concentration. Some chemicals, such as active acids or exfoliants, have the right amounts to be effective while lowering the chance of irritability or negative responses. Particularly for sensitive skin, higher concentrations of some substances could call for additional caution and shorter contact durations.
The distinction between pH and concentration must always be kept in mind. While pH can affect the stability and effectiveness of some compounds, concentration is largely what determines an ingredient's potency and any potential skin side effects. It's important to take pH levels and concentrations into account when selecting skincare products. To maintain a healthy skin barrier, look for products with pH levels that are similar to the skin's natural pH. Consider the concentration of the active components as well, particularly if you have sensitive skin or are taking strong actives like retinoids, BHAs, or AHAs.
Performing a Patch Test
In particular, if you have sensitive skin or a history of allergies, conducting a patch test is essential to determining how your skin responds to a new skincare product or component. Here is a detailed explanation of how to do a patch test:
-
Select a compact space: Choose a small, discrete area of skin, like the inside of your arm or the area behind your ear. The location ought to allow you to quickly monitor any potential reactions.
-
Cleaning the area: Use lukewarm water and a mild cleanser to gently wash the chosen patch test area. Use a fresh towel to pat the area dry.
-
Apply the product: Dab the patch test area lightly with the product you want to test. Use just enough to cover a small patch of skin, but not enough to cause it to spread outside the confines.
-
Leave it on: The recommended time period noted on the product label should be used to let the product remain on the patch test area. The typical time frame for this is 24 hours but always adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines.
-
Watch for reactions: Throughout the testing period, keep a close eye out for any symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as swelling, itching, or redness in the patch test area. Avoid excessive scratching or touching the area as this may cause more irritation.
-
After 24 hours, check: Examine the patch test area after the advised amount of time has passed. It is best to avoid using the product on your face or body if you experience any adverse reactions or discomfort, such as persistent redness or irritation.
-
Also, take into account: Keep in mind that the patch test area may not perfectly represent how your facial skin will react, but it can give you an indication of potential sensitivity. Skin thickness, sensitivity of specific areas (such as the eye area), and overall skin health can all influence the reaction.
A patch test lowers the likelihood of a widespread unpleasant reaction while assisting you in determining whether a product is acceptable for your skin. It's best to avoid using the product completely or get advice from a dermatologist if you have any adverse reactions during the patch test. If you have sensitive skin or are aware of any allergies, always be cautious and take the time to conduct a patch test before using a new product all over your body or face.
Choosing Gentle Products to Pair With Glycolic Acid
In order to reduce the danger of irritation when using glycolic acid in your skincare regimen, it's critical to pick gentle products that work well with it. The following advice will help you choose gentle items to use with glycolic acid:
-
Cleanser: Choose a gentle cleanser that won't strip the skin's natural oils or upset its pH balance. Look for cleansers with words like "gentle," "hydrating," or "pH-balanced." Avoid harsh cleansers containing sulfates or fragrance, as they may aggravate skin sensitivity.
-
Moisturiser: Select a gentle moisturiser that is appropriate for your skin type. Look for formulations that are breathable, non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging), and free of any substances that could cause irritation, such as alcohol, fragrances, or dyes. The skin's moisture barrier can be preserved and hydration restored with the aid of a moisturiser containing calming components like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, or aloe vera.
-
Sunscreen: Sun protection is essential when using glycolic acid, as it can make the skin more sensitive to sunlight. Choose a sunscreen with a broad-spectrum SPF of 30 or higher. Look for formulas that are gentle, fragrance-free, and designed specifically for sensitive skin. The majority of the time, sensitive skin tolerates physical sunscreens made of zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
-
Avoid Harsh Exfoliants: While glycolic acid is an exfoliant in and of itself, it's important to avoid using harsh physical exfoliants like scrubs or brushes when using glycolic acid. Excessive exfoliation can cause skin irritation and sensitivity. Keep to the glycolic acid-based exfoliation and let it do the work.
-
Serums and treatments: Select products that are specially formulated for sensitive skin when selecting serums or treatments to use with glycolic acid. Such calming substances as niacinamide, chamomile extract, or green tea extract should be sought out. If you have sensitive skin in particular, stay away from using other potentially irritating active ingredients, such as retinoids or strong acids, concurrently with glycolic acid.
-
Patch Test New Products: Before adding any new products to your regimen, carry out a patch test to make sure your skin is tolerant of them. Before using the product on your entire face, this enables you to rule out any possible allergic reactions or sensitivities.
-
Consider Your Skin: Observe how your skin responds when applying glycolic acid and complementary products. If you continue to experience persistent redness, itchiness, or discomfort, stop using the product and seek further advice from a dermatologist.
Remember that everyone's skin is different, and what works for one person may not work for another. To maintain a gentle and effective skincare routine, pay attention to how your skin reacts to different products and make adjustments as needed.
How to Incorporate Glycolic Acid into Your Skincare Routine for Sensitive Skin

You should be cautious and thoughtful when including glycolic acid in your skincare regimen, especially if you have sensitive skin. Here's how to incorporate glycolic acid into your routine for sensitive skin, step by step:
-
Start with a low concentration: To begin, use a mild glycolic acid product with a concentration of between 5% and 8%. This reduces the possibility of sensitivity or irritation. You can gradually up the concentration as your skin gets used to it.
-
Patch test: To ensure that the product is well tolerated by your skin, apply it to a small area of skin, such as the inner forearm. Apply a tiny bit of the glycolic acid product and keep an eye out for any unfavourable effects, like redness, itching, or irritation. If you feel any discomfort while applying it to your entire face, stop.
-
Frequency of use: Start by using glycolic acid products sparingly, such as once or twice a week. If there are no symptoms of irritation, watch how your skin responds and then gradually increase the frequency. If necessary, pay attention to your skin and change the frequency.
-
Incorporate it into your night-time routine: It is generally recommended to use glycolic acid in the evening because it can increase the skin's sensitivity to sunlight. It should be applied after cleansing and toning but before any other serums or moisturisers. Allow it to absorb into the skin for a few minutes before proceeding to the next step.
-
Protect and moisturise: To restore the skin's moisture barrier, use a mild, hydrating moisturiser after using glycolic acid. This lessens potential irritation and dryness. Additionally, to shield your skin from the sun's damaging UV rays during the day, use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
-
Avoid combining with other active ingredients: While glycolic acid is an active ingredient itself, it's generally advisable to avoid using other potentially irritating or exfoliating ingredients, such as retinoids or strong acids, at the same time. For sensitive skin in particular, combining multiple actives can increase the risk of irritation or excessive exfoliation. If you want to add additional active ingredients, do so on different days or as your dermatologist recommends.
-
Check-in with your skin: Keep a close eye on how glycolic acid affects your skin. If you continue to experience persistent redness, irritation, or discomfort, stop using the product or use it less frequently. Everybody has a different threshold for their skin, so it's critical to modify your routine to meet your skin's individual requirements.
-
Consult a dermatologist: If you have concerns about incorporating glycolic acid into your skincare routine or need personalised advice, it's always a good idea to consult with a dermatologist. They can evaluate your skin type, address any specific concerns, and provide tailored recommendations.
When introducing glycolic acid into your routine, especially for sensitive skin, keep in mind that a gentle and gradual introduction is essential. To ensure a secure and efficient skincare experience, pay attention to your skin, be patient, and make necessary adjustments.
Best Practices for Using Glycolic Acid in Your Skincare Routine
To ensure safety and maximise its benefits, it's important to follow a few best practices when using glycolic acid in your skincare routine. Here are some guidelines for using glycolic acid correctly:
-
Start with low concentrations: Start with products that have lower concentrations, typically between 5% and 8%, if you're new to using glycolic acid or have sensitive skin. As a result, the likelihood of skin irritation or sensitivity is reduced, and your skin is given time to adjust to the ingredient.
-
Cleanse your skin: Use a mild, pH-balanced cleanser to thoroughly clean your skin before applying glycolic acid. This ensures that the glycolic acid is absorbed as best as possible by removing dirt, oil, and other impurities.
-
Apply to dry skin: Make sure your skin is completely dry before applying glycolic acid. Water on the skin can speed up glycolic acid penetration, potentially making the condition worse.
-
Use a small amount: With glycolic acid, a little goes a long way. Use your fingertips or a cotton pad to apply a small amount to the desired areas, then gently spread it there. Apply it far enough away from the delicate areas of the eyes and lips.
-
Observe the directions: The manufacturer's instructions are listed on the product label; read them and abide by them. Pay close attention to the suggested contact time and usage frequency. The risk of irritation can increase with excessive use of glycolic acid or prolonged application to the skin.
-
Gradually increase usage: If your skin tolerates glycolic acid well, start by using it once or twice a week, and then gradually increase the usage. Make any necessary adjustments if your skin shows any signs of sensitivity or irritation.
-
Time it right: Glycolic acid is typically applied in the evening because it tends to make people more sensitive to the sun. Always follow up with broad-spectrum sunscreen during the day and avoid using it in the morning.
-
Moisturise afterwards: Apply a light moisturiser after using glycolic acid to hydrate and calm your skin. Its moisture balance is preserved as a result, lowering the possibility of dryness or irritability.
-
Combine with no other exfoliants: Other exfoliating products, such as physical scrubs or other chemical exfoliants (e.g., salicylic acid), should not be used in conjunction with glycolic acid. When using multiple exfoliants, you run the risk of over-exfoliation and irritation.
-
Be patient: The effects of glycolic acid may take some time to become apparent. To get the results you want from using it, you must be persistent and patient. Consult a dermatologist if you're unsure of the progress.
-
Check-in with your skin: Pay attention to how glycolic acid affects your skin. Reduce the frequency of application or stop using the product if you experience persistent redness, itching, or irritation. Everybody has different skin, so customise your routine to meet those needs.
You may successfully incorporate glycolic acid into your skincare routine and benefit from its exfoliating and skin-renewing properties while reducing the risk of sensitivity or irritation by adhering to these recommended practices.
Recommended Products for Sensitive Skin
When choosing products for sensitive skin, it's critical to look for gentle, non-irritating formulas that moisturise and support the skin's barrier function. If you have sensitive skin, take into account the following product categories and ingredients:
Cleansers:
Moisturisers:
Sunscreens:
Serums:
Exfoliants:
Soothing Masks:
Ingredient Considerations:
-
Look for products that contain gentle ingredients such as hyaluronic acid, ceramides, aloe vera, chamomile, oat extract, green tea extract, and niacinamide.
-
Avoid products that contain potentially irritating ingredients such as fragrances, dyes, alcohol, and harsh preservatives.
-
Take into account products that have undergone sensitivity testing and are hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic.
Always test new products on a small area of skin first to see how your skin responds because everyone has different levels of sensitivity. A dermatologist or skincare expert you consult with can also offer personalised recommendations based on your unique requirements and issues.
The Importance of Moisturizing and Sun Protection
Every skincare routine should include moisturising and sun protection, even for those with sensitive skin. Here's why these two factors are important:
Moisturising:
-
Keeps skin hydrated: Sensitive skin frequently has a weak skin barrier, which can cause increased moisture loss. In order to keep the skin hydrated and avoid dryness, flakiness, and irritation, moisturisers help replenish and retain moisture.
-
Skin calms and is soothed: Moisturisers with mild ingredients can help calm and soothe sensitive skin. They can alleviate discomfort and pain by reducing redness, inflammation, and sensitivity.
-
Strengthens the skin barrier: Sensitive skin frequently has a weak skin barrier, making it more vulnerable to external irritants. Moisturisers fortify the skin barrier, increasing skin resilience and decreasing the likelihood of irritation and sensitivity.
-
Prepares the skin for additional products: Proper moisturization creates a smooth surface for additional skincare products, allowing them to penetrate and function more effectively.
Sun Protection:
-
Prevents sun damage: For people with sensitive skin, exposure to the sun can make their sensitivity worse and cause skin reactions. UV radiation causes skin damage that results in inflammation, redness, and early ageing. To reduce these effects, it is essential to use sun protection.
-
Reduces the risk of hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure can make hyperpigmentation that already exists on sensitive skin worse. The development of dark spots and uneven skin tone can be avoided by wearing sunscreen.
-
Protects against harmful UV rays: UVA and UVB rays, in particular, can penetrate the skin and damage DNA, increasing the risk of skin cancer. Broad-spectrum sunscreen shields against UVA and UVB rays, lowering the risk of skin cancer, sunburns, and other skin-damaging effects.
-
Supports skin health: By preventing photoaging, wrinkles, and elasticity loss brought on by UV radiation, sunscreen helps maintain overall skin health.
Look for products that are specially developed for delicate skin types when choosing moisturisers and sunscreens for sensitive skin. Select products that are mild, scent-free, and hypoallergenic that contain hyaluronic acid, ceramides, aloe vera, and antioxidants. Choose physical blockers like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which are typically well-tolerated by sensitive skin, and broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if perspiring or swimming, and remember to moisturise daily in the morning and at night. For sensitive skin in particular, consistency and vigilance in moisturising and sun protection are essential to maintaining a healthy and comfortable skincare routine.
Glycolic Acid and Acne: Can It Help Clear Your Skin?
Acne can be effectively treated with glycolic acid, which can also enhance the skin's overall appearance. Using glycolic acid to treat acne can do the following:
-
Exfoliation: Glycolic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that exfoliates the dead skin cells on the skin's surface. It unclogs pores by removing dead skin cells, preventing the formation of whiteheads, blackheads, and acne breakouts.
-
Unclogging pores: Excess oil, debris, and dead skin cells can clog pores, which is one of the main causes of acne. Glycolic acid aids in the dissolution and removal of this build-up, allowing the pores to remain clear and lowering the likelihood of acne formation.
-
Skin renewal: Because glycolic acid promotes cell turnover, it aids in the natural process of shedding dead skin cells and generating new, healthy cells. This can lead to a smoother, more even complexion, as well as a reduction in the visibility of acne scars and hyperpigmentation.
-
Anti-inflammatory properties: Due to its anti-inflammatory qualities, glycolic acid can help reduce acne-related irritation and redness. Additionally, it can aid in minimising the size and colour of active acne lesions.
The following factors should be taken into account when using glycolic acid for acne:
-
Start with a low concentration: If you have sensitive skin, start with a lower concentration of glycolic acid, usually between 5% and 10%. As your skin adapts, you can gradually increase the concentration.
-
Patch test: To make sure you don't have any negative reactions or overly high sensitivity to glycolic acid, perform a patch test on a small patch of skin.
-
Use it properly: The glycolic acid product's instructions should be followed. Before putting on any additional products, apply them to clean, dry skin and give it time to absorb. If your skin accepts it well, start by using it a few times a week and then gradually increase the frequency.
-
Protect and moisturise: To hydrate and calm the skin, apply a moisturiser immediately after using glycolic acid. Additionally, use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 during the day to protect your skin from the sun's harmful UV rays, as glycolic acid can increase sun sensitivity.
Even though glycolic acid can be beneficial for many people with acne-prone skin, it's important to remember that everyone's skin is unique. It's recommended to see a dermatologist if you have severe or persistent acne, as they may offer specialised advice and solutions for your unique skin problems.
















