Small, flat, brown or black spots known as "liver spots," also referred to as "age spots," typically develop on skin that is frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, arms, and shoulders. Despite their name, liver spots are unrelated to the liver or how the liver works. The skin's natural response to years of sun exposure is the development of liver spots. The pigment that gives the skin its color, melanin, is produced in greater amounts when the skin is exposed to the sun. The extra melanin can accumulate over time and group together to create dark spots that are usually referred to as "liver spots."
Although they can occur in younger people as well, liver spots are more common in people over the age of 50. Despite the fact that they are not hazardous and don't need any medical attention, many people elect to have them removed for aesthetic reasons. Topical treatments, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and chemical peels are some of the available therapies for liver spots. If the skin is exposed to the sun for longer periods of time, these treatments might not be able to stop new spots from appearing. So, the key to preventing liver spots is prevention through sun protection.
What are Liver Spots?
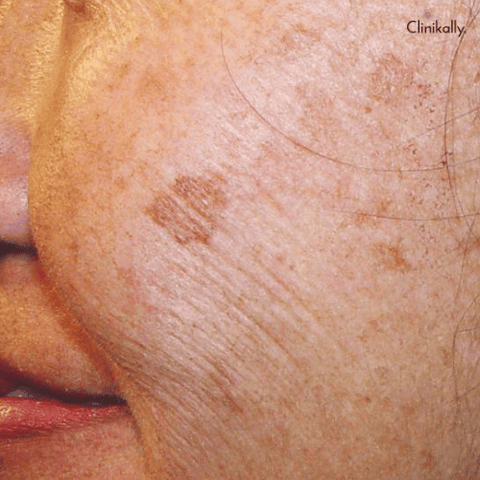
Flat, brown or black lesions on the skin that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, arms, and legs, are known as " liver spots," sometimes known as age spots or solar lentigines. Although these spots are typically painless and harmless, some people may find their appearance bothersome. Contrary to their name, liver spots have nothing to do with liver function and don't signify any issues with the liver.
Identifying Age Spots and Solar Lentigines
Other names for liver spots are "age spots" and "solar lentigines." Age spots, which are brought on by prolonged sun exposure, are more common in older people than younger people. They can appear anywhere on the body, but the face, hands, arms, and shoulders are where they most frequently show up. Age spots and solar lentigines are comparable, but age spots are larger and have more erratic borders. They come in a variety of hues, including gray, black, and brown. Additionally, they show up on exposed skin, including the arms, legs, chest, arms, and face.
Hyperpigmentation and Skin Aging
The most prevalent cause of liver spots is hyperpigmentation. The pigment that gives skin its color, melanin, causes it when the skin produces too much of it. Numerous factors, such as sun exposure, aging, hormonal changes, and some medications, can cause this melanin overproduction. On the skin, melanin overproduction can result in dark spots or patches. A primary contributor to the emergence of liver spots is skin aging. The skin becomes thinner and more fragile as we age, making it more vulnerable to harm from the sun's UV radiation. Additionally, as we get older, our skin's capacity to regenerate and repair itself diminishes, making it more challenging for the skin to recover from trauma such as sun damage. The likelihood of getting liver spots and other types of hyperpigmentation can rise as a result.
Causes and Risk Factors
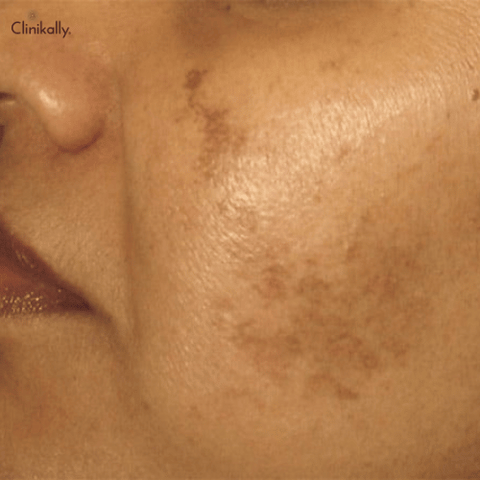
Long-term sun exposure, particularly exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, is the primary contributor to liver spots. The pigment that gives your skin its color, melanin, is produced in greater amounts when your skin is exposed to UV rays. Your skin's melanin helps shield it from the sun's damaging rays, but over time, excessive UV exposure can cause the pigment to clump and develop liver spots. Being older increases your risk of developing liver spots because they tend to occur more frequently with age. A fair complexion, a history of repeated sunburns, and a family history of liver spots are additional risk factors. A number of prescription drugs and health issues, such as diabetes and hepatitis, may also increase your risk of developing liver spots.
Sun Exposure and Melanin Production
The pigment that gives skin, hair, and eyes color is called melanin. Melanocytes, which are cells that are found in the bottom layer of the epidermis, the skin's outermost layer, are responsible for producing it. UV (ultraviolet) energy from the sun stimulates the formation of melanin. The melanocytes create more melanin when the skin is exposed to UV radiation in order to shield the skin from further harm. The reason the skin tans or darkens is due to this. However, prolonged exposure to UV radiation can stimulate the production of too much melanin by the melanocytes, which can result in hyperpigmentation and the development of liver spots. In addition to heredity, aging, and specific drugs, liver spots can also be caused by other factors.
Age, Genetics, and Skin Protection
People's skin changes as they age, including thinning, loss of suppleness, and reduced collagen and natural oil production. These modifications may increase the skin's susceptibility to harm from outside elements, including UV radiation, pollution, and other environmental stresses. Additionally, since some people may be more predisposed to hyperpigmentation or have a family history of the condition, genetics may also be a factor in the emergence of liver spots. Overexposure to the sun is a significant risk factor for liver spots. The sun's UV rays cause the skin to begin producing melanin when they come into contact with it. Melanocytes in the skin create the pigment known as melanin, which gives the skin its color. An increased incidence of liver spots is also present in those with fair skin or a history of frequent sunburns. Additionally, medications that increase your sensitivity to sunlight, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, or even both, can result in liver spots. Liver spots have also been linked to smoking and other tobacco use, along with a number of other skin issues.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
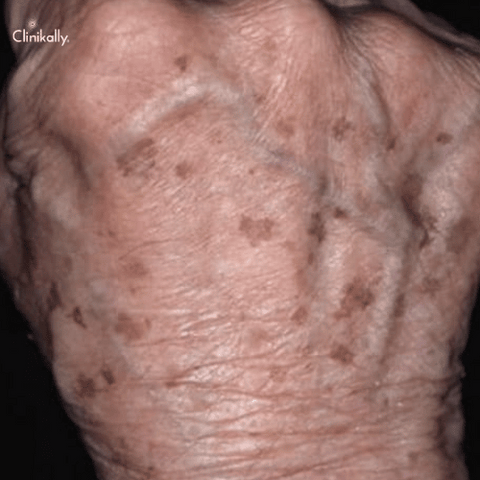
A visual examination is normally sufficient for the diagnosis of liver spots, and no additional testing is typically required. However, a dermatologist may conduct a skin biopsy to rule out skin cancer if a liver spot appears unusual or changes in size, shape, or color. The main objectives of treatment for liver spots are to lessen their appearance and stop the development of new ones. Treatment choices could be:
-
Topical treatments: Creams and lotions with hydroquinone, tretinoin, and azelaic acid can gradually lighten and fade liver spots. These products are available over-the-counter and on prescription.
-
Cryotherapy: This treatment involves freezing the liver spots with liquid nitrogen, resulting in blistering and peeling of the affected skin. Then, new skin grows in its place.
-
Laser therapy: Using various lasers, the melanin in liver spots can be targeted and removed, leaving the skin clearer.
-
Chemical peels: In this procedure, a solution is applied to the skin, causing the top layer to peel away to reveal fresh skin below. Chemical peels can help smooth out the skin's texture and lessen the appearance of liver spots.
-
Microdermabrasion: This procedure involves using a tool to remove the top layer of skin, which helps to improve skin texture and lessen the visibility of liver spots.
It is important to note that while these treatments can reduce the appearance of liver spots, they do not provide a permanent cure, and new spots may form with continued sun exposure. Therefore, avoiding exposure to the sun's rays is the best way to avoid developing liver spots. This can be done by donning protective clothing, hats, and sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Dermatological Consultation
The majority of liver spots, age spots, and solar lentigines are benign and do not need to be treated. However, it is advised to see a dermatologist if you have concerns about the appearance of your skin or if the size, shape, or color of the spots has changed. A dermatologist can inspect the spots and determine whether they are age spots or whether they might be another kind of skin disease that has to be treated, such as seborrheic keratosis or melanoma. The dermatologist may take a biopsy or remove the lesion for additional examination, as needed. Additionally, a dermatologist can suggest topical remedies, chemical peels, or laser therapy to treat the emergence of age spots or solar lentigines. They can also offer advice on how to take precautions to prevent further skin aging and sun damage.
Topical Treatments and Skin Lightening
Among the most popular methods of treating liver spots are topical medications and skin whitening. These procedures could lessen the visibility of liver spots and even out skin tone. The following list includes some of the most popular topical treatments for liver spots:
-
Hydroquinone: Hydroquinone is a skin-bleaching agent that can make liver spots look less noticeable. It functions by preventing the skin's melanin from being produced. Higher concentrations of hydroquinone are only available with a prescription and can be purchased over the counter in concentrations up to 2%.
-
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives known as retinoids can help to smooth out the texture of the skin and lessen the appearance of liver spots. They function by accelerating skin cell turnover and promoting collagen synthesis. Retinoids can only be obtained with a prescription.
-
Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs): AHAs can help exfoliate the skin and improve skin texture. Examples of AHAs include glycolic acid and lactic acid. They might also aid in lessening the visibility of liver spots. AHAs can be obtained over the counter and by prescription in higher concentrations.
-
Vitamin C: As an antioxidant, vitamin C can lessen the appearance of liver spots and protect the skin from free radical damage. It comes in both over-the-counter and prescription-only versions as a serum.
-
Kojic acid: A natural skin-lightening substance that can lessen the appearance of liver spots is kojic acid. It functions by preventing the skin's melanin from being produced. Both over-the-counter and prescription medications contain kojic acid.
It is important to remember that topical treatments might not show any visible results for weeks or even months. These treatments could also irritate or aggravate already sensitive skin, especially for those people. When using a product, it's crucial to adhere to the directions included with it and to stop using it if skin irritation develops.
Professional Treatments for Liver Spots
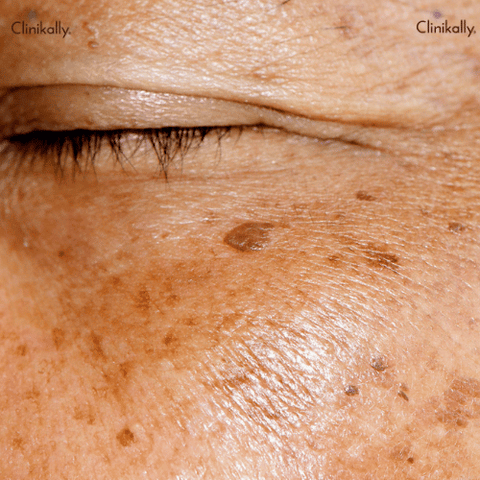
There are numerous professional liver spot treatments available, including:
-
Laser Therapy: A focused beam of light is used in laser therapy to target and eliminate the melanin-producing cells in the affected area. Laser therapy is a popular treatment option for liver spots. The spots may gradually appear lighter as a result of this.
-
Cryotherapy: To kill the cells that produce melanin, cryotherapy involves freezing the affected area with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is typically used for smaller liver spots.
-
Chemical Peels: To exfoliate the top layers of skin and lessen the appearance of liver spots, a chemical solution is applied to the affected area.
-
Microdermabrasion: The top layer of skin is exfoliated using a specialized tool during this non-invasive procedure. This may lessen the visibility of liver spots.
-
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy: IPL therapy targets the melanin-producing cells in the affected area by using high-intensity light pulses. This can help to lighten the appearance of liver spots over time.
A dermatologist should determine the best course of treatment for your specific needs, as well as guarantee the safety and efficacy of any proposed course of treatment.
Laser Therapy, Cryotherapy, and Chemical Peels
Professional treatments for liver spots include chemical peels, cryotherapy, and laser therapy. These remedies function by scraping off the top layer of skin above the liver spots, allowing fresh, clear skin to regenerate in its place.
-
Laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses high-intensity light to target and destroy the cells responsible for pigmentation. This treatment is typically performed on an outpatient basis and requires little to no downtime.
-
Cryotherapy, also known as freezing therapy, involves the use of liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy the cells responsible for pigmentation. This treatment is typically performed in a doctor's office and requires little to no downtime.
-
Chemical peels involve the use of a chemical solution that is applied to the skin, which causes the top layer of skin to peel away, revealing new, unblemished skin underneath. This treatment can be performed in a doctor's office or at home with an over-the-counter kit.
The fact that all of these therapies may temporarily produce redness, swelling, and discomfort should be noted. After treatment, it's crucial to protect the skin from the sun because it can be more vulnerable to its rays.
Microdermabrasion and Other Techniques
Another option for treating liver spots is microdermabrasion. A machine uses a spray of microscopic crystals to remove the top layer of skin during the operation. The device then removes the dead skin cells, which might make liver spots less noticeable. Dermabrasion and fractional laser resurfacing are two more procedures that could be employed. Additionally, liver spots can be treated with chemical peels. A dermatologist will apply a chemical solution to the skin during a chemical peel, which will cause the skin's outer layer to peel off. The skin may become smoother and more uniform in color as it recovers. A dermatologist might suggest a combination of therapies in some circumstances to get the best outcomes. To choose the option that is best for your particular needs, it is crucial to discuss the risks and advantages of each treatment option with a dermatologist.
Prevention and Skin Care Tips
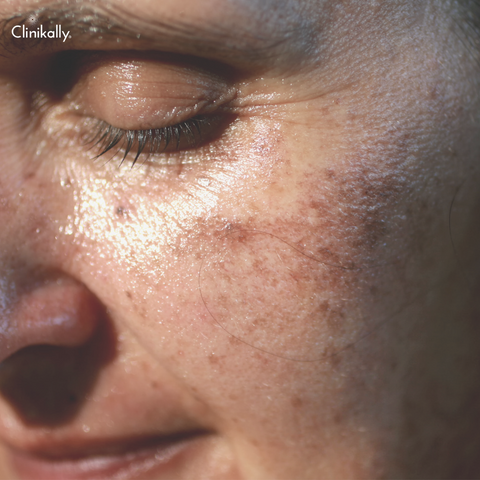
Tips for preventing and treating liver spots on the skin include:
-
Sun protection: Avoid being in the sun for too long, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Wear protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, and cover all exposed skin with a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30.
-
Avoid tanning beds: tanning beds can harm your skin and cause liver spots to develop.
-
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Consume a healthy, balanced diet that is high in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. To maintain good skin, be sure to drink lots of water, get enough rest, and exercise frequently.
-
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can harm your skin and increase your chances of developing liver spots.
-
Use gentle skin care products: Stay away from abrasive soaps, scrubs, and other products that can irritate your skin.
-
Apply moisturizer to your skin: Hydrating your skin can help shield it from harm and dryness.
-
Check your skin frequently: Check your skin frequently to check for any changes or new spots. If you notice any suspicious spots or changes, consult a dermatologist.
Despite the fact that liver spots are benign, it should be noted that they can occasionally resemble other skin conditions, such as skin cancer. Therefore, it is essential to see a dermatologist if you are unsure of the nature of a spot on your skin.
Sunscreen Use and UV Damage Reduction
The prevention of skin damage, hyperpigmentation, and liver spots requires the use of sunscreen and measures to reduce UV rays. Here are some suggestions to lower your chance of getting liver spots:
-
Even on cloudy days, wear sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
-
Avoid spending long periods of time in direct sunlight, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
-
When going outside, wear protective clothing such as long-sleeved shirts, hats, and sunglasses.
-
Seek shade whenever possible, especially during peak sun hours.
-
Tanning beds, which emit harmful UV rays, should be avoided.
-
UV exposure should be avoided at higher altitudes, near water, and when snow is present, as these conditions can intensify UV rays.
-
Check your skin for new or changing spots on a regular basis, and seek medical attention if you notice any changes.
-
Use antioxidant-rich products, such as vitamins C and E, to help protect against free radical damage caused by UV rays.
You can reduce your risk of developing liver spots and other types of sun damage by following these tips.
Maintaining a Healthy Skin Care Routine
For the prevention and treatment of numerous skin diseases, including liver spots, maintaining a healthy skin care regimen is crucial. Here are some pointers for creating a skin care regimen that encourages youthful skin:
-
Cleanse your skin twice a day: Use a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and makeup from your skin. Cleansing your skin twice a day can help prevent clogged pores and acne.
-
Exfoliate once or twice a week: Exfoliating your skin can help remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. To avoid skin irritation and harm, use a mild exfoliating scrub or a chemical exfoliant.
-
Moisturize daily: Moisturizing your skin can help prevent dryness, flakiness, and premature aging. Choose a moisturizer that is appropriate for your skin type and use it on a daily basis.
-
Use sunscreen on a daily basis: Sun damage is a leading cause of liver spots and other skin conditions. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to your face and exposed skin on a daily basis.
-
Drink plenty of water: Staying hydrated can help keep your skin hydrated and healthy.
-
Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol: Smoking and drinking alcohol can have negative effects on your skin, including premature aging and liver spots.
-
Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet can provide your skin with the nutrients and vitamins it needs to function properly. Include plenty of fruits and vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats in your diet.
-
Get enough sleep: Sleep deprivation can lead to stress, which can harm your skin. To promote healthy skin and overall well-being, aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
















